Family name: Rapateaceae Dumortier
Synonym(s): [none]
Common name(s): rapatea family
*Number of genera/species: 16/94
List of genera records in GRIN-Global
seed
Fruit a septicidalsepticidal:
type of capsular dehiscence, opening longitudinally by separating between the septa of adjacent carpels
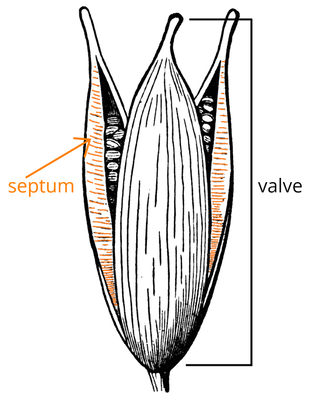 capsulecapsule:
capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary , 3–10 mm long, ovateovate:
, 3–10 mm long, ovateovate:
2D shape—egg-shaped in outline, widest point is towards one end of the organ, the other end tapers gradually, attachment at or near the broad end (compare obovate, ovoid)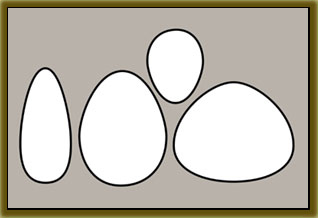 to trigonoustrigonous:
to trigonoustrigonous:
3D shape—having three faces that meet at distinct angles; triangular in outline
, tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 in transection, sometimes stylar remnantstyle base:
in transection, sometimes stylar remnantstyle base:
remnant of a style persistent, with one to many seeds, often 2 or 3 per fruit. Pericarppericarp:
persistent, with one to many seeds, often 2 or 3 per fruit. Pericarppericarp:
fruit wall or fruit coat
yellow, indurateindurate:
texture—hardened or stony; yielding under strong pressure; not deformable without internal structural disruption
, membranousmembranous:
texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough
, smooth.
Seeds globoseglobose:
3D shape—more or less spherical to prismaticprismatic:
to prismaticprismatic:
like a prism; with sharp, definite angles and flat sides
, tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 or flattened in transection,1.2–3 mm long. Seed coat brown, black, or white, dulldull:
or flattened in transection,1.2–3 mm long. Seed coat brown, black, or white, dulldull:
reflecting only a low proportion of incident light, with no apparent sheen , membranousmembranous:
, membranousmembranous:
texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough
, smooth or variously sculptured, with a flattened appendage (Maschalocephalus, Monotrema, Potarophytum, Windsorina,) or without, sometimes raphe conspicuous. Seed coat encrusted with silica and with large hilium (Cephalostemon, Rapatea, Spathanthus). Seeds of Cephalostemon usually have a white, conicalconical:
3D shape—cone-shaped, with the point of attachment at the broad end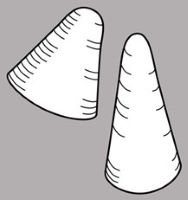 or caplike, spongyspongy:
or caplike, spongyspongy:
soft, light, discontinuous but cohesive, and somewhat resilient
carunclescaruncle:
a localized outgrowth of the seed coat near the hilum of the seed; it functions as an elaiosome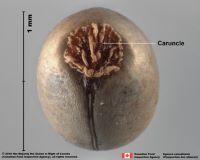 or elaiosomeselaiosome:
or elaiosomeselaiosome:
a lipid and protein-rich fleshy structure attached to some seeds and fruits, it attracts ants which then disperse the disseminule (e.g., caruncle in the Euphorbiaceae, the aril (outgrowth of the funiculus) in the Fabaceae) .
.
Embryo rudimentaryrudimentary:
(of embryo) embryo is small and fills less than a quarter of the seed and can be variable in shapes, such as linear, spatulate, or oval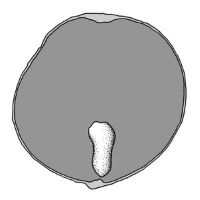 , lenticularlenticular:
, lenticularlenticular:
3D shape—lens-shaped; biconvex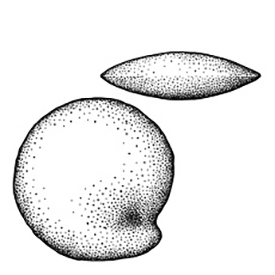 , straight, at micropylarmicropyle:
, straight, at micropylarmicropyle:
an opening in the integuments of an ovule usually acting as a passage for the pollen tube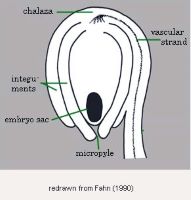 end with flat side appressedappressed:
end with flat side appressedappressed:
pressed close to or lying flat against something, as in hairs on grass bract
to endosperm, 0.1 times the length of the endosperm.
Endosperm copious, fleshy or mealymealy:
loose, dry, and disintegrating in finely granular
pieces like meal or flour
.
| Fruit | |
| Type | capsulecapsule: a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary  |
| Size range | 3–10 mm long |
| Shape(s) | ovoidovoid: 3D shape—ovate 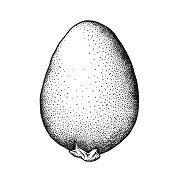 , oblongoblong: , oblongoblong:2D shape—much longer than broad with nearly parallel sides, corners are rounded 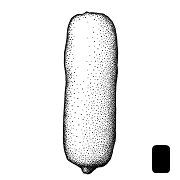 , globoseglobose: , globoseglobose:3D shape—more or less spherical  , ellipsoidellipsoid: , ellipsoidellipsoid:3D shape—elliptic , trigonoustrigonous: 3D shape—having three faces that meet at distinct angles; triangular in outline |
| Texture | indurateindurate: texture—hardened or stony; yielding under strong pressure; not deformable without internal structural disruption , membranousmembranous: texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough |
| Surface relief | smooth |
| Color(s) | yellow |
| Seed | |
| Size range | 1.2–3 mm long |
| Shape(s) | oblongoblong: 2D shape—much longer than broad with nearly parallel sides, corners are rounded  , globoseglobose: , globoseglobose:3D shape—more or less spherical  , ellipsoidellipsoid: , ellipsoidellipsoid:3D shape—elliptic , teardrop-shapedteardrop-shaped: 2D shape—widest point is toward one end of the fruit, the other end tapers sharply to a pointed end 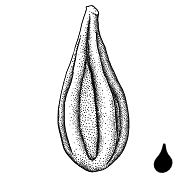 , fusiformfusiform: , fusiformfusiform:spindle-shaped; broadest at the middle and tapering at both ends 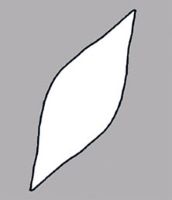 , prismaticprismatic: , prismaticprismatic:like a prism; with sharp, definite angles and flat sides , C-shapedC-shaped: 2D-shape—semiannulate, curved into the shape of the letter 'C' , lens-shapedlens-shaped: 2D shape—round and flattened with two curved (convex) surfaces , ovoidovoid: 3D shape—ovate  , reniformreniform: , reniformreniform:2D or 3D shape—kidney-shaped 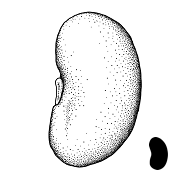 |
| Surface relief | reticulatereticulate: surface relief—netted, raised walls or concave grooves forming a net-like surface pattern with flat, concave, or convex interspaces 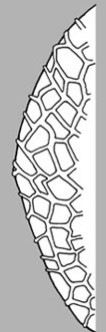 , striatestriate: , striatestriate:surface relief—having fine, parallel lines, grooves or ridges 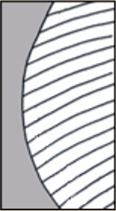 , alveolatealveolate: , alveolatealveolate:surface relief—reticulated, honeycombed; ridges that intersect to form polygonal cells with a regular size and shape similar to a honeycomb 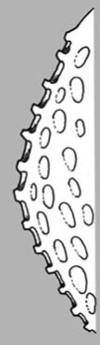 , punctatepunctate: , punctatepunctate:surface relief—dotted with pits or with translucent, sunken glands or with colored dots, similar to pitted  , glandularglandular: , glandularglandular:surface relief—covered with small, raised secretory glands, regular or irregularly shaped, translucent or opaque, and maybe distinctly colored 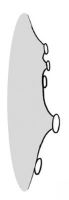 , papillatepapillate: , papillatepapillate:surface relief—bearing minute, distinct, broad-based projections, tapering to a rounded apex 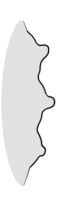 , wrinkledwrinkled: , wrinkledwrinkled:surface relief—shallow, irregular folds and furrows covering the surface; appearing overall though crumpled and then spread out 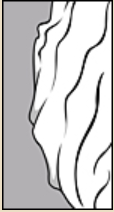 , spinyspiny: , spinyspiny:having slender, stiff, sharp projections oriented in the general plane of the structure 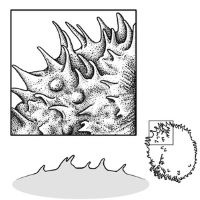 |
| Color(s) | brown, black, white |
| Other | |
| Embryo | rudimentaryrudimentary: (of embryo) embryo is small and fills less than a quarter of the seed and can be variable in shapes, such as linear, spatulate, or oval  , lenticularlenticular: , lenticularlenticular:3D shape—lens-shaped; biconvex  , straight, at micropylarmicropyle: , straight, at micropylarmicropyle:an opening in the integuments of an ovule usually acting as a passage for the pollen tube  end with flat side appressedappressed: end with flat side appressedappressed:pressed close to or lying flat against something, as in hairs on grass bract to endosperm, 0.1 times the length of the endosperm |
| Nutritive tissue | endosperm copious, fleshy or mealymealy: loose, dry, and disintegrating in finely granular pieces like meal or flour |
Tropics, South America, West Africa.
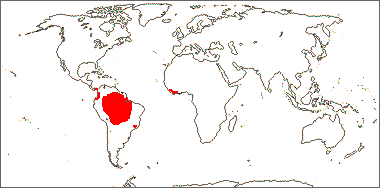
Distribution map courtesy of Angiosperm Phylogeny Website.
Baskin and Baskin 2021Baskin and Baskin 2021:
Baskin C and Baskin J. 2021. Relationship of the lateral embryo (in grasses) to other monocot embryos: A status up-grade. Seed Science Research 31 (3): 199-210. doi:10.1017/S0960258521000209; Berryberry:
an indehiscent, fleshy fruit with one or a few to many seeds. The flesh may be homogenous throughout. Or, if the outer part is hard, firm, or leathery, referred to as an hesperidium. Septa are present in some, and the seeds may be arillate or with a fleshy testa.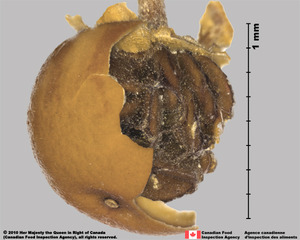 et al. 1995; Dahlgren et al. 1985Dahlgren et al. 1985:
et al. 1995; Dahlgren et al. 1985Dahlgren et al. 1985:
Dahlgren RMT, Clifford HT, and Yeo PF. 1985. The families of the monocotyledons: structure, evolution, and taxonomy. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 520 pp.; de S. Praia et al. 2016de S. Praia et al. 2016:
de S. Praia T, dos S. Braganccedil;a Gil A, and Secco Ricardo de S. 2016. Rapateaceae in the state of Paraacute;, Brazil. Acta Botanica Brasilica 30 (4): 628-643. https://doi.org/10.1590/0102-33062016abb0162; Kirkbride et al. 2006Kirkbride et al. 2006:
Kirkbride JH, Jr, Gunn CR, and Dallwitz MJ. 2006. Family guide for fruits and seeds, vers. 1.0. Accessed September 2020-January 2022. URL: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/seedsfruits/keys/frsdfam/index.cfm .; Kubitzki et al. 1990+Kubitzki et al. 1990+:
Kubitzki K et al., eds. 1990+. The families and genera of vascular plants. 7+ vols. Berlin etc.; Stevenson and Loconte 1995Stevenson and Loconte 1995:
Stevenson DW and Loconte H. 1995. A cladistic analysis of monocot families. In: Rudall PJ, Cribb PJ, Cutler DF, and Humphries CJ, eds. Monocotyledons: Systematics and Evolution. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
*The number of genera and species is based on Christenhusz and Byng 2016Christenhusz and Byng 2016:
Christenhusz MJM and Byng JW. 2016. The number of known plant species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 261 (3): 201-217. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1, which may differ from the number of genera in GRIN-Global.