Content is from Kirkbride et al. 2006Kirkbride et al. 2006:
Kirkbride JH, Jr, Gunn CR, and Dallwitz MJ. 2006. Family guide for fruits and seeds, vers. 1.0. Accessed September 2020-January 2022. URL: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/seedsfruits/keys/frsdfam/index.cfm ., without modification.
Updates are forthcoming.
Fruits: Pistil(s) compound, or simple; 1; 1-pistillate; with carpels united. Fruit pericarpium, or anthocarpanthocarp:
simple or compound and including some tissue of non-ovarian origin (accessory tissue) ; simple; of authors, but not Spjut, (1994) berryberry:
; simple; of authors, but not Spjut, (1994) berryberry:
an indehiscent, fleshy fruit with one or a few to many seeds. The flesh may be homogenous throughout. Or, if the outer part is hard, firm, or leathery, referred to as an hesperidium. Septa are present in some, and the seeds may be arillate or with a fleshy testa.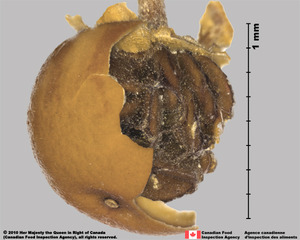 , or drupedrupe:
, or drupedrupe:
(indehiscent drupe) a fleshy, indehiscent fruit with one more hard pits enclosing seeds, derived from single, superior, simple or compound ovary; (dehiscent drupe) a fruit with a dry or fibrous to fleshy or leathery outer husk that early to tardily breaks apart (or opens), exposing one or more nutlike pits enclosing the seeds ; berryberry:
; berryberry:
an indehiscent, fleshy fruit with one or a few to many seeds. The flesh may be homogenous throughout. Or, if the outer part is hard, firm, or leathery, referred to as an hesperidium. Septa are present in some, and the seeds may be arillate or with a fleshy testa. indehiscent; berryberry:
indehiscent; berryberry:
an indehiscent, fleshy fruit with one or a few to many seeds. The flesh may be homogenous throughout. Or, if the outer part is hard, firm, or leathery, referred to as an hesperidium. Septa are present in some, and the seeds may be arillate or with a fleshy testa. without central placental mass; compound; sorosus; without persistent central column; not within accessory organ(s); 1-seeded; 1-seeded; with Peperomia (1–)4-carpellate (really (1-)3–4); with carpels united; with carpels remaining united at maturity; with carpels not radiating at maturity; with carpels remaining connected at stylestyle:
without central placental mass; compound; sorosus; without persistent central column; not within accessory organ(s); 1-seeded; 1-seeded; with Peperomia (1–)4-carpellate (really (1-)3–4); with carpels united; with carpels remaining united at maturity; with carpels not radiating at maturity; with carpels remaining connected at stylestyle:
in a flower, the narrow and elongated part of the pistil between the stigma and the ovary; sometimes persisting in fruit ; without sterilesterile:
; without sterilesterile:
lacking male and/or female reproductive parts; also, not producing fruit or seed
 carpels; not sulcatesulcate:
carpels; not sulcatesulcate:
surface relief—having one or more elongate, relatively narrow and shallow depressions or grooves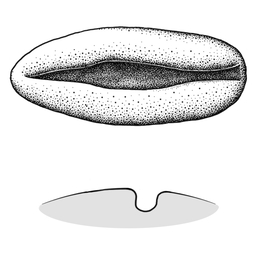 ; apexapex:
; apexapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ not beaked; indehiscentindehiscent:
not beaked; indehiscentindehiscent:
not opening on its own, as in a fruit
 . Epicarpepicarp:
. Epicarpepicarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with exocarp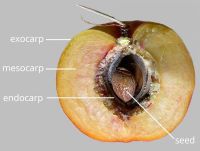 durable; glabrousglabrous:
durable; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
; with armature, or without armature; with prickles (with barbedbarbed:
(of awns or bristles) with short, sharp, hair-like projections
apicesapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ Zippelia), or warts; without armature glochidiate; smooth, or not smooth; without wing(s); without apicalapical:
Zippelia), or warts; without armature glochidiate; smooth, or not smooth; without wing(s); without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
respiratory hole. Mesocarpmesocarp:
the middle layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers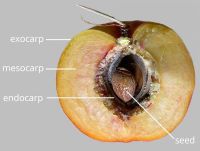 present. Endocarpendocarp:
present. Endocarpendocarp:
the inner layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers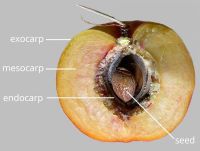 present, or absent; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
present, or absent; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with epicarp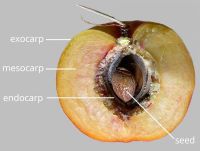 ; hard; not splitting into 1-seeded pyrenes; without operculumoperculum:
; hard; not splitting into 1-seeded pyrenes; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; without secretory cavities; without longitudinallongitudinal:
; without secretory cavities; without longitudinallongitudinal:
of or relating to length or the lengthwise dimension
ridges. Funiculusfuniculus:
(alt. funicle) stalk connecting the ovule (later seed) to the ovary (later fruit) placenta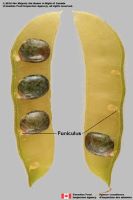 short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
bristles or spines with curved or backwards pointing tips, or with secondary bristles along their length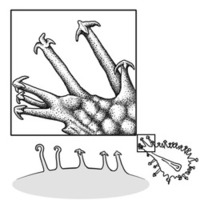 (retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
(retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
Seeds: Arilaril:
(broad sense) appendicular structure that wholly or partly envelops a seed and is produced from or a modification of the funicle, raphe, or outer integument; usually fleshy or pulpy, sometimes spongy or tufted-capillate, often brightly colored absent. Seed 1 to less than 5 mm long, or 5 to less than 10 mm long; 1–6 mm long; circularcircular:
absent. Seed 1 to less than 5 mm long, or 5 to less than 10 mm long; 1–6 mm long; circularcircular:
(of embryo) linear embryo is curved into an "O" shape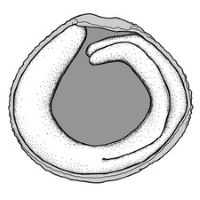 , or oblongoblong:
, or oblongoblong:
2D shape—much longer than broad with nearly parallel sides, corners are rounded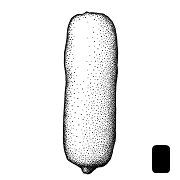 ; in transection tereteterete:
; in transection tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 ; not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
; not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered ; without caudatecaudate:
; without caudatecaudate:
tapering to a long, tail-like appendage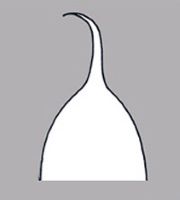 appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves; with endosperm and perispermperisperm:
appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves; with endosperm and perispermperisperm:
seed nutritive tissue comparable to the endosperm, but derived from the nucellus (maternal tissue)
; without canavanine. Sarcotestasarcotesta:
pulpy or fleshy outer layer of the seed coat, simulates aril absent. Testatesta:
absent. Testatesta:
seed coat
 present, or absent; without embryo surrounded and capped by viscid tissue; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
present, or absent; without embryo surrounded and capped by viscid tissue; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
at, on, or close to the margin or border
tissue; without fleshy or leatheryleathery:
texture—moderately thick, tough, and very pliable
layer over hard layer; tight; without crease or line separating cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle; without notch along margin where cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle tip approach each other; without glands; without bristles; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
; without wings; without collar; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; colored; monochrome; brown (all shades); thin, or hard (cartilagenous); not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
; colored; monochrome; brown (all shades); thin, or hard (cartilagenous); not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
resembling mucilage; moist and sticky
when wetted; surrounding food reserve. Endosperm development nuclear, or cellular (Peperomia); scant; with starch (Piper); with oils and proteins (Peperomia); without fatty acid containing cyclopropene; without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
lobes; without chlorophyll; without isodiametric faceted surface; without odor. Perispermperisperm:
seed nutritive tissue comparable to the endosperm, but derived from the nucellus (maternal tissue)
copious; sub cartilaginouscartilaginous:
texture—firm, dense, tough, somewhat pliable, and resilient, like cartilage
, or mealymealy:
loose, dry, and disintegrating in finely granular
pieces like meal or flour
; with starch; with starch composed of clustered grains (usually); smooth. Embryo differentiated from food reserve, or undifferentiated from food reserve; rudimentaryrudimentary:
(of embryo) embryo is small and fills less than a quarter of the seed and can be variable in shapes, such as linear, spatulate, or oval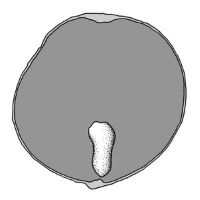 ; 1 per seed; partially filling testatesta:
; 1 per seed; partially filling testatesta:
seed coat
 (with food reserve); 0.04–0.2 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; lenticularlenticular:
(with food reserve); 0.04–0.2 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; lenticularlenticular:
3D shape—lens-shaped; biconvex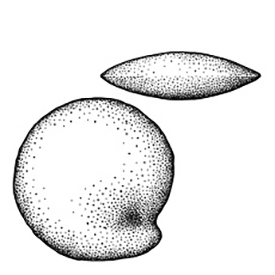 , or turbinateturbinate:
, or turbinateturbinate:
3D shape—broadly obovoid-obconic
; straight; surrounding perispermperisperm:
seed nutritive tissue comparable to the endosperm, but derived from the nucellus (maternal tissue)
(in hollowed center); with cotyledons gradually connected to hypocotyl-radicle; without coleorhiza; without simmondsin; without stomata; not green; with 2 or more cotyledons, or acotyledonous. Cotyledons 2; scarcely differentiated, or tiny; to 0.4 times length of embryo; as wide as hypocotyl-radicle (assumed); 1 times wider than hypocotyl-radicle; not concealing hypocotyl-radicle; not foliaceous; smooth; with apicesapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ entire; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
entire; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
surface relief—dotted with pits or with translucent, sunken glands or with colored dots, similar to pitted dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle vestigial to small; straight; not thickened.
dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle vestigial to small; straight; not thickened.
General references: Baillon, H.E. 1866–95. Histoire des plantes, 13 vols. Hachette & Co., Paris, Corner, E.J.H. 1976. The seeds of Dicots, esp. vol. 2. Cambridge University Press, New York, Cronquist, A. 1981. An integrated system of classification of flowering plants, 1,262 p. Columbia University Press, New York, Engler, A. & K. Prantl. 1924 and onward. Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilimien. W. Engelman, Leipzig, Gaertner, J. 1788–1805. De fructibus et seminibus plantarum. The Author, Stuttgart, Goldberg, A. 1986 (dicots) & 1989 (monocots). Classification, evolution, and phylogeny of the familes of Dicotyledons. Smithsonian Contr. Bot. 58 for dicots (314 pp.) & 71 for monocots (74 pp.). [Goldberg's illustrations are reproduced from older publications and these should be consulted], Gunn, C.R. & C.A. Ritchie. 1988. Identification of disseminulesdisseminule:
detachable plant part capable of being disseminated and of propagating, commonly a seed or fruit
listed in the Federal Noxious Weed Act. Techn. Bull. U.S.D.A. 1719:1–313, Gunn, C.R., J.H. Wiersema, C.A. Ritchie, & J.H. Kirkbride, Jr. 1992 & amendments. Families and genera of Spermatophytes recognized by the Agricultural Research Service. Techn. Bull. U.S.D.A. 1796:1–500, LeMaout, E. & J. Decaisne. 1876. A general system of botany, 1,065 p. Longmans, Green, & Co., London, Mabberley, D.J. 1987. The plant-book, 706 p. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Roosmalen, M.G.M. van. 1985. Fruits of the Guianan flora, 483 pp. Institute of Systematic Botany, Wageningen Agricultural University. Drukkerij Veenman B.V., Wageningen, and Spjut, R.W. 1994. A systematic treatment of fruit types. Mem. New York Bot. Gard. 70:1–182.