Family name: Mayacaceae K. Kunth
Synonym(s): [none]
Common name(s): mayaca family
*Number of genera/species: 1/6
List of genera records in GRIN-Global
seed
Fruit a loculicidal capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary , sometimes foraminicidalforaminicidal:
, sometimes foraminicidalforaminicidal:
type of capsular dehiscence, fruits opening irregularly
, 2–6 mm long, globoseglobose:
3D shape—more or less spherical to ellipsoidellipsoid:
to ellipsoidellipsoid:
3D shape—elliptic
, often appearing lumpy, sometimes perianthperianth:
collective term for calyx and corolla of a flower
 persistent. Pericarppericarp:
persistent. Pericarppericarp:
fruit wall or fruit coat
membranousmembranous:
texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough
and pubescentpubescent:
surface relief—bearing hairs
.
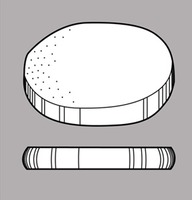
Seeds globoseglobose:
3D shape—more or less spherical to ovoidovoid:
to ovoidovoid:
3D shape—ovate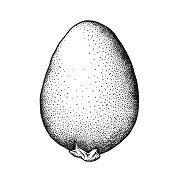 , tereteterete:
, tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 in transection, 0.75–2.5 mm long, minutely beakedbeak:
in transection, 0.75–2.5 mm long, minutely beakedbeak:
a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered beakbeak:
beakbeak:
a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered ) 0.15–0.4 mm long), which is often misinterpreted as an operculumoperculum:
) 0.15–0.4 mm long), which is often misinterpreted as an operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence . Seed coat black, brown, or red, dulldull:
. Seed coat black, brown, or red, dulldull:
reflecting only a low proportion of incident light, with no apparent sheen , thick, usually pittedpitted:
, thick, usually pittedpitted:
surface relief—surface with small depressions in which the areas between the hollows do not take on the appearance of a true reticular net or reticulatereticulate:
or reticulatereticulate:
surface relief—netted, raised walls or concave grooves forming a net-like surface pattern with flat, concave, or convex interspaces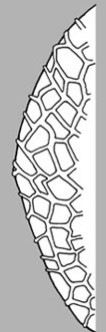 , ribbedribbed:
, ribbedribbed:
surface relief—wide, prominent, linear ridges that are generally rounded and longitudinally situated on the surface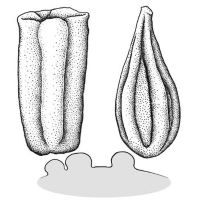 , wrinkledwrinkled:
, wrinkledwrinkled:
surface relief—shallow, irregular folds and furrows covering the surface; appearing overall though crumpled and then spread out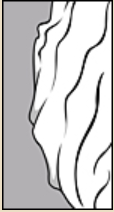 , or striatestriate:
, or striatestriate:
surface relief—having fine, parallel lines, grooves or ridges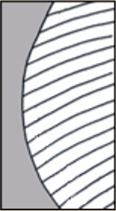 .
.
Embryo rudimentaryrudimentary:
(of embryo) embryo is small and fills less than a quarter of the seed and can be variable in shapes, such as linear, spatulate, or oval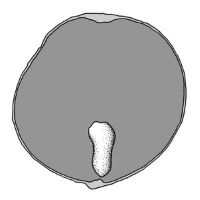 , discoiddiscoid:
, discoiddiscoid:
3D shape—resembling a disc
 , basalbasal:
, basalbasal:
at or pertaining to the point of attachment; (of embryo) embryo occupies one end of the seed
, capping one end of endosperm at the micropylarmicropyle:
an opening in the integuments of an ovule usually acting as a passage for the pollen tube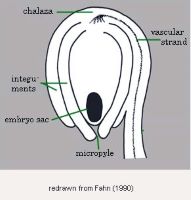 end.
end.
Endosperm copious, mealy.
Mayaca fluviatilis is an aquatic state noxious weed in Puerto Rico.
Aquarium & Pond Plants of the World tool includes descriptions and images, which may be encountered.
| Fruit | |
| Type | capsulecapsule: a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary  |
| Size range | 2–6 mm long |
| Shape(s) | globoseglobose: 3D shape—more or less spherical  , ellipsoidellipsoid: , ellipsoidellipsoid:3D shape—elliptic |
| Texture | membranousmembranous: texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough |
| Surface relief | pubescentpubescent: surface relief—bearing hairs |
| Unique features | Membranousmembranous: texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough , pubescentpubescent: surface relief—bearing hairs capsulescapsule: a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary  with few to many seeds. Shape of seeds through thin pericarppericarp: with few to many seeds. Shape of seeds through thin pericarppericarp:fruit wall or fruit coat may give capsulescapsule: a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary  a lumpy appearance. a lumpy appearance. |
| Seed | |
| Size range | 0.75–2.5 mm long |
| Shape(s) | globoseglobose: 3D shape—more or less spherical  , ovoidovoid: , ovoidovoid:3D shape—ovate  |
| Surface relief | reticulatereticulate: surface relief—netted, raised walls or concave grooves forming a net-like surface pattern with flat, concave, or convex interspaces  , ribbedribbed: , ribbedribbed:surface relief—wide, prominent, linear ridges that are generally rounded and longitudinally situated on the surface  , wrinkledwrinkled: , wrinkledwrinkled:surface relief—shallow, irregular folds and furrows covering the surface; appearing overall though crumpled and then spread out  , striatestriate: , striatestriate:surface relief—having fine, parallel lines, grooves or ridges  , pittedpitted: , pittedpitted:surface relief—surface with small depressions in which the areas between the hollows do not take on the appearance of a true reticular net  |
| Color(s) | black, brown, red |
| Unique features | Small globoseglobose: 3D shape—more or less spherical  to ovoidovoid: to ovoidovoid:3D shape—ovate  seeds, minutely beakedbeak: seeds, minutely beakedbeak:a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered  (0.15–0.4 mm long), and with thick, pittedpitted: (0.15–0.4 mm long), and with thick, pittedpitted:surface relief—surface with small depressions in which the areas between the hollows do not take on the appearance of a true reticular net  seed coats. seed coats. |
| Other | |
| Embryo | rudimentaryrudimentary: (of embryo) embryo is small and fills less than a quarter of the seed and can be variable in shapes, such as linear, spatulate, or oval  , discoiddiscoid: , discoiddiscoid:3D shape—resembling a disc  , basalbasal: , basalbasal:at or pertaining to the point of attachment; (of embryo) embryo occupies one end of the seed , capping one end of endosperm at the micropylarmicropyle: an opening in the integuments of an ovule usually acting as a passage for the pollen tube  end end |
| Nutritive tissue | endosperm copious, mealymealy: loose, dry, and disintegrating in finely granular pieces like meal or flour |
Tropical America, one species in Africa.
Distribution map courtesy of Angiosperm Phylogeny Website.
Baskin and Baskin 2021Baskin and Baskin 2021:
Baskin C and Baskin J. 2021. Relationship of the lateral embryo (in grasses) to other monocot embryos: A status up-grade. Seed Science Research 31 (3): 199-210. doi:10.1017/S0960258521000209; Dahlgren et al. 1985Dahlgren et al. 1985:
Dahlgren RMT, Clifford HT, and Yeo PF. 1985. The families of the monocotyledons: structure, evolution, and taxonomy. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 520 pp.; Davidse et al. 2009–2018Davidse et al. 2009–2018:
Davidse GM, Sousa Sánchez M, Knapp S. and Chiang Cabrera F, eds. 2009–2018. Flora Mesoamericana. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO. Accessed: January–April 2024. URL: http://legacy.tropicos.org/Project/FM; Flora of North America Editorial Committee 1993+Flora of North America Editorial Committee 1993+:
Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. Flora of North America Association, New York and Oxford. Accessed January-March 2024. URL: http://beta.floranorthamerica.org.; Kirkbride et al. 2006Kirkbride et al. 2006:
Kirkbride JH, Jr, Gunn CR, and Dallwitz MJ. 2006. Family guide for fruits and seeds, vers. 1.0. Accessed September 2020-January 2022. URL: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/seedsfruits/keys/frsdfam/index.cfm .; Kubitzki et al. 1990+Kubitzki et al. 1990+:
Kubitzki K et al., eds. 1990+. The families and genera of vascular plants. 7+ vols. Berlin etc.; Stevenson and Loconte 1995Stevenson and Loconte 1995:
Stevenson DW and Loconte H. 1995. A cladistic analysis of monocot families. In: Rudall PJ, Cribb PJ, Cutler DF, and Humphries CJ, eds. Monocotyledons: Systematics and Evolution. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
*The number of genera and species is based on Christenhusz and Byng 2016Christenhusz and Byng 2016:
Christenhusz MJM and Byng JW. 2016. The number of known plant species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 261 (3): 201-217. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1, which may differ from the number of genera in GRIN-Global.