Cerambyx sutor Linnaeus, 1758: 392
Length: 15–26 mm.
Elytral length:width ratio: length > 2x width.
Face: shape wide rectangle; genagena:
the part of the cranium on each side below the eye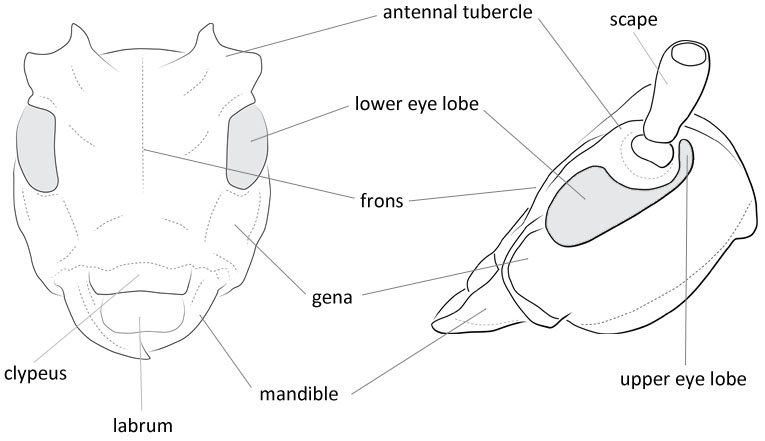 length longer than lower eye lobeeye lobe:
length longer than lower eye lobeeye lobe:
used to refer to the upper or lower portion when the eye is emarginate or separated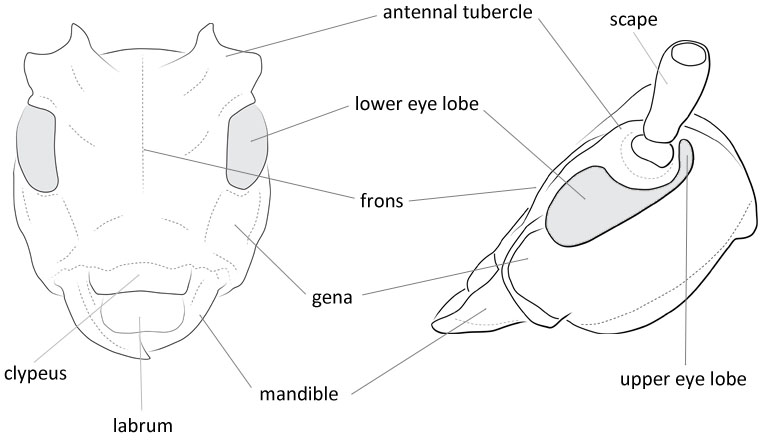 or subequal to lower eye lobeeye lobe:
or subequal to lower eye lobeeye lobe:
used to refer to the upper or lower portion when the eye is emarginate or separated .
.
Pronotum:pronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
dense setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
on dorsum of lateral spines absent; maculaemacula:
a spot or mark
on pronotal disk: 2–4 dots present; posteromedial tubercletubercle:
a small knoblike or rounded protuberance
absent; lateral erect setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
: present posterior and anterior to spinespine:
a protuberance with an acute (sharp) distal end
.
Scutellum:scutellum:
a small sclerite located directly posterior to the pronotum, bordered laterally by the elytra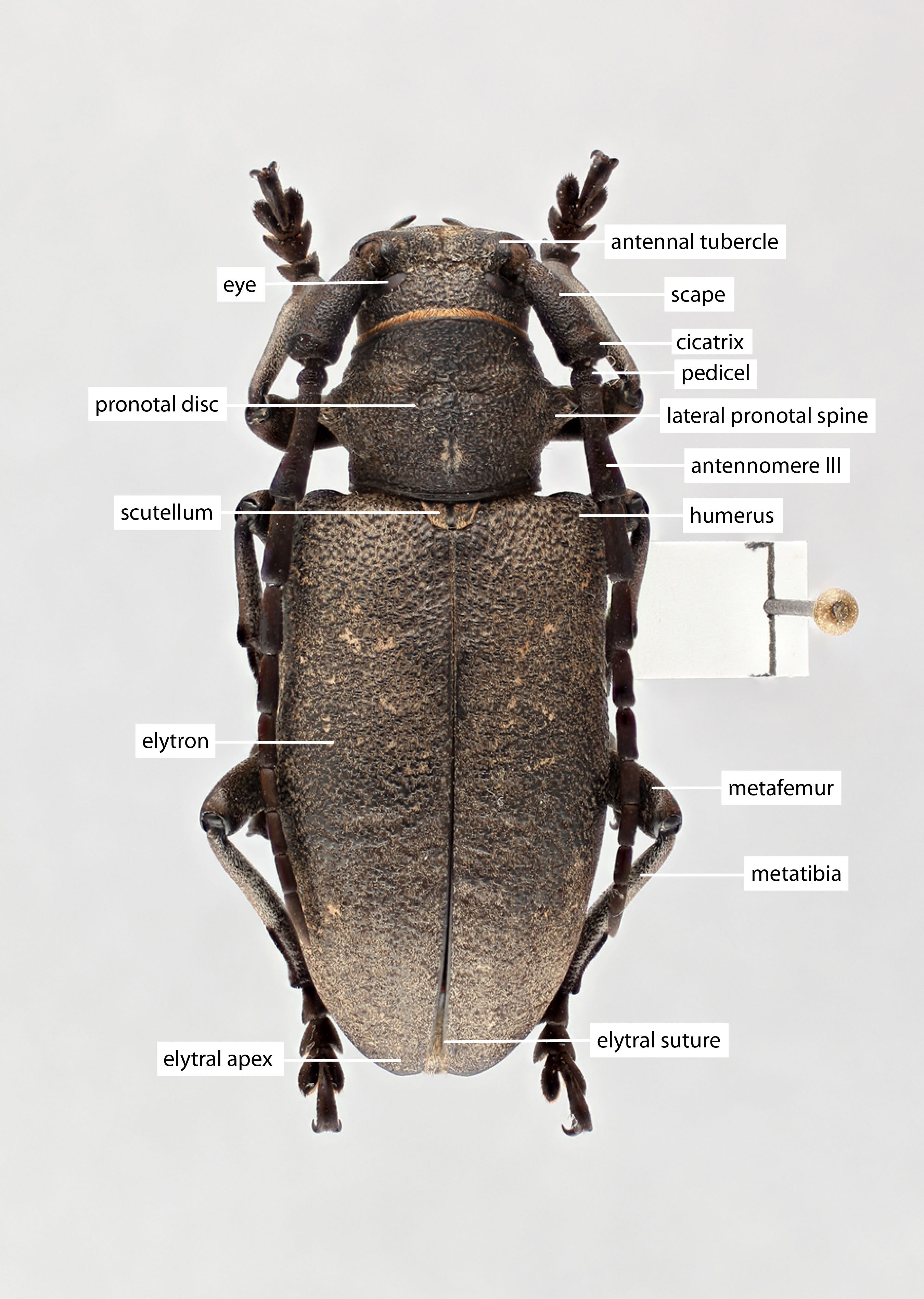 pubescence broken at least partially along midline.
pubescence broken at least partially along midline.
Elytra:elytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
elytral integument color black; elytral maculaemacula:
a spot or mark
: many small circular spots, sparse ash-like pubescence or absent; elytral sutural apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
rounded; elevation in basal third followed by impression absent; basal granulation dense and coarse; middle to apical punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
coarse.
Antennal length (female): >3.5 segments beyond elytral apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
.
Aedeagus:aedeagus:
in male beetles, the penis
paramereparamere:
A pair of finger-like structures that are located where the male genitalia exits the abdomen.
mediobasal tooth present; apical tip (ventral view) tr uncateuncate:
hooked; barbed
; terminal segment absent; scleritesclerite:
any hardened plate of the body wall bounded by membrane or sutures; sometimes found floating in the internal sac of male genitalia
in internal sac: contains a scleritesclerite:
any hardened plate of the body wall bounded by membrane or sutures; sometimes found floating in the internal sac of male genitalia
in internal sac.
Body moderately elongateelongate:
much longer than wide
. Head not broader than pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
, with deep median longitudinal groove, deep uneven punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
and dense or sparse gray or brownish hairs. Antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
long, 2.5 times longer (male) or considerably shorter, less than 1.5 times longer than body, extending beyond apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
of elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
by 8th segment (female), with minute granular (male) or simple compact (female) punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
. Eyes sharply faceted, broadly emarginateemarginate:
notched at the margin ; upper ocular lobes closer to each other, distance between them less than interspace between antennal bases. Pronotumpronotum:
; upper ocular lobes closer to each other, distance between them less than interspace between antennal bases. Pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
basally and apically with gentle flange, here with thin transversetransverse:
broader than long
striae (folds), disk convex, with uneven striatestriate:
marked with parallel, fine, longitudinal, impressed lines or furrows
punctation and gray, very sparse, sometimes unevenly dense, adherent, laterally with dark brown erect hairs. Lateral tubercles of pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax
conically extended. Pronotal shield flat, length not more than width, basally with dense adherent gray or yellowish hairs, medially with longitudinal glabrousglabrous:
smooth, devoid of pubescence; devoid of any sculpturing
band, rounded posteriorly. Elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
parallel-sided, disk convex, beyond basebase:
the part of any appendage or structure that is nearest the body
entire, without perceptible transversetransverse:
broader than long
notch, in anterior half with coarse deep, in posterior half much finer, on hind clivus evanescent punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
, with dense brownish adherent hairs and minute white pilose (especially in female) specks (form typica) or with rusty pilose specks (ab.fuscomaculatus Petri); often brownish hairs sparse, not forming continuous pubescence, and elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
appear glabrousglabrous:
smooth, devoid of pubescence; devoid of any sculpturing
(m, pellio Germ.). Body ventrally with short adherent gray and long semierect brownish hairs. Midtibiae on outer side with dense apical brush of golden or brownish bristles. Body length 15–26 mm. (Cherepanov 1990Cherepanov 1990:
Cherepanov AI. 1990. Cerambycidae of Northern Asia, Vol. 3. Lamiinae, Part I. Oxonian Press, New Delhi 4: i–xiii + 1–300, 120 figs.)
M. galloprovincialis, M. scutellatus, M. impluviatus, M. saltuarius
In contrast to M. galloprovincialis, M. sutor has long erect setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
anterior and posterior to pronotal spines, a complete glabrousglabrous:
smooth, devoid of pubescence; devoid of any sculpturing
line in the scutellumscutellum:
a small sclerite located directly posterior to the pronotum, bordered laterally by the elytra , a shining appearance, and often has setal spots randomly arranged; the male genitalia has a tooth at the paramereparamere:
, a shining appearance, and often has setal spots randomly arranged; the male genitalia has a tooth at the paramereparamere:
A pair of finger-like structures that are located where the male genitalia exits the abdomen.
base, and the sclerites are folded and form a vague “beak” shape. The elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
have coarser punctationpunctation:
pits or depression of variable size in cuticle
than M. scutellatus which is usually ashy instead of composed of many spots, and there are no sclerites in the male genitalia. M. impluviatus is on average smaller, very weakly punctatepunctate:
set with fine, impressed points or punctures appearing as pin-pricks
in comparison, and has a different genital scleritesclerite:
any hardened plate of the body wall bounded by membrane or sutures; sometimes found floating in the internal sac of male genitalia
shape.
Europe east to Japan and Korea
Abies, Larix, Picea, Pinus
The subspecies M. s. longulus is used for eastern specimens that have much less pubescence on the elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
. Its validity has not been tested molecularly, but it seems to act similarly to M. sartor subspecies which are genetically distinct.
Cerambyx atomarius DeGeer, 1775: 65
Monachamus sutor var. fuscomaculatus Petri, 1912: 249
Lamia heinrothi Cederhjelm, 1798: 88
Monachamus sutor var. hybrida Petri, 1912: 249
Monohammus obscurior Abeille de Perrin, 1869: 42
Lamia pellio Germar, 1818: 244
Lamia rosenmuelleri Cederhjelm, 1798: 89