Family: Siricidae
Subfamily: Siricinae
Genus: Sirex Linnaeus, 1760
Species: Sirex atricornis Kjellander, 1945
Common names: none
Sirex atricornis is a rare species known only from northern Europe (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
See Sirex for genus-level diagnostic characteristics.
Females:
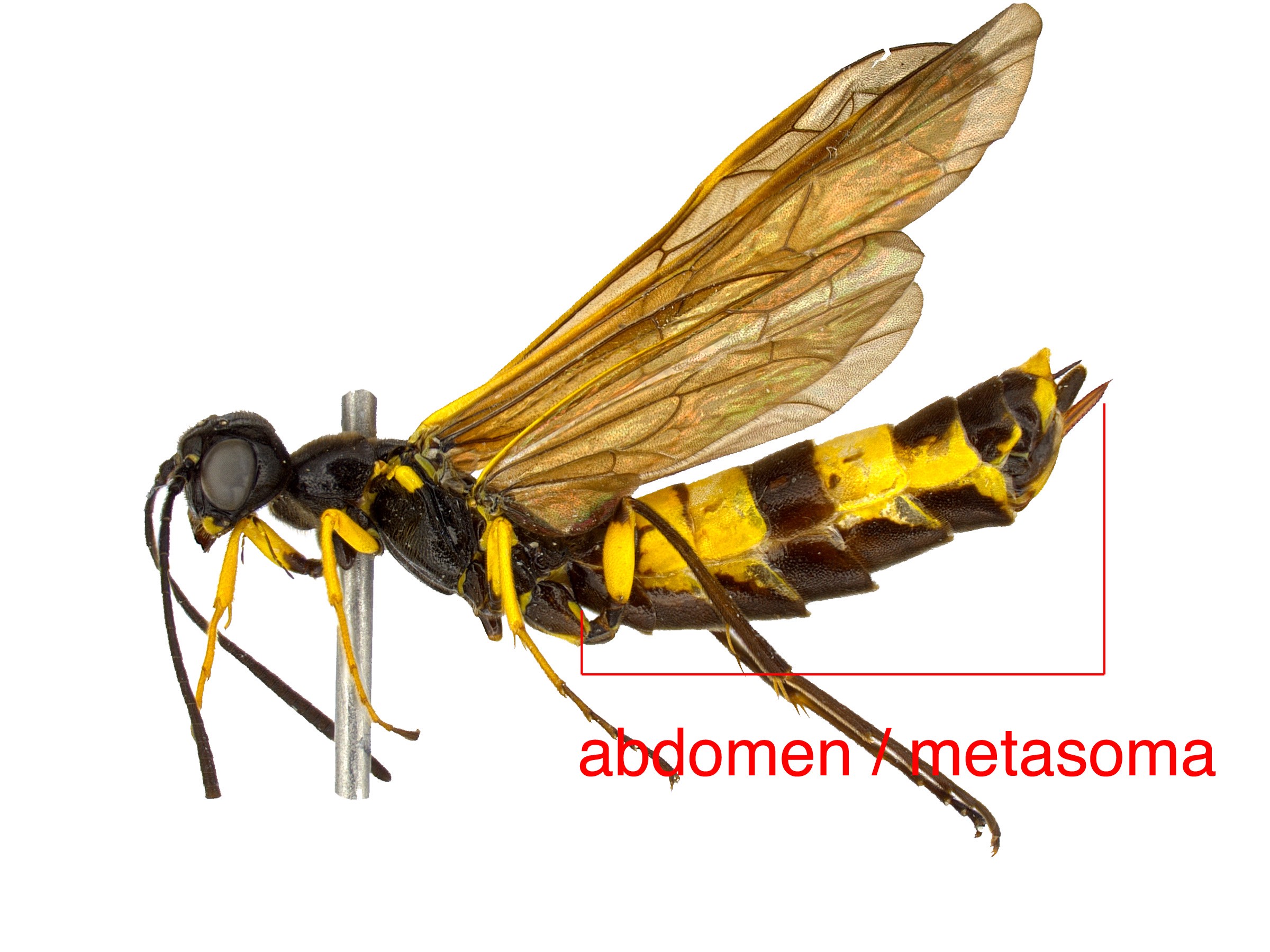 blue-black with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
blue-black with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:Sirex atricornis can be distinguished from the similar NearcticNearctic:
describing the region of the Northern Hemisphere that includes North America south through northern Mexico
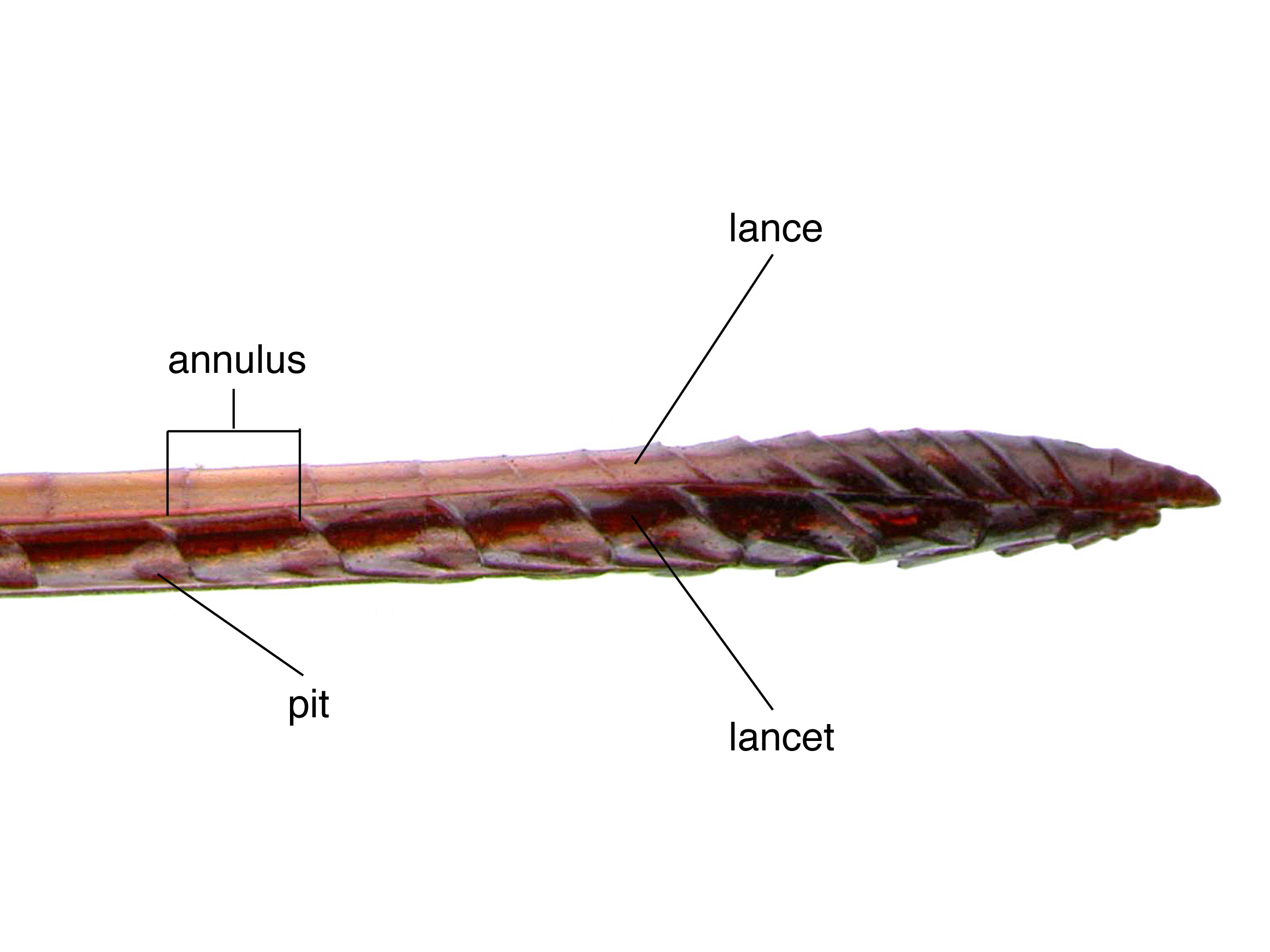
 species S. nitidus only by the shape of the second annulusannulus:
species S. nitidus only by the shape of the second annulusannulus:
a ring wrapped around any structure; a division line on the lancet
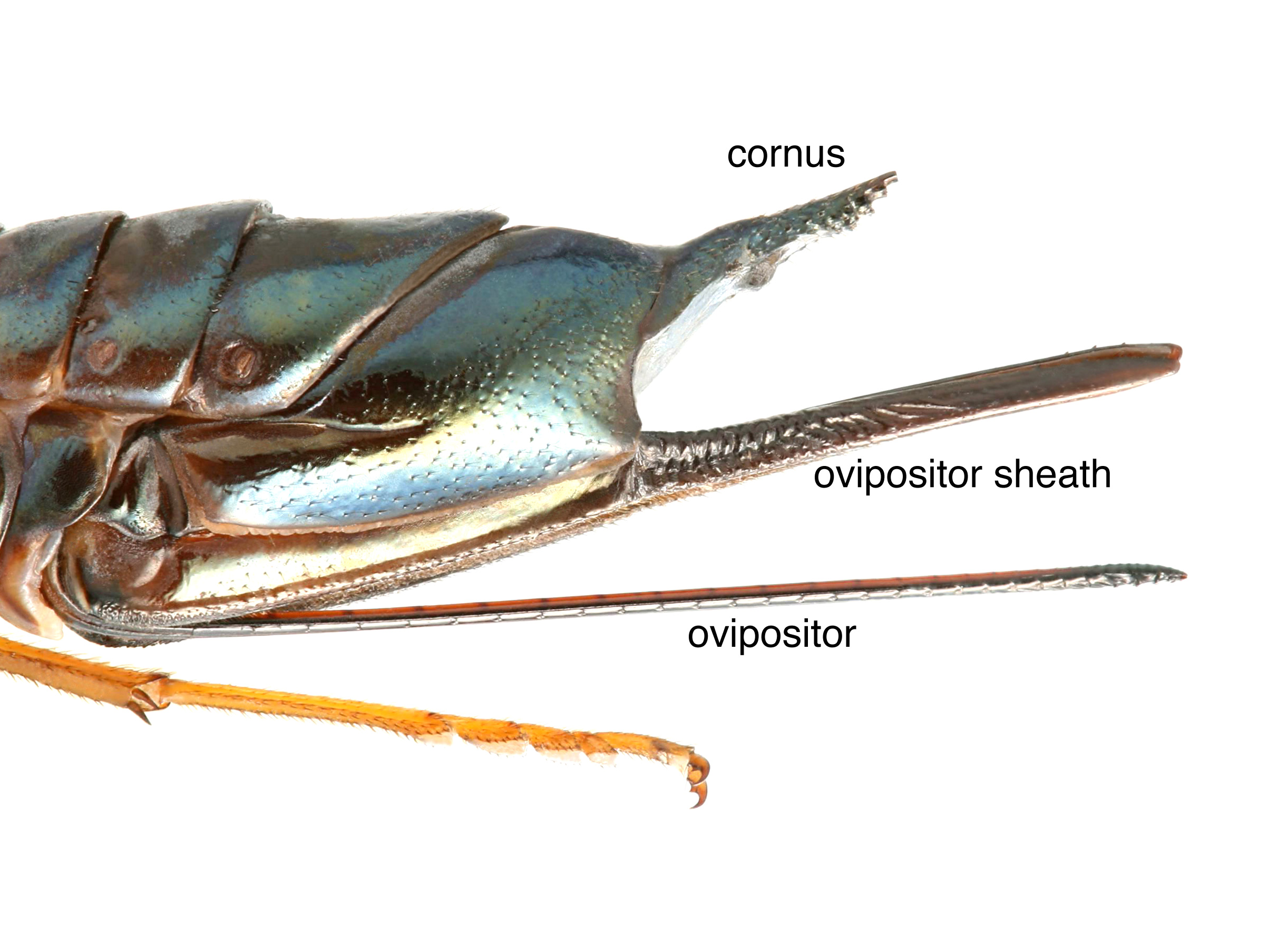
 of the ovipositorovipositor:
of the ovipositorovipositor:
the female organ that deposits eggs and is used to drill into plant tissue, located at the apex of the abdomen, made up of the lance and lancet
 (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
none recorded
Sirex species feed on trees of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae. Sirex atricornis is recorded from Pinus sylvestris (Viitasaari 1984Viitasaari 1984:
Viitasaari M. 1984. Sahapistiauml;iset 3. Siricicoidea, Orussoidea, ja Cephoidea. University of Helsinki, Department of Agricultural and Forest Zoology Reports 6.) and likely feeds on other Pinus spp. (pine) (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
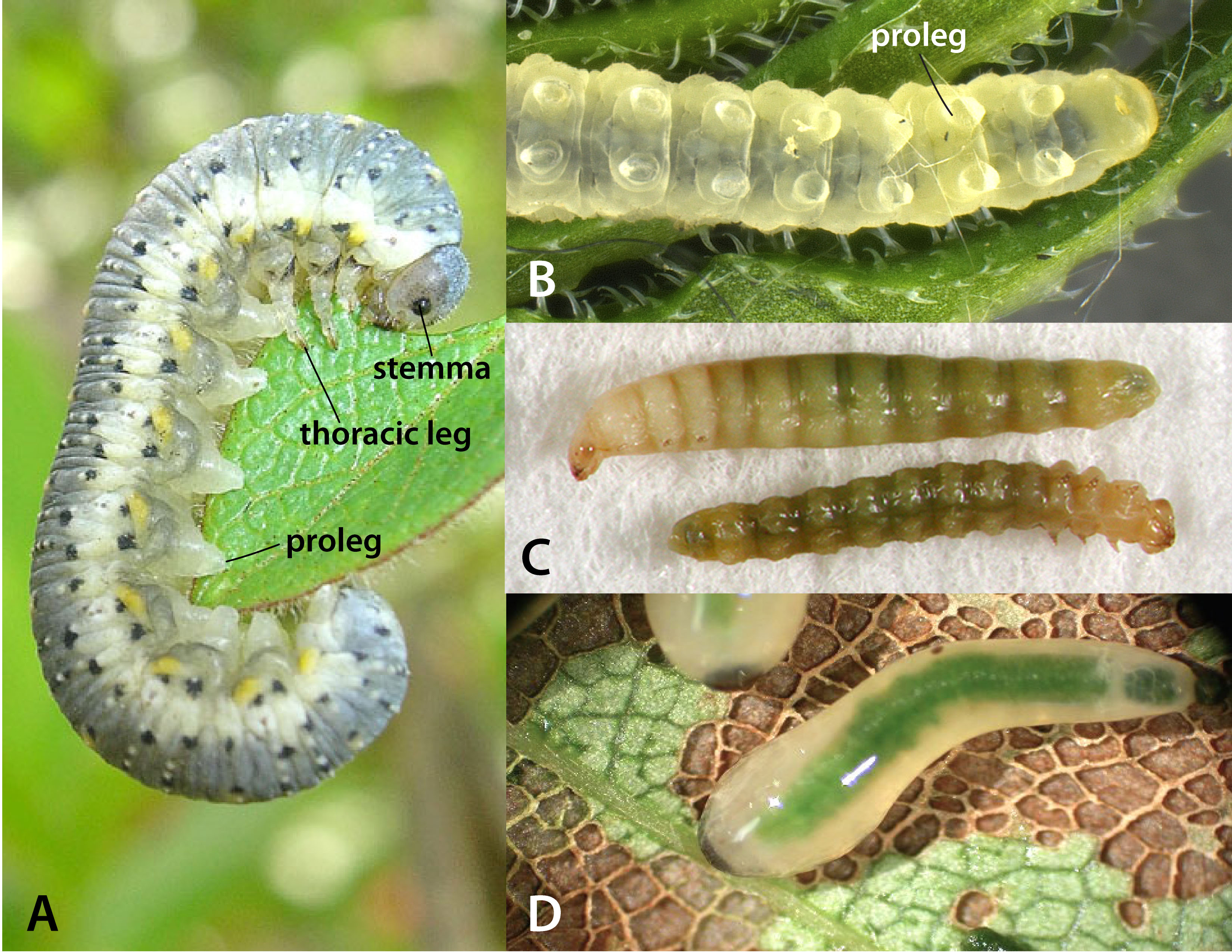
Female Sirex harbor symbiotic basidiomycete fungus in abdominal glands called mycangia. During oviposition, the site is inoculated with the fungus (Amylostereum spp.), which begins to decompose the surrounding wood. LarvaeLarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Larvae are creamy white and grub-like in appearance with a dark head capsule. As with adults, larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 possess a short dorsaldorsal:
possess a short dorsaldorsal:
of or on the top surface of the body or structure
horn on the posterior end of the body. The larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
The specific biology of Sirex atricornis is unknown.
World: Sirex atricornis is found in northern Scandinavia, Finland, and Russia (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
North America: not recorded
Map data from: GBIF.org (26 June 2019) GBIF Occurrence Download Sirex atricornis
Details about data used for maps can be found here.