Family: Siricidae
Subfamily: Siricinae
Genus: Sirex Linnaeus, 1760
Species: Sirex californicus (Ashmead, 1904)
Common names: none
Sirex californicus is a western NearcticNearctic:
describing the region of the Northern Hemisphere that includes North America south through northern Mexico
 species with two color forms (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
species with two color forms (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
See Sirex for genus-level diagnostic characteristics.
Females:
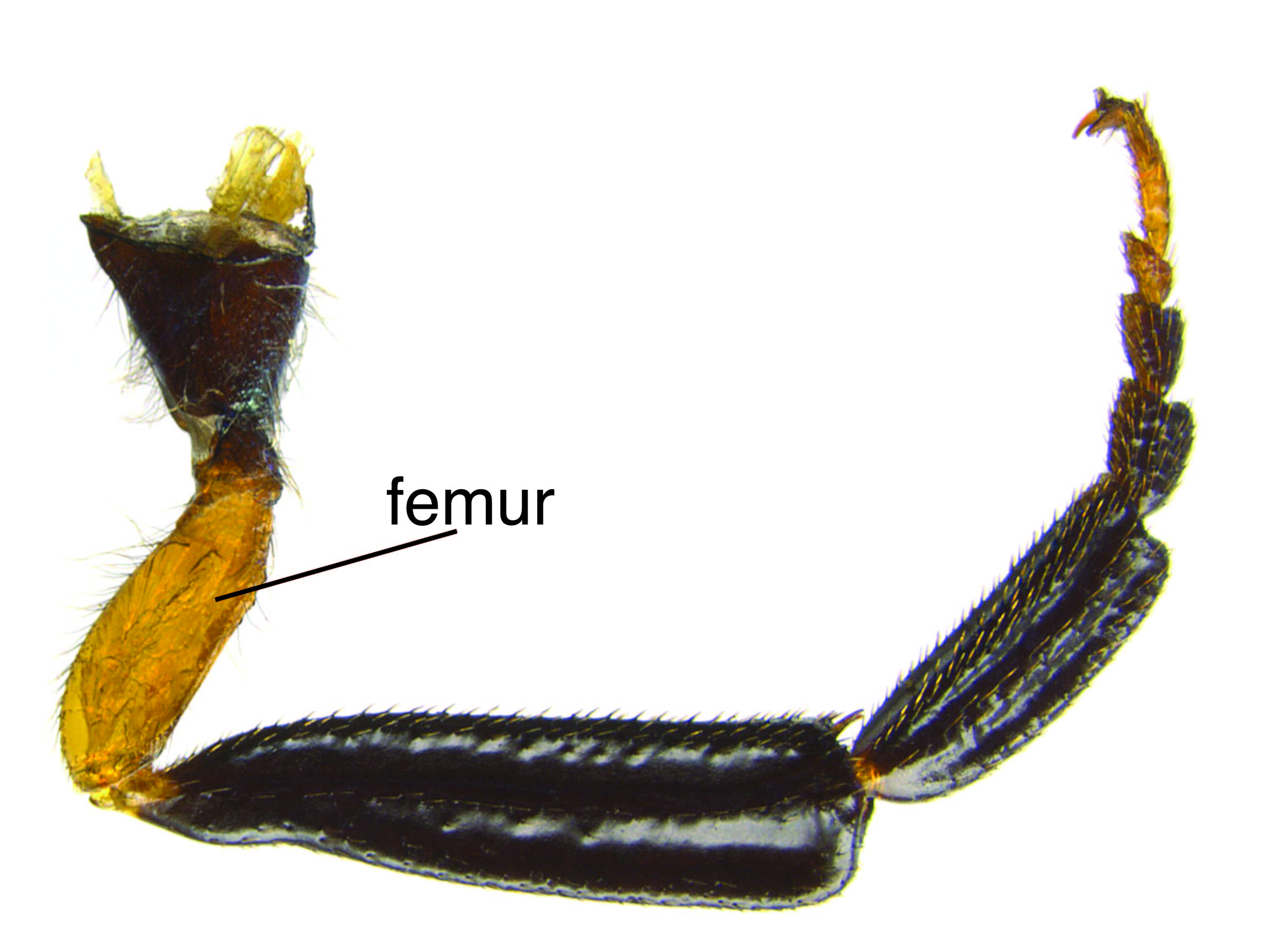 , tibiaetibia:
, tibiaetibia: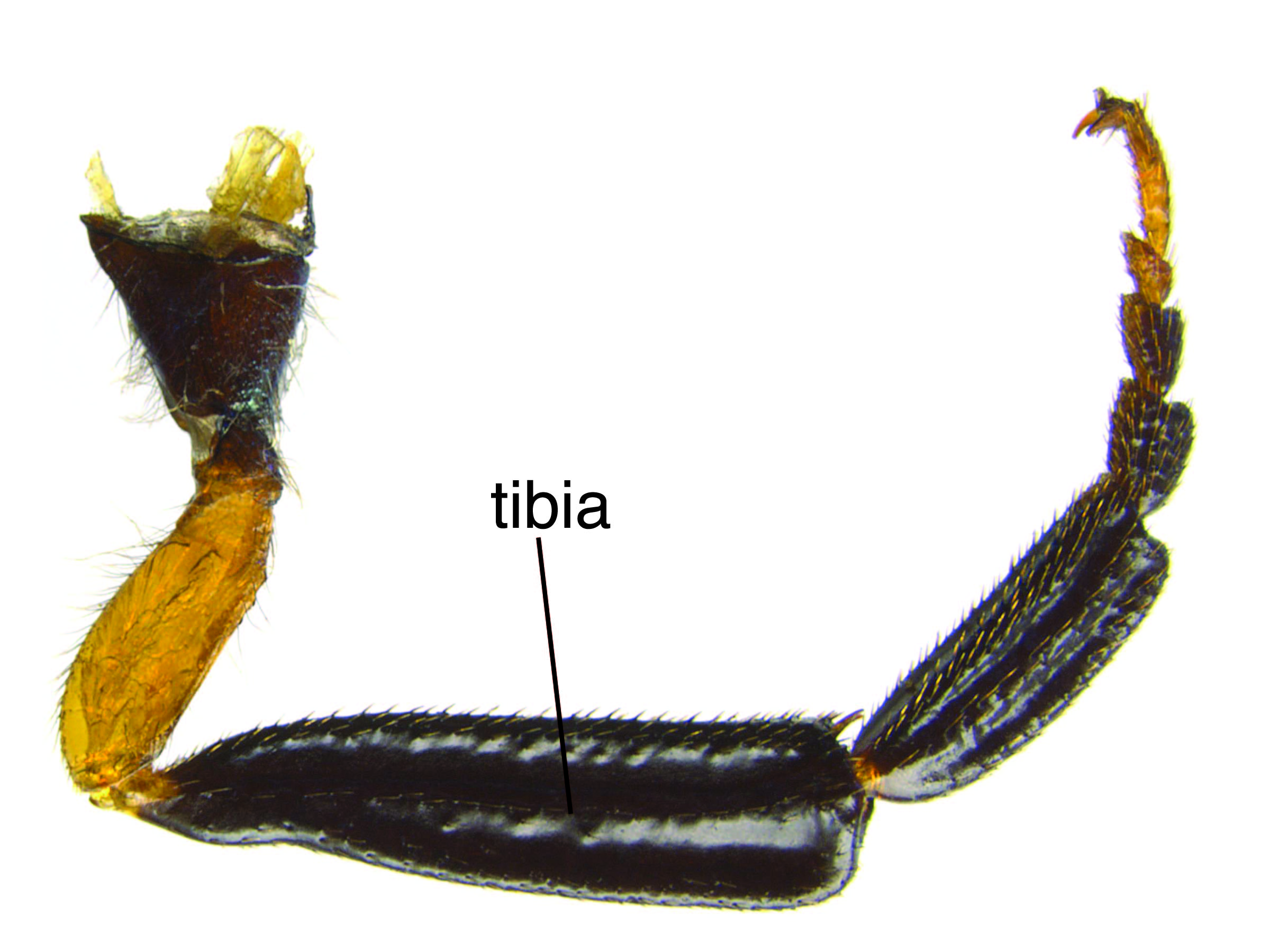 , and tarsomeres 1–4, remaining leg black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
, and tarsomeres 1–4, remaining leg black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: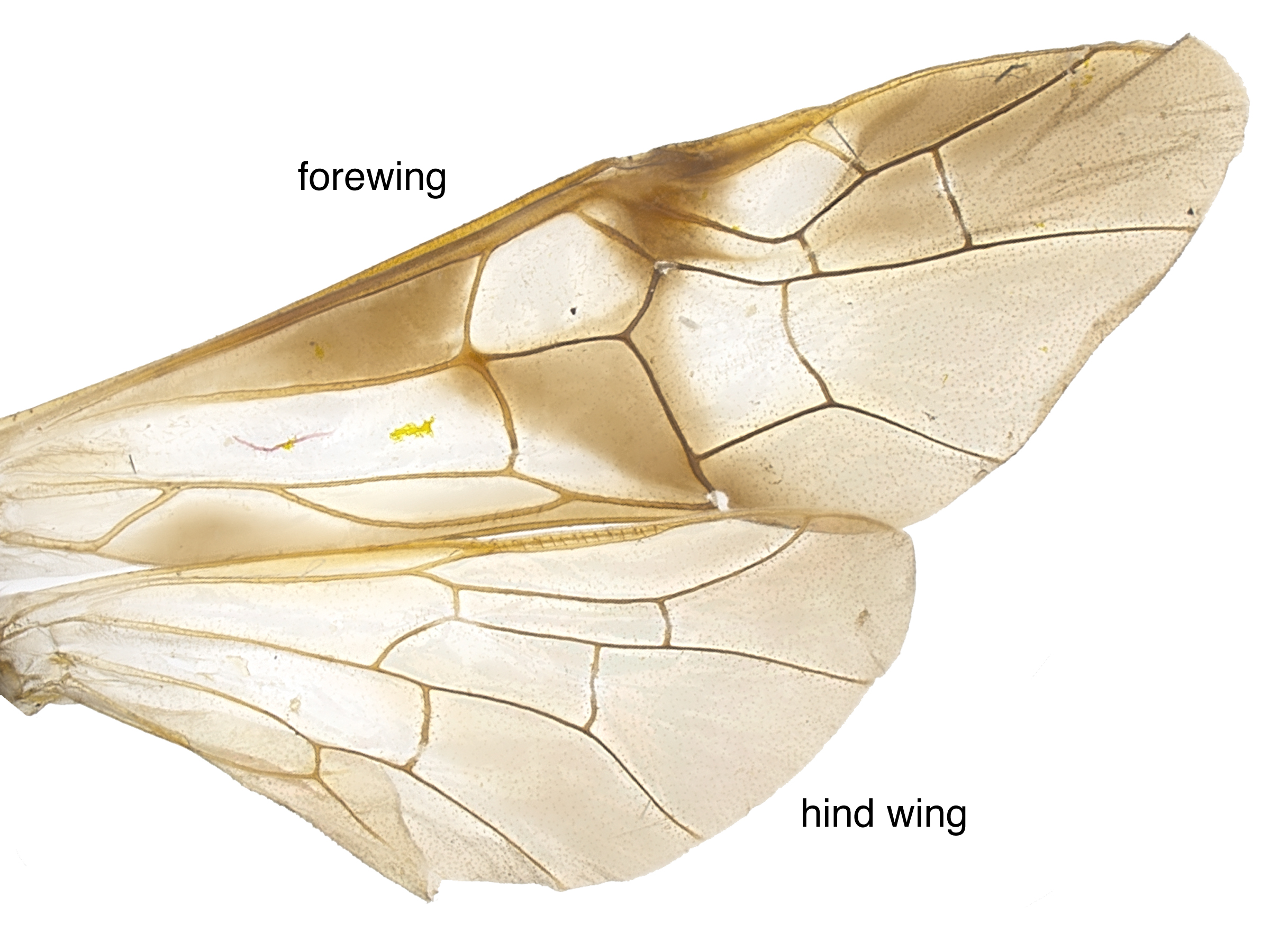 entirely darkened, or with darkened bands at stigmastigma:
entirely darkened, or with darkened bands at stigmastigma: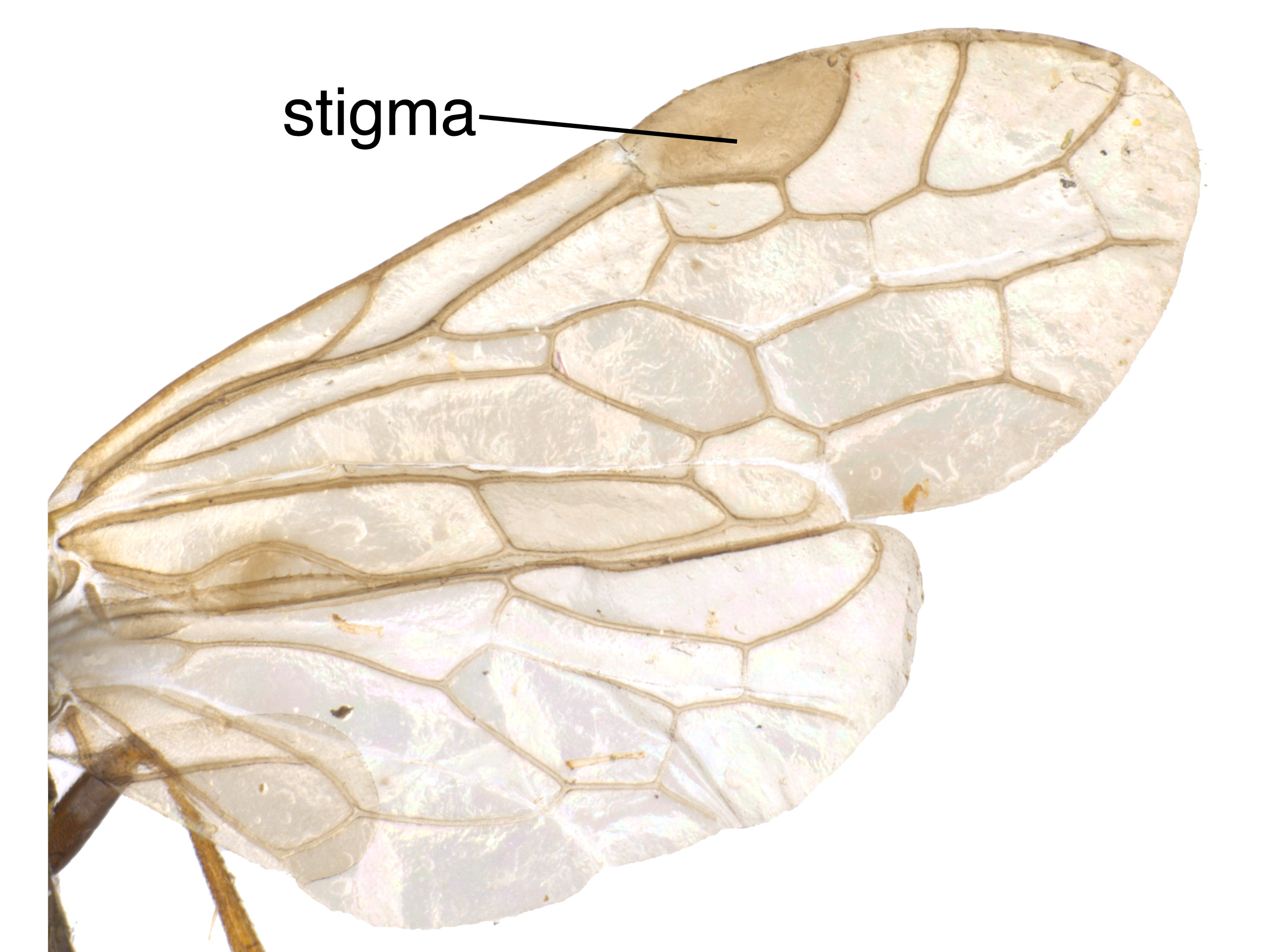 and apexapex:
and apexapex: vein 3A absent (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
vein 3A absent (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: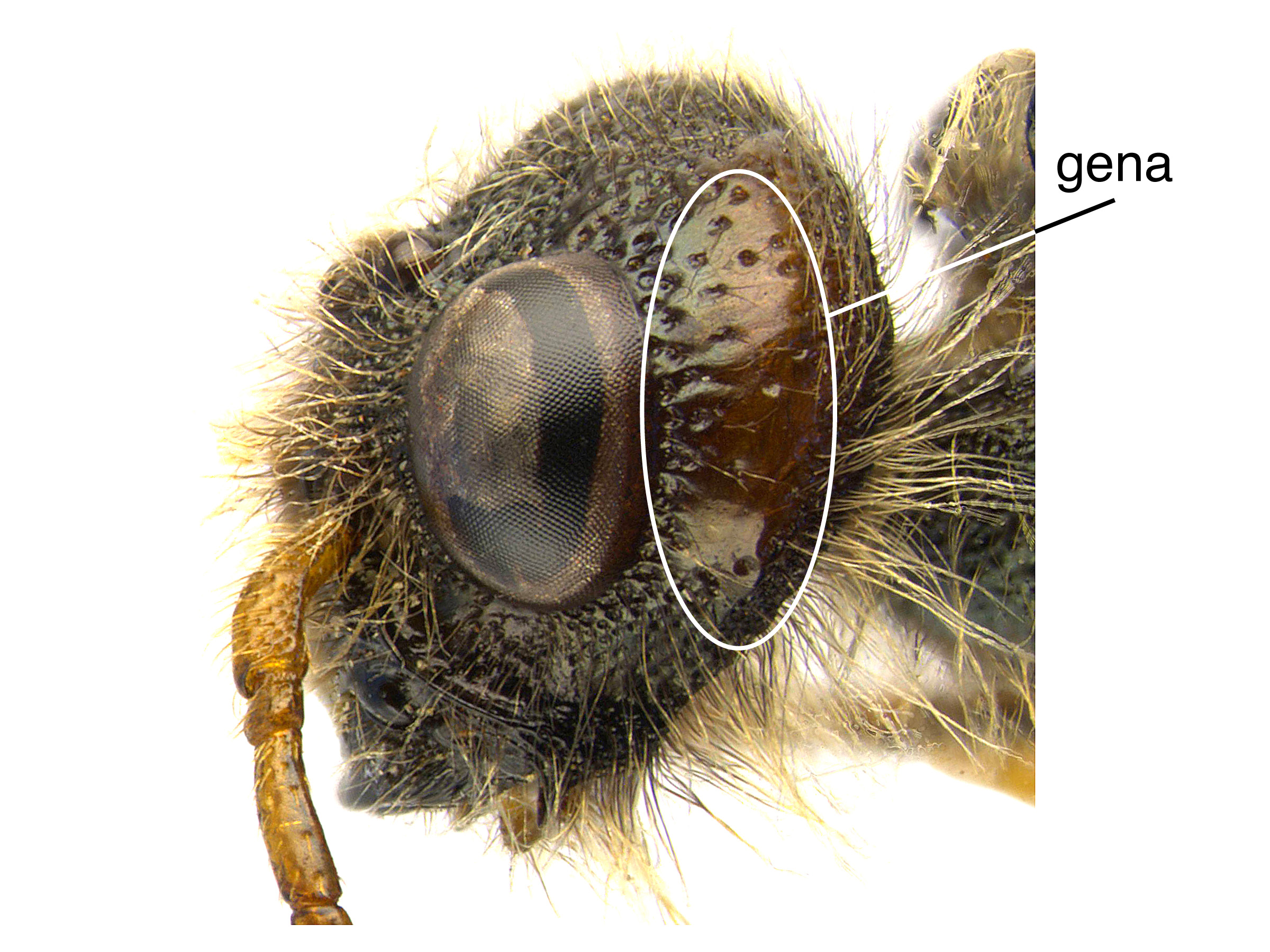 pits scattered, about 2–4 pit diameters apart (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
pits scattered, about 2–4 pit diameters apart (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: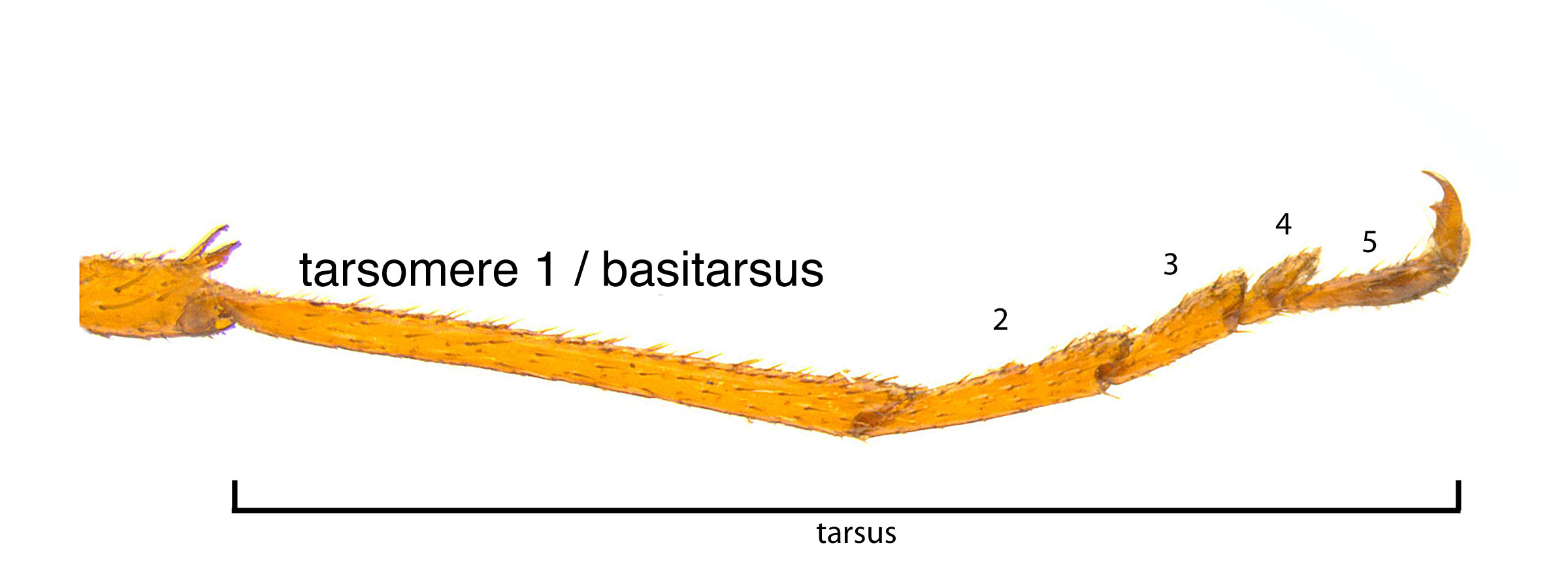 more than twice as long as wide (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
more than twice as long as wide (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: pits with margins raised in a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
pits with margins raised in a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: with pulvilluspulvillus:
with pulvilluspulvillus: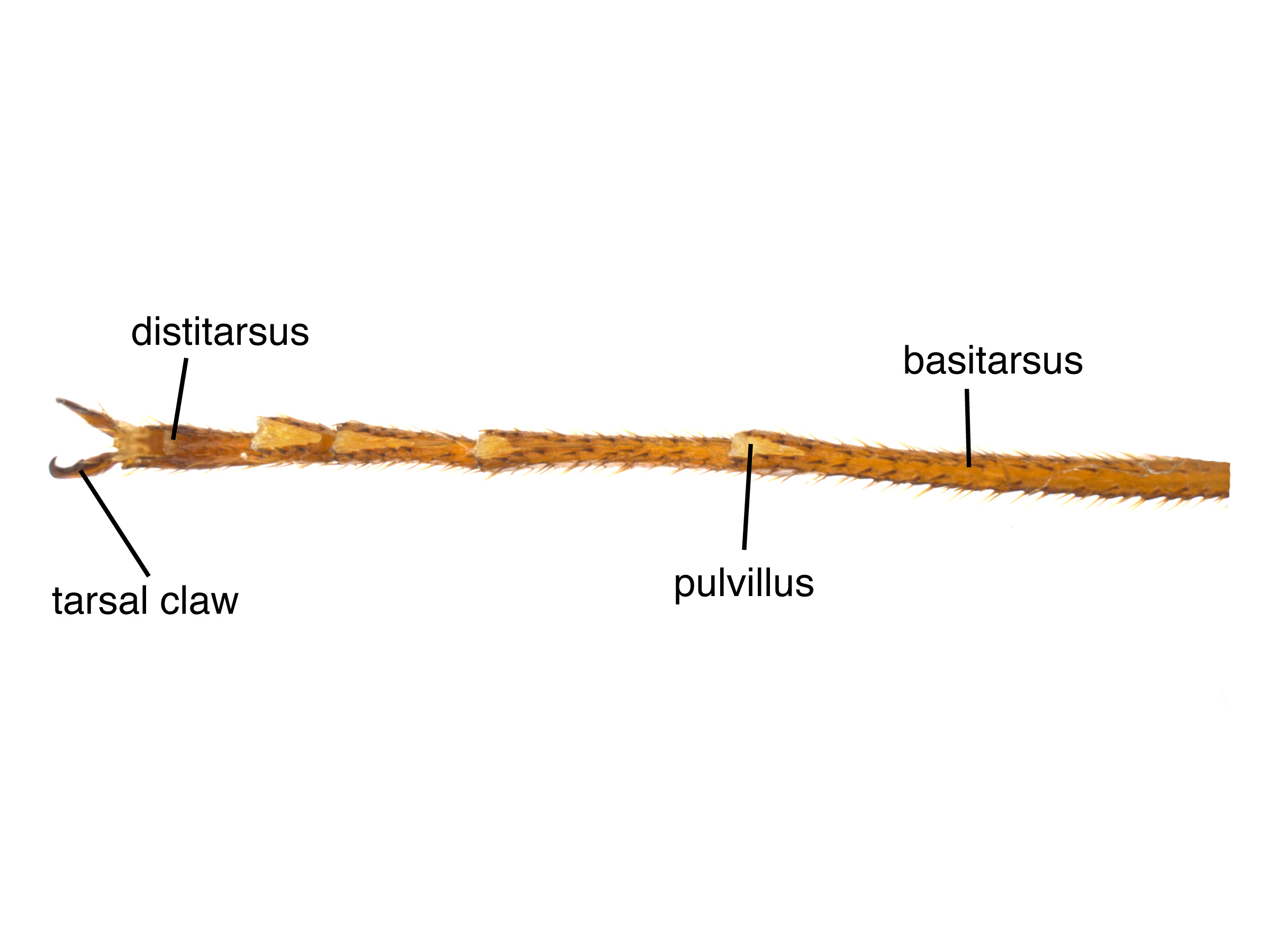 about half length of tarsomeretarsomere:
about half length of tarsomeretarsomere: (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:Males:
 completely blue-black with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
completely blue-black with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: and vertexvertex:
and vertexvertex: clear, sometimes with a light yellow tint (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
clear, sometimes with a light yellow tint (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: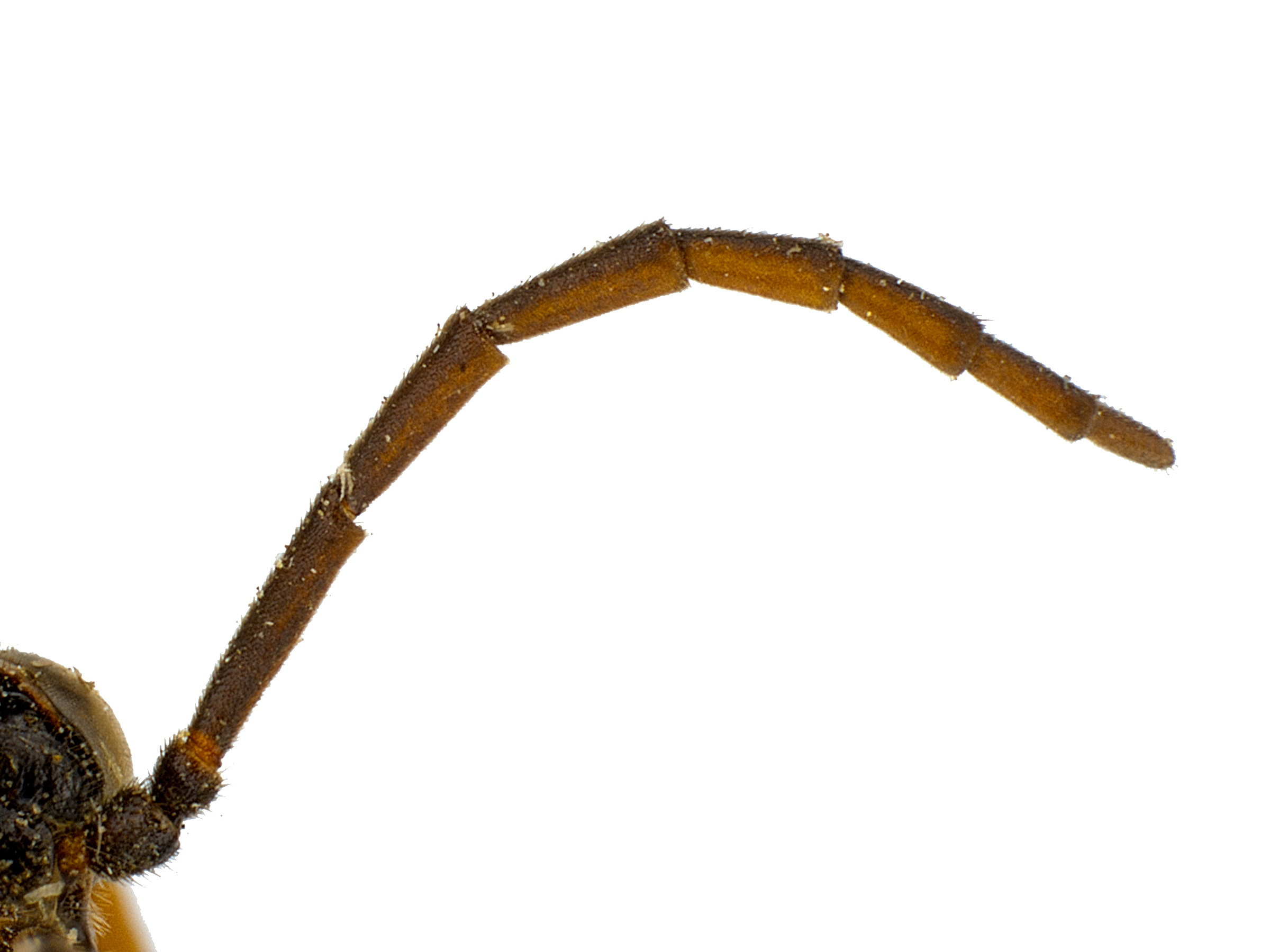 reddish-brown at basebase:
reddish-brown at basebase:Sirex californicus females can be distinguished from most Sirex by the completely black legs and darkened fore wingsfore wing:
the anterior wing of each pair of wings; usually the largest wing of the pair
 , and from S. obesus and S. nigricornis by the small, scattered pits on the genagena:
, and from S. obesus and S. nigricornis by the small, scattered pits on the genagena:
the area of the head between the compound eye and clypeus; also called the cheek
 and vertexvertex:
and vertexvertex:
the dorsal portion of the head between the compound eyes, between the occiput and frons
. Males are distinguished by the reddish-brown legs and the bicolored antennaeantenna:
the sensory organ emerging from the front of the head, usually between the compound eyes and above the clypeus; includes the flagellum, scape and pedicel
 (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
There are two color morphs of S. californicus females. The dark form with entirely dark legs is common throughout the range, while the pale form, with light-colored legs, is found in the northern regions of the range (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Sirex species feed on trees of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae. Sirex californicus is recorded on Pinaceae species Larix occidentalis (western larch), Pinus albicaulis (whitebark pine), Pinus ponderosa (ponderosa pine), Pinus contorta (lodgepole pine), Pinus coulteri (Coulter pine), Pinus jeffreyi (Jeffrey pine), Pinus lambertiana (sugar pine), Pinus monticola (western white pine), and Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine). There is one record of an emergence from Cupressus macrocarpa (Monterey cypress). The majority of specimens reared (99%) have been on Pinus spp. (pine) (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Female Sirex harbor symbiotic basidiomycete fungus in abdominal glands called mycangia. During oviposition, the site is inoculated with the fungus, which begins to decompose the surrounding wood. LarvaeLarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
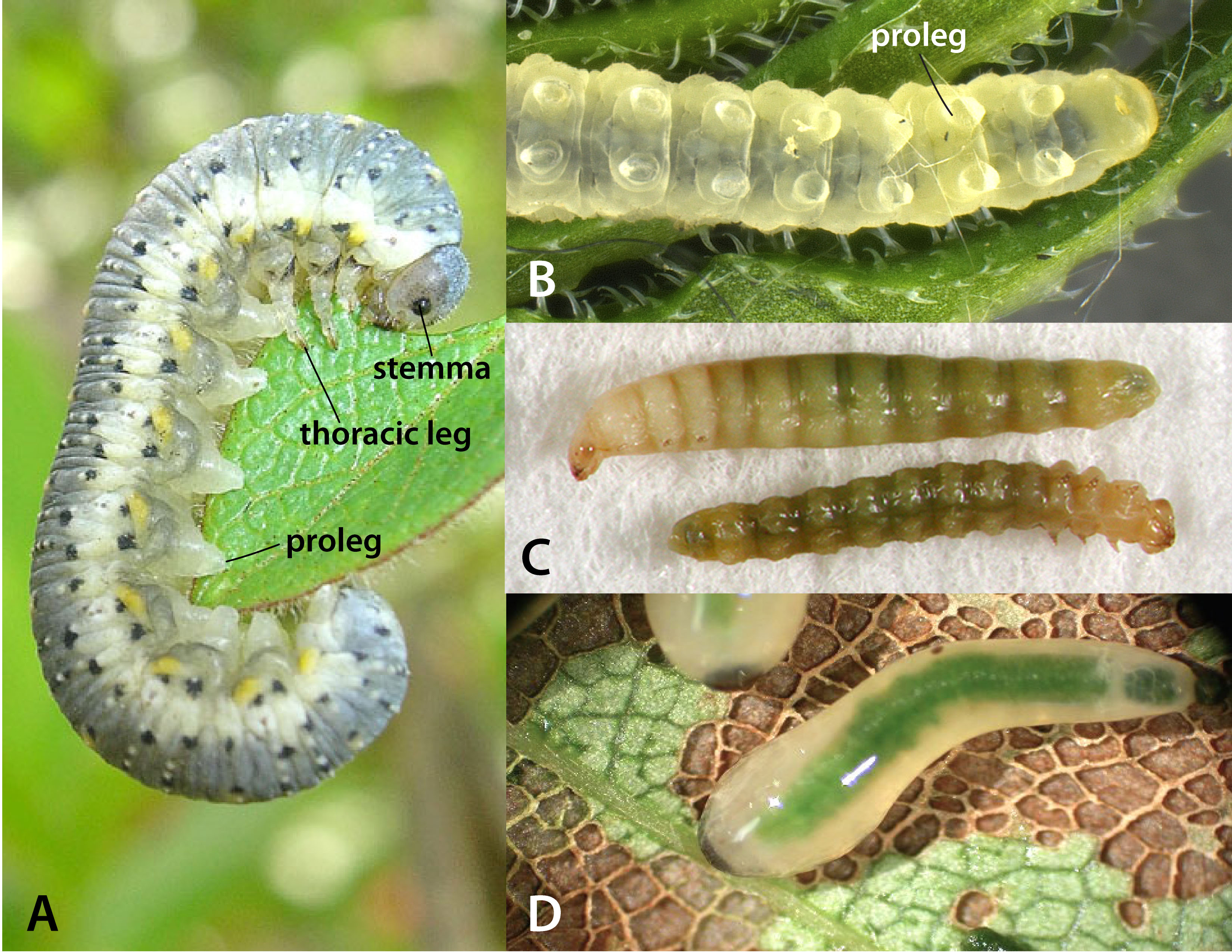 feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Johnson 1930Johnson 1930:
feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Johnson 1930Johnson 1930:
Johnson CW. 1930. On the variation and abundance of Sirex nitidus Harris. Psyche 37 (3): 281-282. https://doi.org/10.1155/1930/62786, Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.). It is unknown what species of fungus is harbored by the mycangia of S. californicus, but Amylostereum areolatum and A. chailletii are associated with other NearcticNearctic:
describing the region of the Northern Hemisphere that includes North America south through northern Mexico
 Sirex (Hajek et al. 2013Hajek et al. 2013:
Sirex (Hajek et al. 2013Hajek et al. 2013:
Hajek AE, Nielsen C, Kepler RM, Long SJ, and Castrillo L. 2013. Fidelity among Sirex woodwasps and their fungal symbionts. Microbial Ecology 65: 753-762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0218-z).
Larvae are creamy white and grub-like in appearance with a dark head capsule. As with adults, larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 possess a short dorsaldorsal:
possess a short dorsaldorsal:
of or on the top surface of the body or structure
horn on the posterior end of the body. The larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
The documented flight period of S. californicus is late July through late September, with most collections in late August (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.). There is some evidence that trees with sustained damage, either from drought-related stress, weather, or other insect infestations, are preferred as hosts (Burnip et al. 2010Burnip et al. 2010:
Burnip GM, Voice D, and Brockerhoff EG. 2010. Interceptions and incursions of exotic Sirex species and other siricids (Hymenoptera: Siricidae). New Zealand Journal of Forestry Science 40: 133-140.).
World: North America. At least one interception has been recorded from New Zealand (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
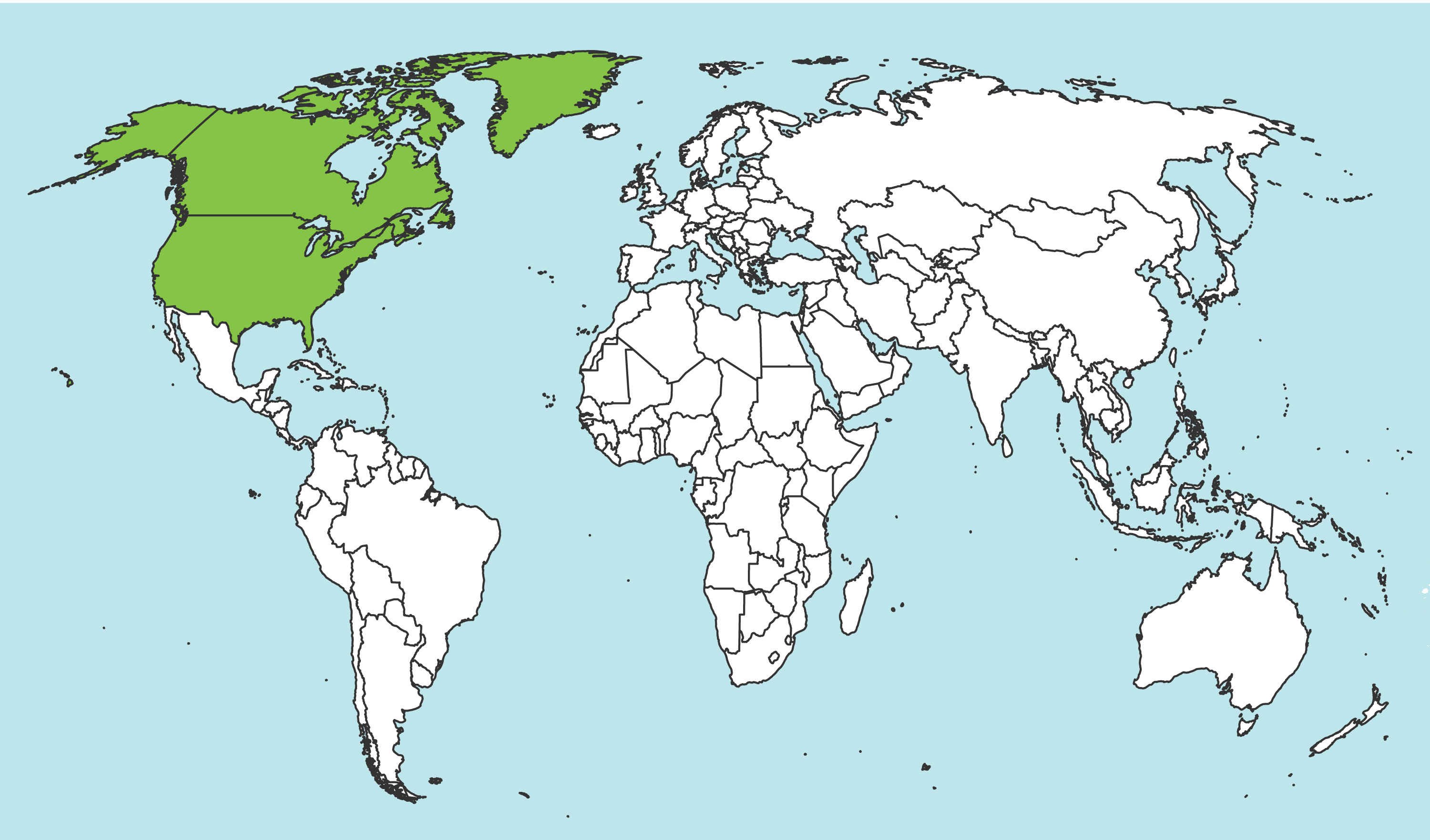
North America: Sirex californicus occurs in the Rocky Mountain region west to the Pacific Ocean, as far north as British Columbia, and south to New Mexico (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Map data from Washington State Department of Agriculture Entomology Collection.
Details about data used for maps can be found here.