Monochamus obtusus Casey, 1891: 47
Length: 14–24 mm.
Elytral length:width ratio: length < 2x width.
Face: shape wide rectangle; genagena:
the part of the cranium on each side below the eye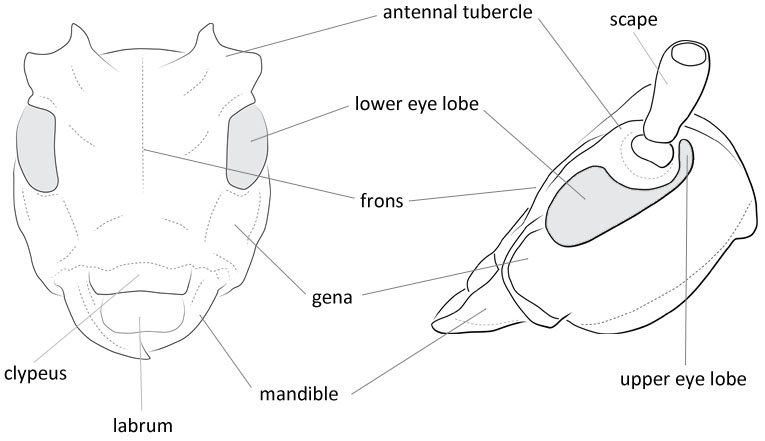 length shorter than lower eye lobeeye lobe:
length shorter than lower eye lobeeye lobe:
used to refer to the upper or lower portion when the eye is emarginate or separated or subequal to lower eye lobeeye lobe:
or subequal to lower eye lobeeye lobe:
used to refer to the upper or lower portion when the eye is emarginate or separated .
.
Pronotum:pronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
dense setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
on dorsum of lateral spines absent; maculaemacula:
a spot or mark
on pronotal disk: 2–4 dots present or absent; posteromedial tubercletubercle:
a small knoblike or rounded protuberance
absent; lateral erect setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
: only present posterior to spinespine:
a protuberance with an acute (sharp) distal end
.
Scutellum:scutellum:
a small sclerite located directly posterior to the pronotum, bordered laterally by the elytra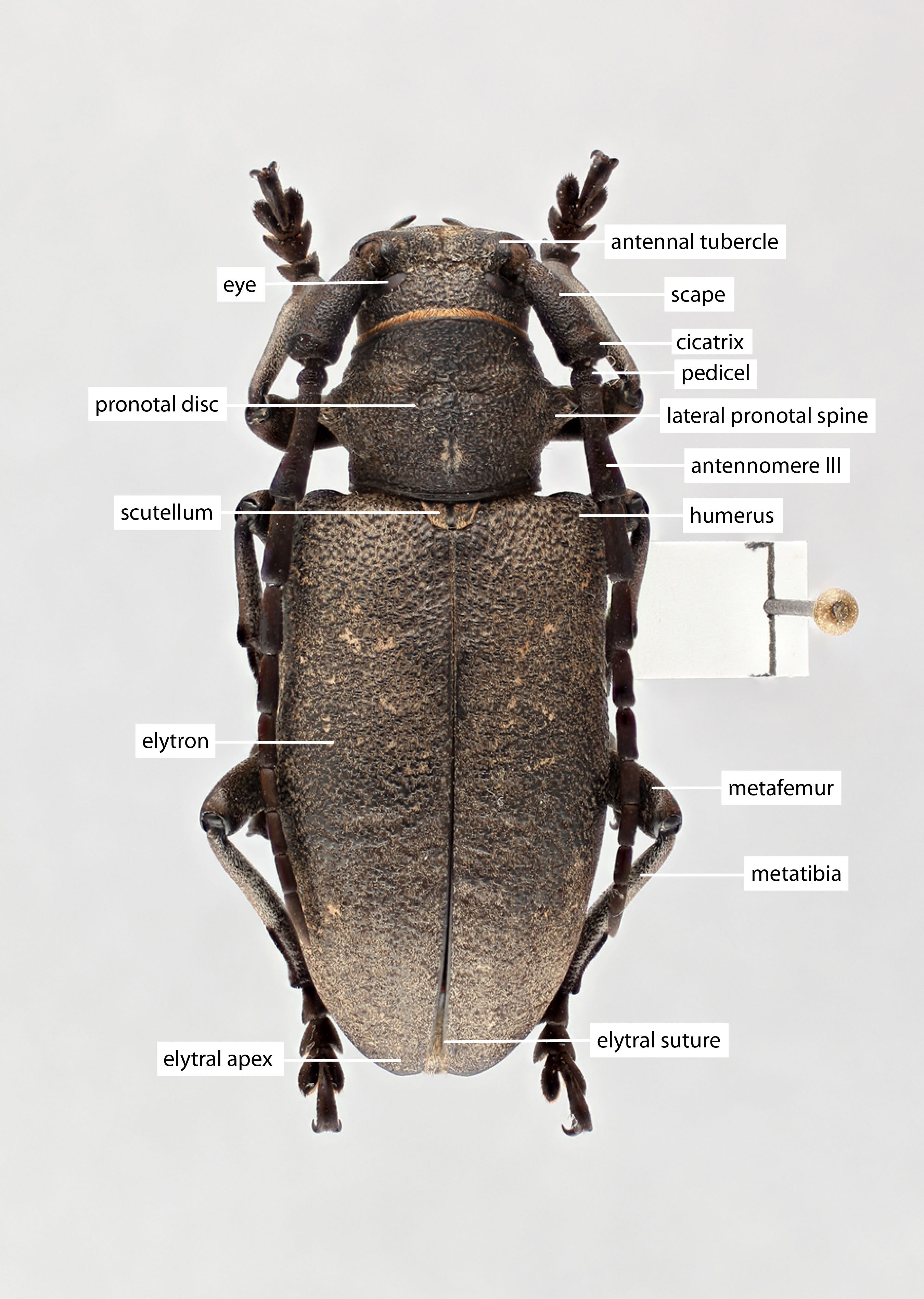 pubescence broken at least partially along midline.
pubescence broken at least partially along midline.
Elytra:elytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
elytral integument color orange to red; elytral maculaemacula:
a spot or mark
: dense velvety pubescentpubescent:
downy; clothed with soft, short, fine, loosely set hair
patches present, rarely pubescence forming horizontal band(s); elytral sutural apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
rounded; elevation in basal third followed by impression absent; basal granulation dense and smooth or dense and coarse; middle to apical punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
fine.
Antennal length (female): 2–3.5 segments beyond elytral apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
.
Aedeagus:aedeagus:
in male beetles, the penis
paramereparamere:
A pair of finger-like structures that are located where the male genitalia exits the abdomen.
mediobasal tooth present; apical tip (ventral view) slightly rounded; scleritesclerite:
any hardened plate of the body wall bounded by membrane or sutures; sometimes found floating in the internal sac of male genitalia
in internal sac: scleritesclerite:
any hardened plate of the body wall bounded by membrane or sutures; sometimes found floating in the internal sac of male genitalia
absent.
Male. Form moderate-sized, cylindricalcylindrical:
shaped like a cylinder, parallel sided
, vaguely tapering posteriorly; integument deep to pale reddish-brown, abdomen black, submetallic; pubescence mottled, grayish and pale and dark brownish. Head with front shallowly convex, shallowly, usually densely punctatepunctate:
set with fine, impressed points or punctures appearing as pin-pricks
, irregularly to very densely pubescentpubescent:
downy; clothed with soft, short, fine, loosely set hair
; genaegena:
the part of the cranium on each side below the eye short, slightly convergent toward apexapex:
short, slightly convergent toward apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
; antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
extending about five segments beyond elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
, segments minutely asperate, moderately densely clothed with very short, depressed, dark hairs, scapescape:
the first proximal segment of the antenna moderately clothed with short gray, recumbent pubescence, segments three to ten with apical sensory areas. Pronotumpronotum:
moderately clothed with short gray, recumbent pubescence, segments three to ten with apical sensory areas. Pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
as broad as or broader than long, lateral tubercles moderate in size, apicesapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
narrowly rounded; apical and basal impressions transversely rugoserugose:
wrinkled
; disk with an irregular, glabrousglabrous:
smooth, devoid of pubescence; devoid of any sculpturing
, median callus; middle rugoserugose:
wrinkled
around callus; sides confluently punctatepunctate:
set with fine, impressed points or punctures appearing as pin-pricks
; pubescence irregular, mottled, fulvous at sides; prosternum ruguloserugulose:
minutely rugose; minutely wrinkled
, very densely to irregularly pubescentpubescent:
downy; clothed with soft, short, fine, loosely set hair
; meso- and metasternum irregularly to densely clothed with recumbent gray pubescence, suberect, yellowish hairs numerous. Elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
about twice as long as broad, sides slightly explanate behind humerihumerus:
shoulder; the basal exterior angle of the elytra ; basebase:
; basebase:
the part of any appendage or structure that is nearest the body
with numerous, rounded asperities; punctures behind asperities irregular, dense, becoming obsolete to apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
; pubescence consisting of light to dark brown patches with gray pubescence sparse to dense around brown patches, brown patches more extensive over apical one-half; apicesapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
rounded. Scutellumscutellum:
a small sclerite located directly posterior to the pronotum, bordered laterally by the elytra white pubescentpubescent:
white pubescentpubescent:
downy; clothed with soft, short, fine, loosely set hair
at sides, apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
broadly V-shaped. Legs very densely to moderately densely pubescentpubescent:
downy; clothed with soft, short, fine, loosely set hair
, pubescence interrupted by small dots. Abdomen confluently punctatepunctate:
set with fine, impressed points or punctures appearing as pin-pricks
at sides; pubescence irregular to very dense, often covering surface; last sternite truncatetruncate:
cut off squarely at the tip
at apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
, apical hair tufts very sparse. Length, 14–24 mm.
Female. Form similar. Antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
extending three segments beyond elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
; segments broadly white annulateannulate:
surrounded by a ring of a different color
basally; abdomen with last sternite truncatetruncate:
cut off squarely at the tip
at apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
, hair tufts dense. Length, 17–24 mm. (Linsley and Chemsak 1984Linsley and Chemsak 1984:
Linsley EG and Chemsak JA. 1984. The Cerambycidae of North America. Part VII, No. 1. Taxonomy and Classification of the Subfamily Lamiinae, Tribes Parmenini Through Acanthoderini. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles. 258 pp.)
Monochamus clamator clamator, Monochamus clamator latus
M. obtusus is unique in the very stout elytral shape, orange color, and rounded elytral apicesapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
. When comparing to lighter M. clamator with weak apical armature, the prontum of M. obtusus being reddish in the center bordered anteriorly and posteriorly by black will help distinguish it.
North America: Pacific Coast states, British Columbia, and Idaho
Pinus, Abies, Pseudotsuga menziesii
There is no evidence to support subspecies in M. obtusus. Molecular data show the current subspecies are not monophyletic.
Monochamus obtusus fulvomaculatus Linsley, 1933: 118