Content is from Kirkbride et al. 2006Kirkbride et al. 2006:
Kirkbride JH, Jr, Gunn CR, and Dallwitz MJ. 2006. Family guide for fruits and seeds, vers. 1.0. Accessed September 2020-January 2022. URL: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/seedsfruits/keys/frsdfam/index.cfm ., without modification.
Updates are forthcoming.
Fruits: Pistil(s) compound; 1; 1-pistillate; with carpels united. Fruit anthocarpanthocarp:
simple or compound and including some tissue of non-ovarian origin (accessory tissue) , or pericarpium; simple, or schizocarpschizocarp:
, or pericarpium; simple, or schizocarpschizocarp:
usually dry fruit splitting between two or more locules to form distinct, indehiscent, usually one seeded segments; fruit derived from a single, superior or inferior, compound ovary; compare to mericarp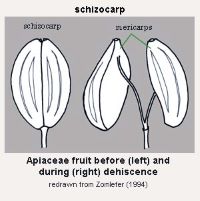 ; capsulecapsule:
; capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary ; coccarium, or microbasarium (Spjut 5 families: Boraginaceae, Callitrichaceae, Convolvulaceae, Lamiaceae, Verbenaceae); what type of capsule?; capsulecapsule:
; coccarium, or microbasarium (Spjut 5 families: Boraginaceae, Callitrichaceae, Convolvulaceae, Lamiaceae, Verbenaceae); what type of capsule?; capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary not inflated; capsulecapsule:
not inflated; capsulecapsule:
a dry, dehiscent fruit derived from a compound ovary without operculumoperculum:
without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; simple; pseudosamara (Pitraea but spelled Petraea in Spjut); without persistent central column, or with persistent central column; valves not diverging at top of central column; with styles(s); at apexapex:
; simple; pseudosamara (Pitraea but spelled Petraea in Spjut); without persistent central column, or with persistent central column; valves not diverging at top of central column; with styles(s); at apexapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ ; within accessory organ(s), or not within accessory organ(s); within calyxcalyx:
; within accessory organ(s), or not within accessory organ(s); within calyxcalyx:
the outer whorl of the perianth; all the sepals of a flower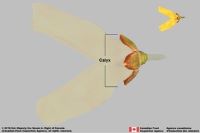 (enlarged or not, membranousmembranous:
(enlarged or not, membranousmembranous:
texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough
or not, my be cupuliform, induate); accrescentaccrescent:
growing continuously
; persistent; 1-seeded to more than 1 but less than 10-seeded; 1–10-seeded (1–4(-8–10)); less than 1 cm long to from 1–5 cm long; 0.7–3.5 cm long; with 4–8-carpellate (4–5,8); with carpels united; with carpels remaining united at maturity; with carpels not radiating at maturity; with carpels remaining connected at stylestyle:
in a flower, the narrow and elongated part of the pistil between the stigma and the ovary; sometimes persisting in fruit ; not sulcatesulcate:
; not sulcatesulcate:
surface relief—having one or more elongate, relatively narrow and shallow depressions or grooves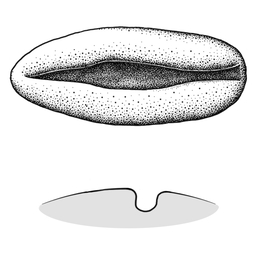 ; in transection tereteterete:
; in transection tereteterete:
approximately circular in cross section; width and thickness approximately equal
 ; apexapex:
; apexapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ not beaked; indehiscentindehiscent:
not beaked; indehiscentindehiscent:
not opening on its own, as in a fruit
 , or dehiscentdehiscent:
, or dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) . Dehiscentdehiscent:
. Dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) unit seed(s). Dehiscentdehiscent:
unit seed(s). Dehiscentdehiscent:
(v. dehisce) splitting open at maturity to release contents (of a fruit) and shedding seeds; without replumreplum:
and shedding seeds; without replumreplum:
the rim, formed by the persistent placentas, and connected by a false septum in Brassicaceae fruits. The fruit valves are attached to this rim and separate from it in dehiscent fruits. . Epicarpepicarp:
. Epicarpepicarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with exocarp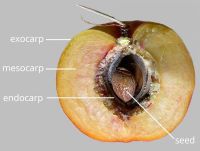 black, or blue, or brown (all shades), or green, or orange, or purple, or red, or yellow; shinyshiny:
black, or blue, or brown (all shades), or green, or orange, or purple, or red, or yellow; shinyshiny:
uniformly reflecting a high proportion of incident light at all angles , or dulldull:
, or dulldull:
reflecting only a low proportion of incident light, with no apparent sheen ; durable; membranousmembranous:
; durable; membranousmembranous:
texture—extremely thin, pliable, and fairly tough
; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
, or not glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
(with hairs); hairs not glandularglandular:
surface relief—covered with small, raised secretory glands, regular or irregularly shaped, translucent or opaque, and maybe distinctly colored ; without armature, or with armature; with spines; without armature glochidiate; smooth, or not smooth; roughenedroughened:
; without armature, or with armature; with spines; without armature glochidiate; smooth, or not smooth; roughenedroughened:
texture—having a small, stout, stiff, more or less acute protrusions
, or ridgedridged:
surface relief—raised, thick ridges, sharp edged or rounded, usually in a series that may cover the entire surface , or rugoserugose:
, or rugoserugose:
wrinkled ; without wing(s); without apicalapical:
; without wing(s); without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
respiratory hole. Mesocarpmesocarp:
the middle layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers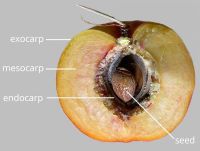 present, or absent; fleshy; composed of 1 unified layer; without lactiform cavity system; & endocarpendocarp:
present, or absent; fleshy; composed of 1 unified layer; without lactiform cavity system; & endocarpendocarp:
the inner layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers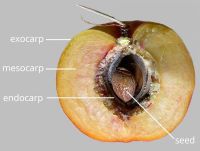 sharply differentiated. Endocarpendocarp:
sharply differentiated. Endocarpendocarp:
the inner layer of the pericarp, if divided into layers present, or absent; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
present, or absent; not separating from exocarpexocarp:
outer layer of fruit wall or pericarp, if divided into layers; note here used synonymously with epicarp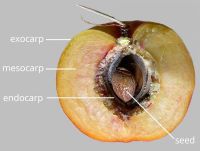 ; thin, or hard; splitting into 1-seeded pyrenespyrene:
; thin, or hard; splitting into 1-seeded pyrenespyrene:
the hard inner portion of a drupe, consisting of a bony endocarp and an enclosed seed
, or not splitting into 1-seeded pyrenes; stone unilocular, or plurilocular; stone 2-loculate; smooth; without wing; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; without secretory cavities; without mechanism for seedling escape; without grooves; without longitudinallongitudinal:
; without secretory cavities; without mechanism for seedling escape; without grooves; without longitudinallongitudinal:
of or relating to length or the lengthwise dimension
ridges. Funiculusfuniculus:
(alt. funicle) stalk connecting the ovule (later seed) to the ovary (later fruit) placenta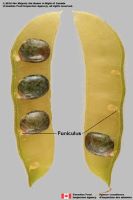 short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
short; short without seed bearing hookswith hooks:
bristles or spines with curved or backwards pointing tips, or with secondary bristles along their length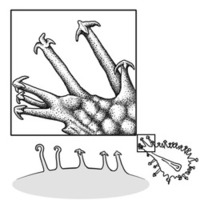 (retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
(retinacula); not persisting in fruit after seed shed.
Seeds: Arilaril:
(broad sense) appendicular structure that wholly or partly envelops a seed and is produced from or a modification of the funicle, raphe, or outer integument; usually fleshy or pulpy, sometimes spongy or tufted-capillate, often brightly colored absent. Seed larger than minute; not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
absent. Seed larger than minute; not bowl shaped; not nutlike; without winglike beakbeak:
a usually firm, terminal appendage, sometimes tapered ; without caudatecaudate:
; without caudatecaudate:
tapering to a long, tail-like appendage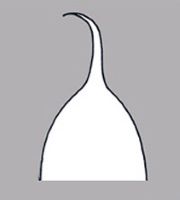 appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves, or without food reserves, or without apparent food reserves; with endosperm; without canavanine. Sarcotestasarcotesta:
appendage(s); at maturity with food reserves, or without food reserves, or without apparent food reserves; with endosperm; without canavanine. Sarcotestasarcotesta:
pulpy or fleshy outer layer of the seed coat, simulates aril absent. Testatesta:
absent. Testatesta:
seed coat
 present; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
present; without markedly different marginalmarginal:
at, on, or close to the margin or border
tissue; without fleshy or leatheryleathery:
texture—moderately thick, tough, and very pliable
layer over hard layer; tight; surface smooth; without crease or line separating cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle; without notch along margin where cotyledons from hypocotyl-radicle tip approach each other; without glands; without bristles; glabrousglabrous:
without hairs
; without wings; without collar; without operculumoperculum:
a dehiscent cap (or lid) of a seed or fruit that opens during germination or dehiscence ; colored; monochrome; thin; not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
; colored; monochrome; thin; not becoming mucilaginousmucilaginous:
resembling mucilage; moist and sticky
when wetted; surrounding embryo, or surrounding food reserve. Hilumhilum:
on seeds, the scar indicating where the funiculus was attached; on grass caryopses, the scar visible on the outer fruit surface revealing where the seed is attached on the inner fruit wall surface; or in Asteraceae cypselae, the scar visible on the outer fruit wall revealing where the fruit was attached to the receptacle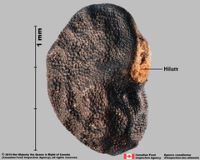 punctate (assumed). Endosperm development cellular; scant, or moderate (Avicennia); fleshy-soft, or fleshy; smooth; with oils; without fatty acid containing cyclopropene; without apicalapical:
punctate (assumed). Endosperm development cellular; scant, or moderate (Avicennia); fleshy-soft, or fleshy; smooth; with oils; without fatty acid containing cyclopropene; without apicalapical:
at or pertaining to the end of the seed or fruit distal from its point of attachment (i.e., base)
lobes; without chlorophyll; without isodiametric faceted surface; without odor. Embryo differentiated from food reserve; well developed; 1 per seed; completely filling testatesta:
seed coat
 (no food reserve), or nearly filling testatesta:
(no food reserve), or nearly filling testatesta:
seed coat
 (trace or scanty food reserve), or partially filling testatesta:
(trace or scanty food reserve), or partially filling testatesta:
seed coat
 (with food reserve); 0.9 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; axileaxile:
(with food reserve); 0.9 times the length of food reserve; at one end of seed not extending into a depression or cup; axileaxile:
on or of the axis
and centric; foliatefoliate:
appearing leaf-like
, or linearlinear:
(shape) long, narrow, and uniform in width; (of embryo) embryo is straight and much longer than wide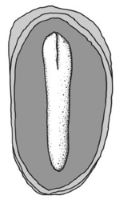 (more or less); with spatulatespatulate:
(more or less); with spatulatespatulate:
2D shape—like a spatula; rounded at the apex, with base long and tapered; (of embryo) embryo is straight and axile and centric with the cotyledons expanded to form the shape of a spatula or spoon; (of cotyledons) cotyledons expanded and wider than the stalk but not invested into the stalk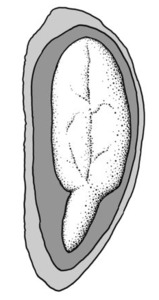 cotyledons, or investinginvesting:
cotyledons, or investinginvesting:
(of embryo) embryo is nearly or completely filling seed coat, straight, and axile and centric with spatulate cotyledons and covering the stalk for at least half its length; (of cotyledons) cotyledons spatulate and covering the stalk for at least half its length
cotyledons; straight, or arcuate; parallel to seed length; embedded in endosperm; with cotyledons abruptly connected to hypocotyl-radicle, or gradually connected to hypocotyl-radicle; without coleorhiza; without simmondsin; with cotyledons containing oils; without stomata; not green; with 2 or more cotyledons, or acotyledonous (Stibye). Cotyledons 2; well developed; 0.5–0.8 times length of embryo; somewhat to significantly wider than hypocotyl-radicle; 1.3–3 times wider than hypocotyl-radicle; not concealing hypocotyl-radicle, or partially concealing hypocotyl-radicle; not foliaceous, or foliaceous; thin; flat, or once-folded, or plicate (Avicennia); smooth; with apicesapex:
the point farthest from the point of attachment, or the "tip" of an organ entire; with margins separate; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
entire; with margins separate; basally entire; equal in size; not punctatepunctate:
surface relief - dotted with pits or with translucent, sunken glands or with colored dots, similar to pitted dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle moderately developed, or well developed, or small; straight (radicleradicle:
dotted. Hypocotyl-radicle moderately developed, or well developed, or small; straight (radicleradicle:
the embryonic root of the embryo pubscent in Avicennia); not thickened.
pubscent in Avicennia); not thickened.
Literature specific to this family: Jansen-Jacobs, M.J. 1988. 148. Verbenaceae. In: A.R.A. Gorts-van Rijn, ed., Flora of the Guianas, fasc. 4, pp. 1–114. Koeltz Scientific Books, Koenigstein.
General references: Cronquist, A. 1981. An integrated system of classification of flowering plants, 1,262 p. Columbia University Press, New York, Engler, A. & K. Prantl. 1924 and onward. Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilimien. W. Engelman, Leipzig, Gaertner, J. 1788–1805. De fructibus et seminibus plantarum. The Author, Stuttgart, Goldberg, A. 1986 (dicots) & 1989 (monocots). Classification, evolution, and phylogeny of the familes of Dicotyledons. Smithsonian Contr. Bot. 58 for dicots (314 pp.) & 71 for monocots (74 pp.). [Goldberg's illustrations are reproduced from older publications and these should be consulted], Gunn, C.R. & J.V. Dennis. 1976. World guide to tropical drift seeds and fruits, 240 pp. The New York Times Book Co., New York, Gunn, C.R. & C.A. Ritchie. 1988. Identification of disseminules listed in the Federal Noxious Weed Act. Techn. Bull. U.S.D.A. 1719:1–313, Gunn, C.R., J.H. Wiersema, C.A. Ritchie, & J.H. Kirkbride, Jr. 1992 & amendments. Families and genera of Spermatophytes recognized by the Agricultural Research Service. Techn. Bull. U.S.D.A. 1796:1–500, Mabberley, D.J. 1987. The plant-book, 706 p. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Martin, A.C. 1946. The comparative internal morphology of seeds. Amer. Midl. Naturalist 36:513–660, Schopmeyer, C.S. 1974. Seeds of Woody plants in the United States. Agric. Handb. 450:1–883, and Spjut, R.W. 1994. A systematic treatment of fruit types. Mem. New York Bot. Gard. 70:1–182.