Content is from Kirkbride et al. 2006Kirkbride et al. 2006:
Kirkbride JH, Jr, Gunn CR, and Dallwitz MJ. 2006. Family guide for fruits and seeds, vers. 1.0. Accessed September 2020-January 2022. URL: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/seedsfruits/keys/frsdfam/index.cfm ., without modification.
Updates are forthcoming.
Fruits: Pistil(s) compound; 1; 1-pistillate; with carpels united. Fruit pericarpium; simple; carceruluscarcerulus:
simple, multicarpellate, indehiscent fruit consisting of one or more seeds and air space enclosed by an undifferentiated pericarp (Spjut 1994)
(Spjut only listed Afrostyrax, which is indehiscentindehiscent:
not opening on its own, as in a fruit
 , but he did not record the fruit for Hua which is dehiscentdehiscent:
, but he did not record the fruit for Hua which is dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) ), or capsulecapsule:
), or capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary (Hua not Spjut); loculicidalloculicidal:
(Hua not Spjut); loculicidalloculicidal:
type of capsular dehiscence, opening longitudinally through the locules (compare septicidal)
 capsulecapsule:
capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary (assumed); capsulecapsule:
(assumed); capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary not inflated; capsulecapsule:
not inflated; capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary without operculumoperculum:
without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; without persistent central column; not within accessory organ(s); 1-seeded to more than 1 but less than 10-seeded; 1–2-seeded; with 5-carpellate (for Afrostyrax, but what about Hua); with carpels united; with carpels remaining united at maturity; without sterilesterile:
; without persistent central column; not within accessory organ(s); 1-seeded to more than 1 but less than 10-seeded; 1–2-seeded; with 5-carpellate (for Afrostyrax, but what about Hua); with carpels united; with carpels remaining united at maturity; without sterilesterile:
lacking male and/or female reproductive parts; also, not producing fruit or seed
 carpels; not sulcatesulcate:
carpels; not sulcatesulcate:
surface relief—having one or more elongate, relatively narrow and shallow depressions or grooves ; in transection tereteterete:
; in transection tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 ; apexapex:
; apexapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ not beaked; Afrostyrax indehiscentindehiscent:
not beaked; Afrostyrax indehiscentindehiscent:
not opening on its own, as in a fruit
 , or dehiscentdehiscent:
, or dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) (Hua). Dehiscentdehiscent:
(Hua). Dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) unit seed(s). Dehiscentdehiscent:
unit seed(s). Dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) regularly; at apexapex:
regularly; at apexapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ ; and shedding seeds; without replumreplum:
; and shedding seeds; without replumreplum:
the rim, formed by the persistent placentas, and connected by a false septum in Brassicaceae fruits. The fruit valves are attached to this rim and separate from it in dehiscent fruits.
. Epicarpepicarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with exocarp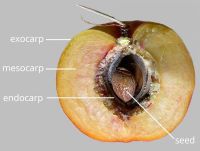 durable; glabrousglabrous:
durable; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
(assumed); without armature; without wing(s); without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
respiratory hole. Endocarpendocarp:
the inner layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers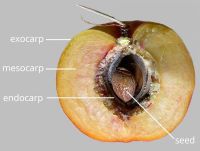 present; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
present; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with epicarp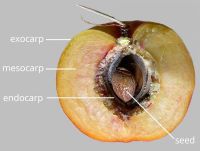 ; thin; not splitting into 1-seeded pyrenes; smooth; without wing; without operculumoperculum:
; thin; not splitting into 1-seeded pyrenes; smooth; without wing; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; without secretory cavities; without mechanism for seedling escape; without grooves; without longitudinallongitudinal:
; without secretory cavities; without mechanism for seedling escape; without grooves; without longitudinallongitudinal:
of or relating to length or the lengthwise dimension
ridges. Funiculusfuniculus:
(alt. funicle) stalk connecting the ovule (later seed) to the ovary (later fruit) placenta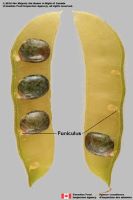 short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
bristles or spines with curved or backwards pointing tips, or with secondary bristles along their length (retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
(retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
Seeds: Arilaril:
(broad sense) appendicular structure that wholly or partly envelops a seed and is produced from or a modification of the funicle, raphe, or outer integument; usually fleshy or pulpy, sometimes spongy or tufted-capillate, often brightly colored absent. Seed larger than minute; Afrostyrax circularcircular:
absent. Seed larger than minute; Afrostyrax circularcircular:
(of embryo) linear embryo is curved into an "O" shape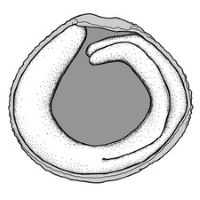 , or oblongoblong:
, or oblongoblong:
2D shape—much longer than broad with nearly parallel sides, corners are rounded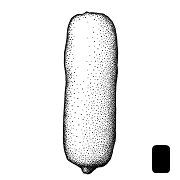 (Hua); not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
(Hua); not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered ; without caudatecaudate:
; without caudatecaudate:
tapering to a long, tail-like appendage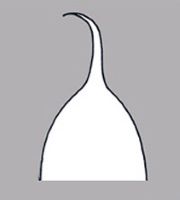 appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves; with endosperm; without canavanine. Sarcotestasarcotesta:
appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves; with endosperm; without canavanine. Sarcotestasarcotesta:
pulpy or fleshy outer layer of the seed coat, simulates aril absent. Testatesta:
absent. Testatesta:
seed coat
 present; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
present; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
at, on, or close to the margin or border
tissue; without fleshy or leatheryleathery:
texture—moderately thick, tough, and very pliable
layer over hard layer; tight; without crease or line separating cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle; without notch along margin where cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle tip approach each other; without glands; without bristles; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
; without wings; without collar; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; colored; monochrome; not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
; colored; monochrome; not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
resembling mucilage; moist and sticky
when wetted; surrounding food reserve. Hilumhilum:
on seeds, the scar indicating where the funiculus was attached; on grass caryopses, the scar visible on the outer fruit surface revealing where the seed is attached on the inner fruit wall surface; or in Asteraceae cypselae, the scar visible on the outer fruit wall revealing where the fruit was attached to the receptacle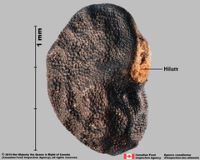 basalbasal:
basalbasal:
at or pertaining to the point of attachment; (of embryo) embryo occupies one end of the seed
. Endosperm copious; without fatty acid containing cyclopropene; without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
lobes; without chlorophyll; without isodiametric faceted surface; with odor of garlic. Embryo differentiated from food reserve; well developed; 1 per seed; partially filling testatesta:
seed coat
 (with food reserve); 0.8 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; axileaxile:
(with food reserve); 0.8 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; axileaxile:
on or of the axis
and centric; conicalconical:
3D shape—cone-shaped, with the point of attachment at the broad end ; straight; parallel to seed length; with cotyledons gradually connected to hypocotyl-radicle; without coleorhiza; without simmondsin; without stomata; not green; with 2 or more cotyledons. Cotyledons 2; well developed; 0.75 times length of embryo; as wide as hypocotyl-radicle; 1 times wider than hypocotyl-radicle; not concealing hypocotyl-radicle; not foliaceous; thin; flat; smooth; with apicesapex:
; straight; parallel to seed length; with cotyledons gradually connected to hypocotyl-radicle; without coleorhiza; without simmondsin; without stomata; not green; with 2 or more cotyledons. Cotyledons 2; well developed; 0.75 times length of embryo; as wide as hypocotyl-radicle; 1 times wider than hypocotyl-radicle; not concealing hypocotyl-radicle; not foliaceous; thin; flat; smooth; with apicesapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ entire; with margins separate; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
entire; with margins separate; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
surface relief—dotted with pits or with translucent, sunken glands or with colored dots, similar to pitted dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle moderately developed; straight; not thickened.
dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle moderately developed; straight; not thickened.
Literature specific to this family: Perkins, J. 1928. Übersicht über die Gattungen der Styracaceae sowie Zusammenstellung der Abbildungen und Literator über die Arten dieser Familie bis zum Jahre 1928, 36 pp. Wilhelm Engelmann, Leipzig.
General references: Cronquist, A. 1981. An integrated system of classification of flowering plants, 1,262 p. Columbia University Press, New York, Gunn, C.R., J.H. Wiersema, C.A. Ritchie, & J.H. Kirkbride, Jr. 1992 & amendments. Families and genera of Spermatophytes recognized by the Agricultural Research Service. Techn. Bull. U.S.D.A. 1796:1–500, Mabberley, D.J. 1987. The plant-book, 706 p. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, and Spjut, R.W. 1994. A systematic treatment of fruit types. Mem. New York Bot. Gard. 70:1–182.