Family: Siricidae
Subfamily: Siricinae
Genus: Sirex Linnaeus, 1760
Species: Sirex nitidus (Harris, 1841)
Common names: none
Sirex nitidus is a northern NearcticNearctic:
describing the region of the Northern Hemisphere that includes North America south through northern Mexico
 species with a typical metallic blue-black coloration (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
species with a typical metallic blue-black coloration (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
See Sirex for genus-level diagnostic characteristics.
Females:
 usually light reddish-brown and rarely partially black or entirely black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
usually light reddish-brown and rarely partially black or entirely black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: metallic blue-black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
metallic blue-black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: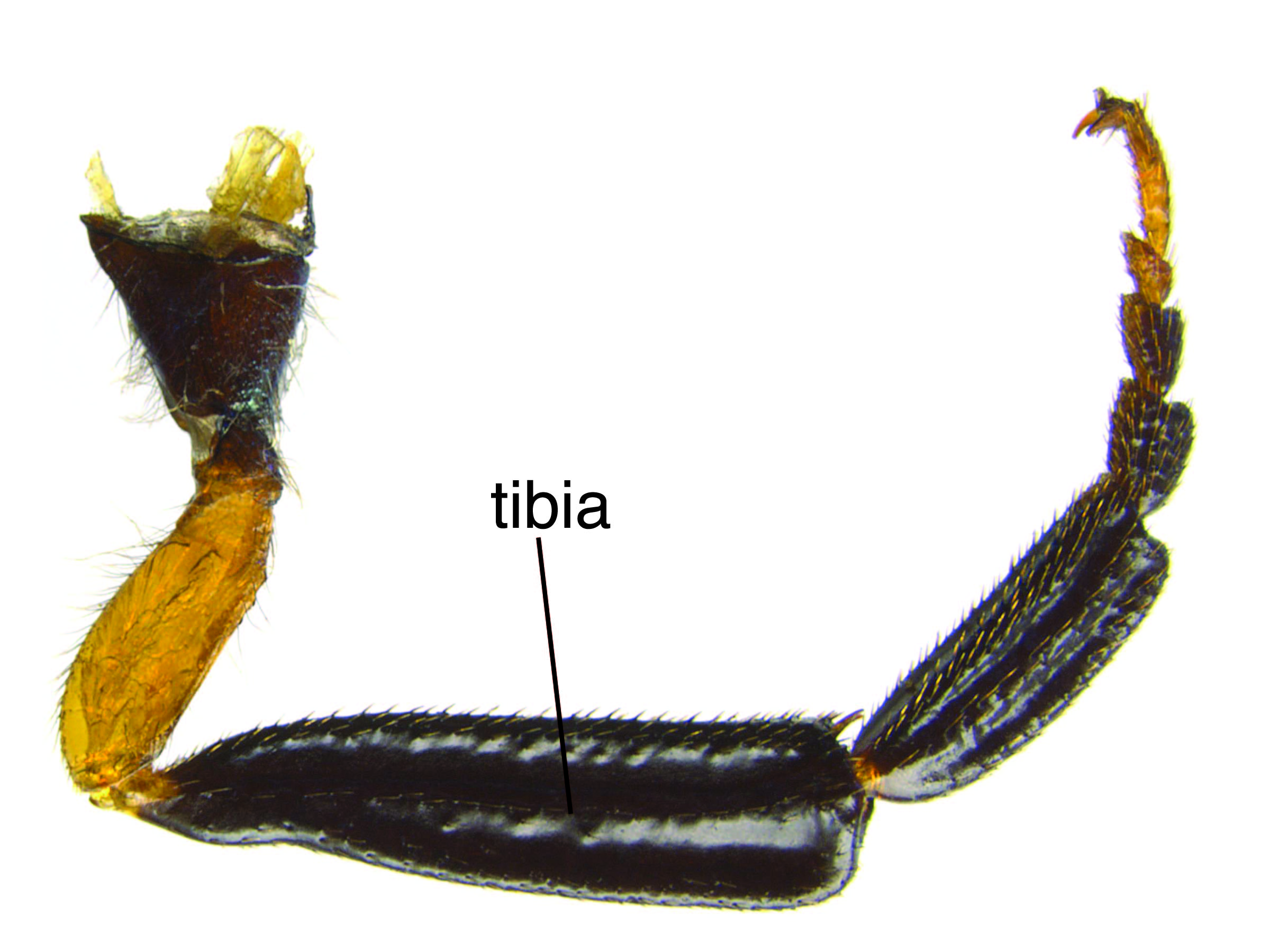 light reddish-brown (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
light reddish-brown (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: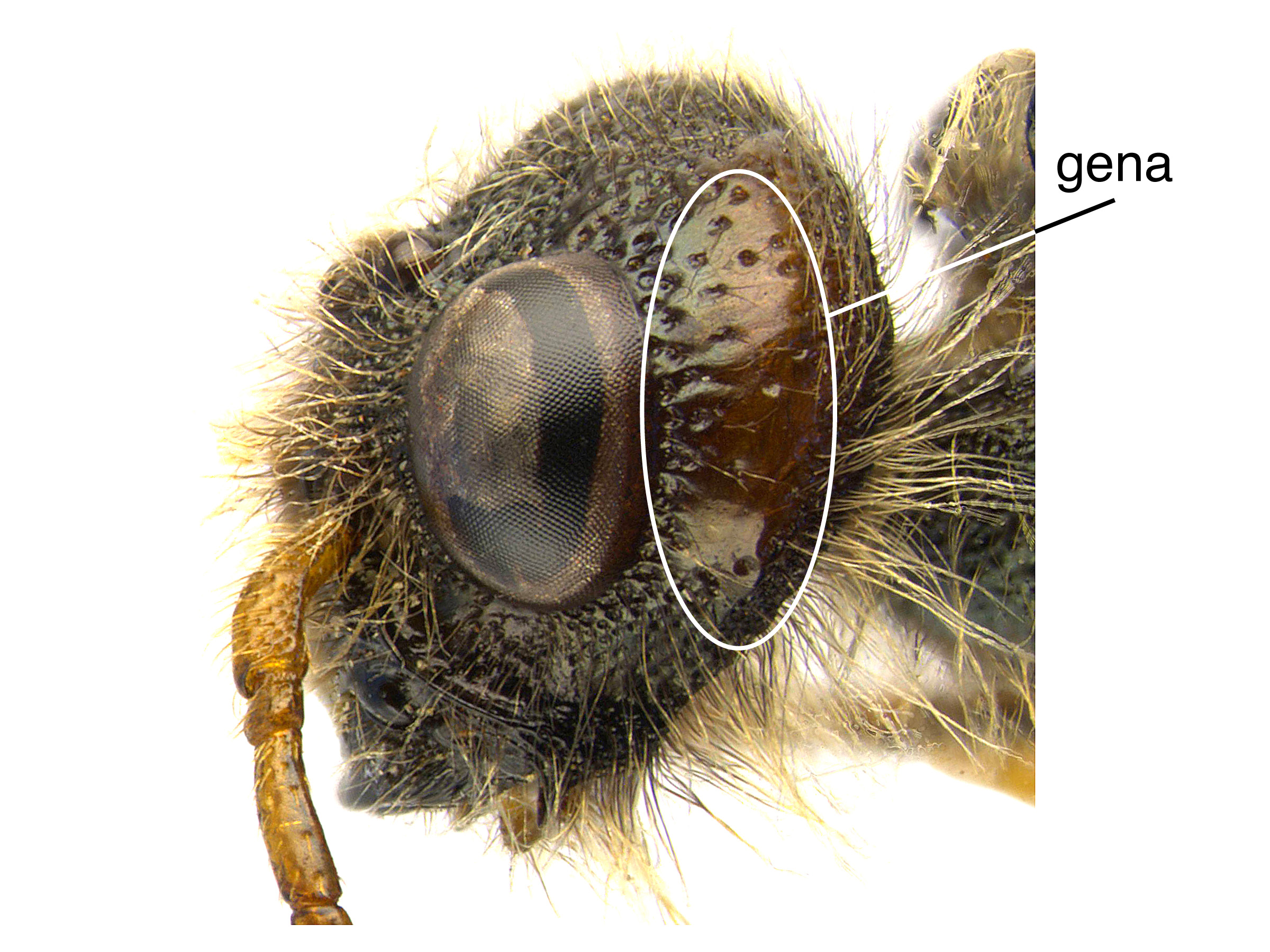 small, about 0.1–0.25 times size of laterallateral:
small, about 0.1–0.25 times size of laterallateral: scattered, about 2–10 pit diameters apart (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
scattered, about 2–10 pit diameters apart (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: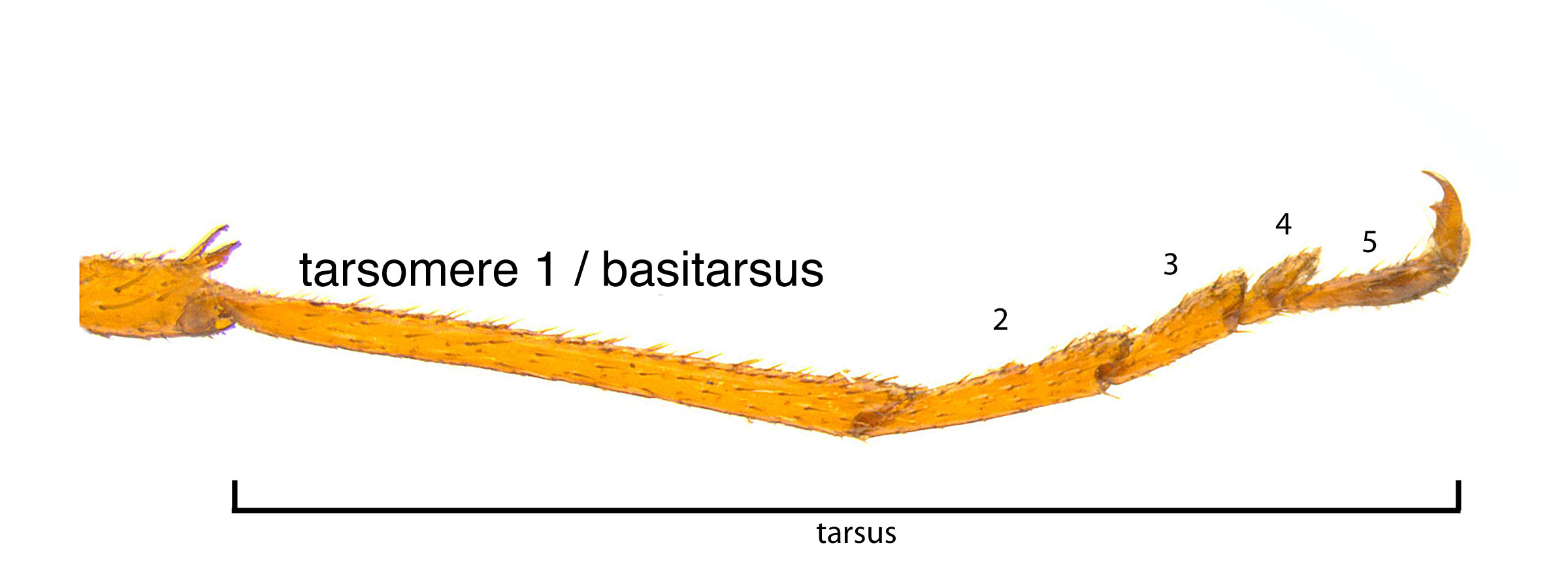 2–3.5 times as long as wide (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
2–3.5 times as long as wide (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: pits with projections, forming a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
pits with projections, forming a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: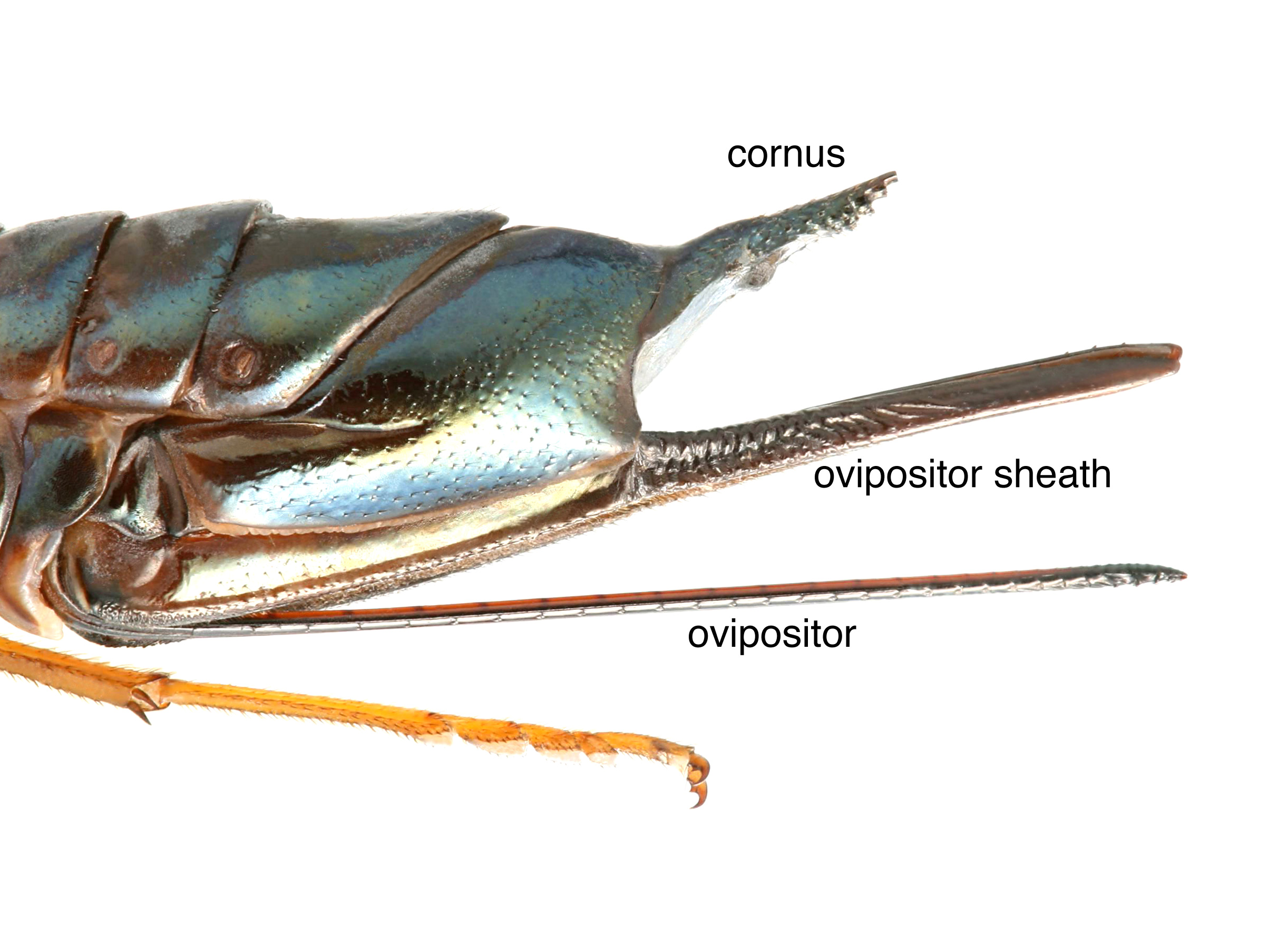 with clear pits, including annulusannulus:
with clear pits, including annulusannulus: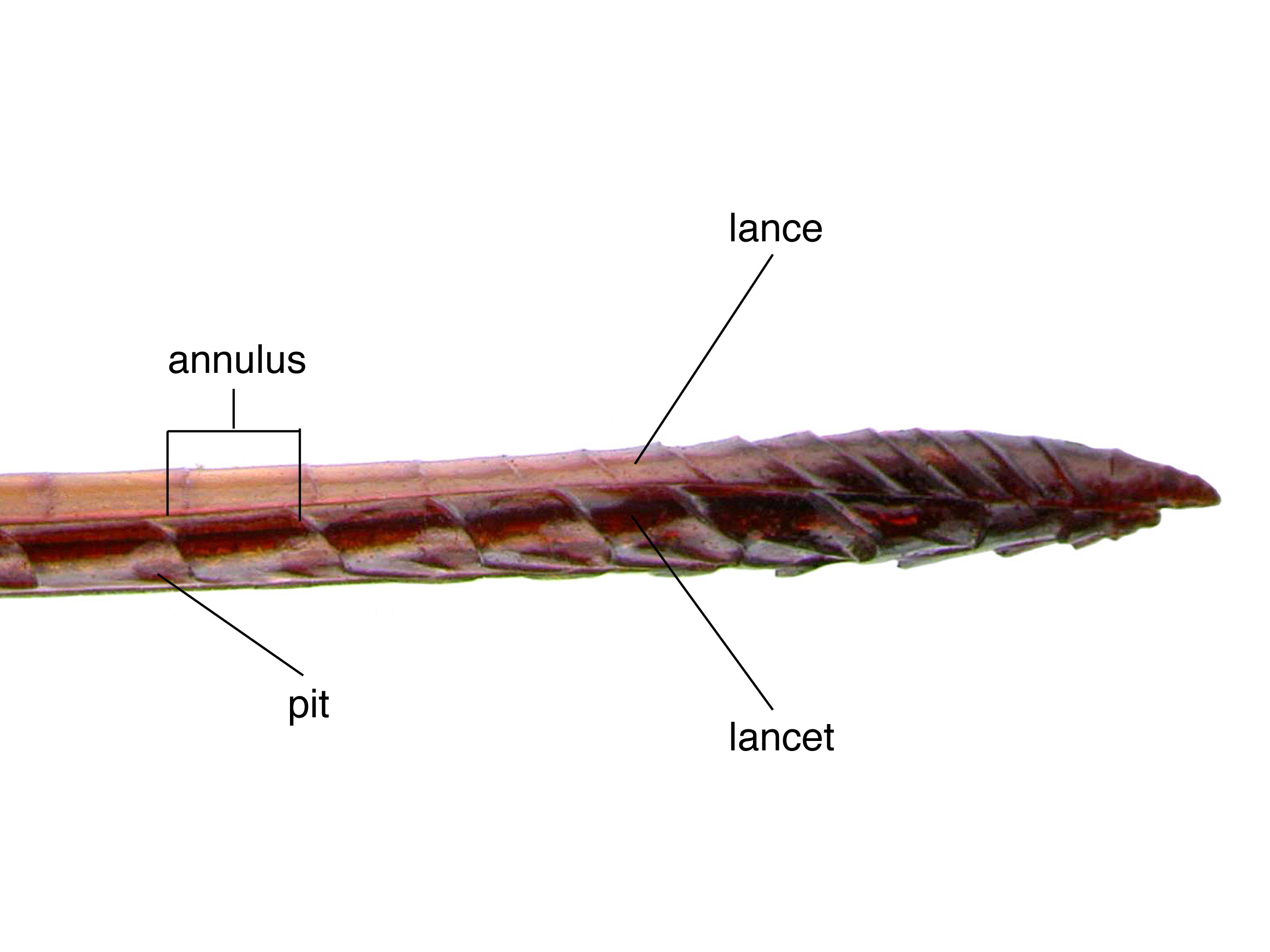 2; some pits smaller than others towards the middle (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
2; some pits smaller than others towards the middle (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: with pulvilluspulvillus:
with pulvilluspulvillus: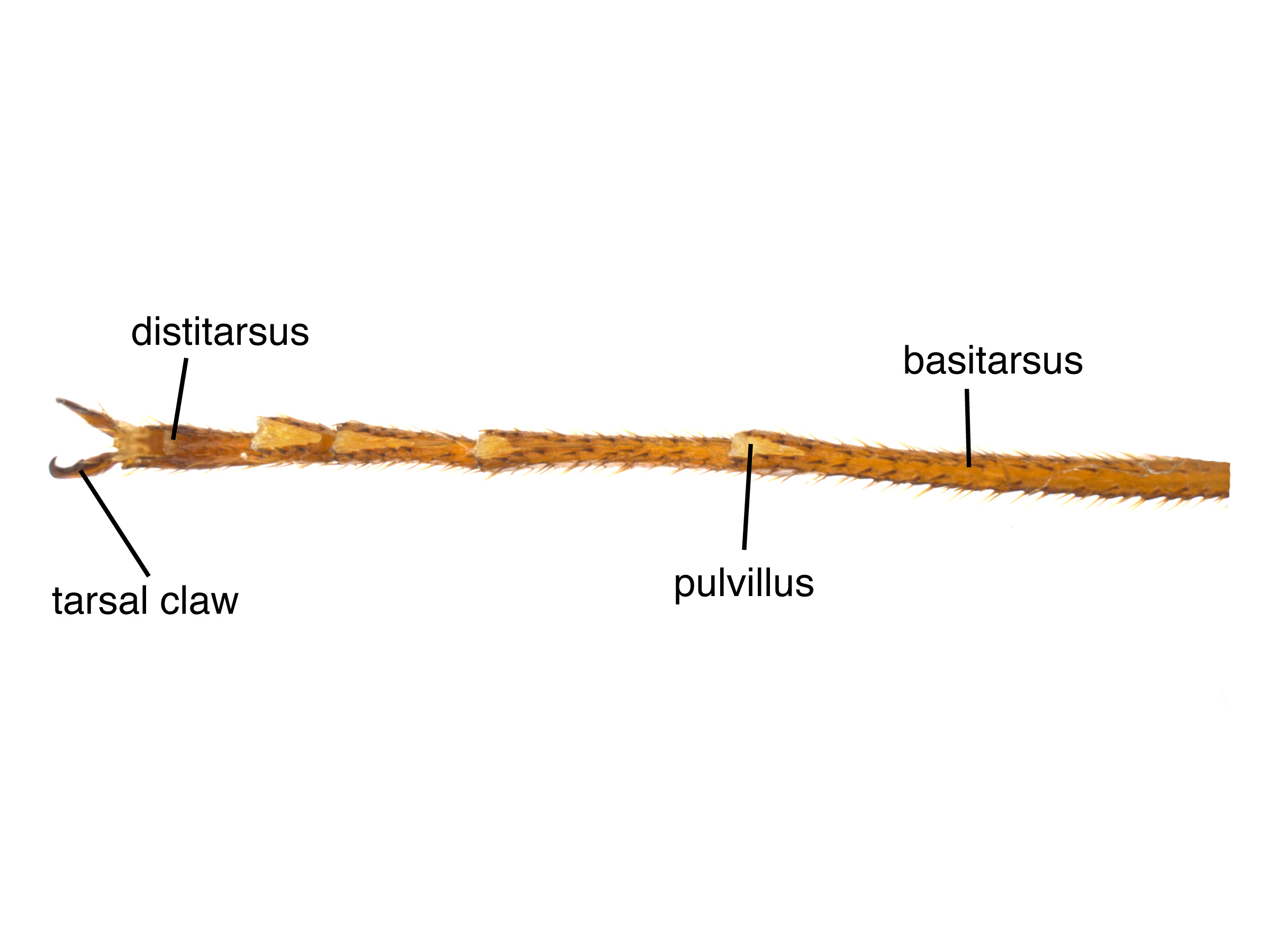 0.8 times length of tarsomeretarsomere:
0.8 times length of tarsomeretarsomere: (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: annulusannulus:
annulusannulus: 10 length 1.3–2 times width (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
10 length 1.3–2 times width (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:Males:
 completely reddish-brown (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
completely reddish-brown (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: dark blue with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
dark blue with metallic reflections (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: usually with narrow band of reddish-brown at basebase:
usually with narrow band of reddish-brown at basebase: completely black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
completely black (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: pits with projections, margins forming a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
pits with projections, margins forming a net-like pattern (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: and/or mid basitarsusbasitarsus:
and/or mid basitarsusbasitarsus: (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012: pits generally 1–3 diameters apart posterodorsallyposterodorsal:
pits generally 1–3 diameters apart posterodorsallyposterodorsal:Sirex nitidus females can be distinguished from S. cyaneus and S. abietinus by the presence of a pit on the second annulusannulus:
a ring wrapped around any structure; a division line on the lancet
 , and from S. californicus and S. noctilio by the relative length of the pulvilluspulvillus:
, and from S. californicus and S. noctilio by the relative length of the pulvilluspulvillus:
soft pads used for surface adhesion, located in sawflies on the first 4 segments of the tarsus
 on the second hind tarsomeretarsomere:
on the second hind tarsomeretarsomere:
a segment of the tarsus
 . It is difficult to distinguish from European species S. torvus and S. atricornis without geographical range or host information as differences are very subtle. The most reliable way to distinguish S. torvus is by slightly denser and smaller pits on the genagena:
. It is difficult to distinguish from European species S. torvus and S. atricornis without geographical range or host information as differences are very subtle. The most reliable way to distinguish S. torvus is by slightly denser and smaller pits on the genagena:
the area of the head between the compound eye and clypeus; also called the cheek
 (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
(Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
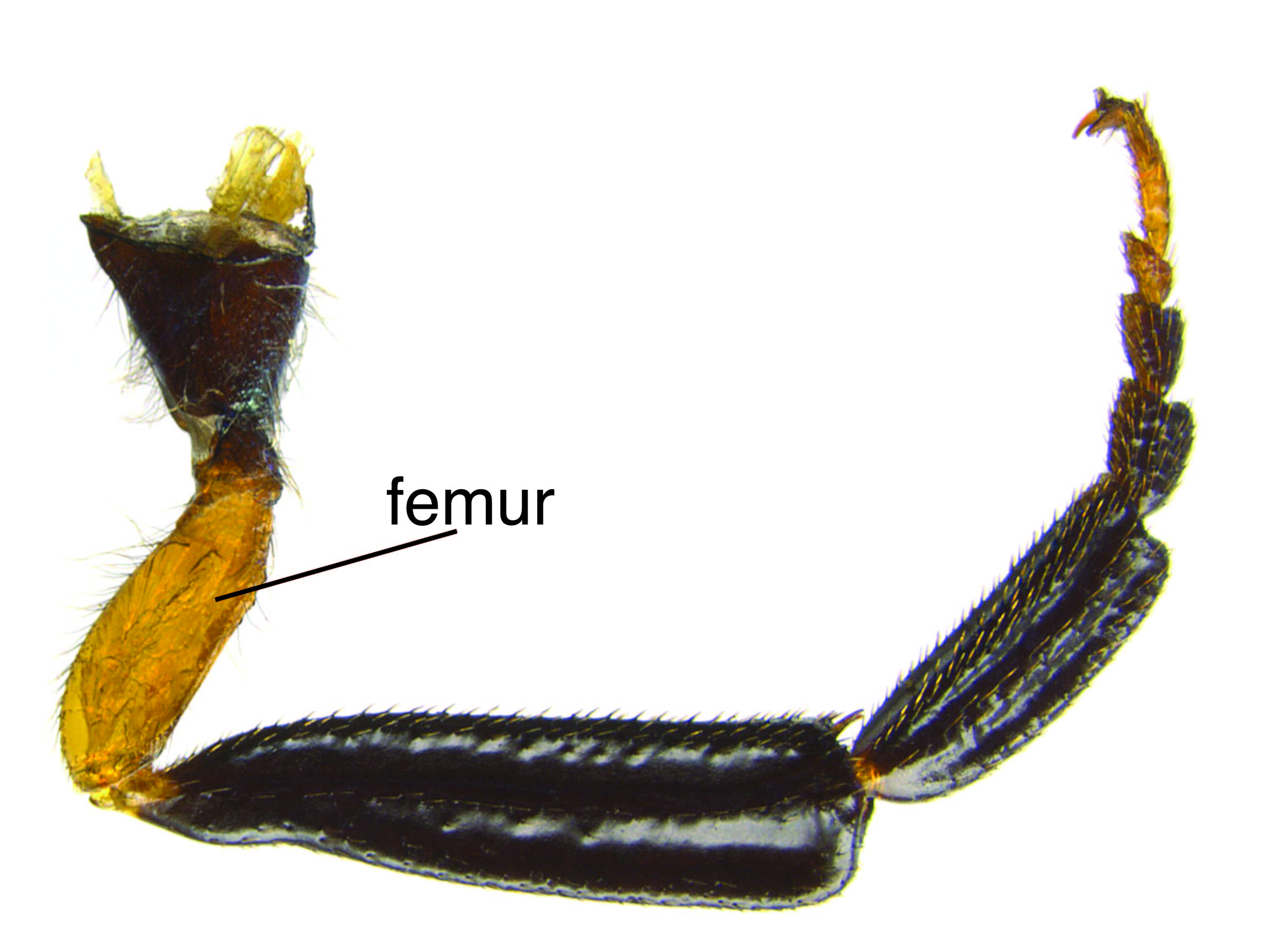
Individuals of S. nitidus fall into two color patterns. The common form, with reddish-brown femorafemur:
the third segment of the leg between the trochanter and the tibia
 , is found throughout the species’ range, while the black form, with mostly black femorafemur:
, is found throughout the species’ range, while the black form, with mostly black femorafemur:
the third segment of the leg between the trochanter and the tibia
 , occurs only in Alaska, Yukon, northern British Columbia, and Alberta. There are also several intermediate forms in overlapping regions (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
, occurs only in Alaska, Yukon, northern British Columbia, and Alberta. There are also several intermediate forms in overlapping regions (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Sirex species feed on trees of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae. Sirex nitidus is recorded on Thuja plicata (western red cedar), Abies balsamea (balsam fir), Abies lasiocarpa (subalpine fir), Larix laricina (tamarack), Picea engelmannii (Engelmann spruce), Picea glauca (white spruce), Picea mariana (black spruce), Picea rubens (red spruce), other Picea sp., Pinus contorta (lodgepole pine), Pinus ponderosa (ponderosa pine), Pseudotsuga menziesii (Douglas fir), and Tsuga heterophylla (western hemlock). The majority of specimens reared (88%) have been on Picea spp. (spruce) (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Female Sirex harbor symbiotic basidiomycete fungus in abdominal glands called mycangia. During oviposition, the site is inoculated with the fungus, which begins to decompose the surrounding wood. LarvaeLarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
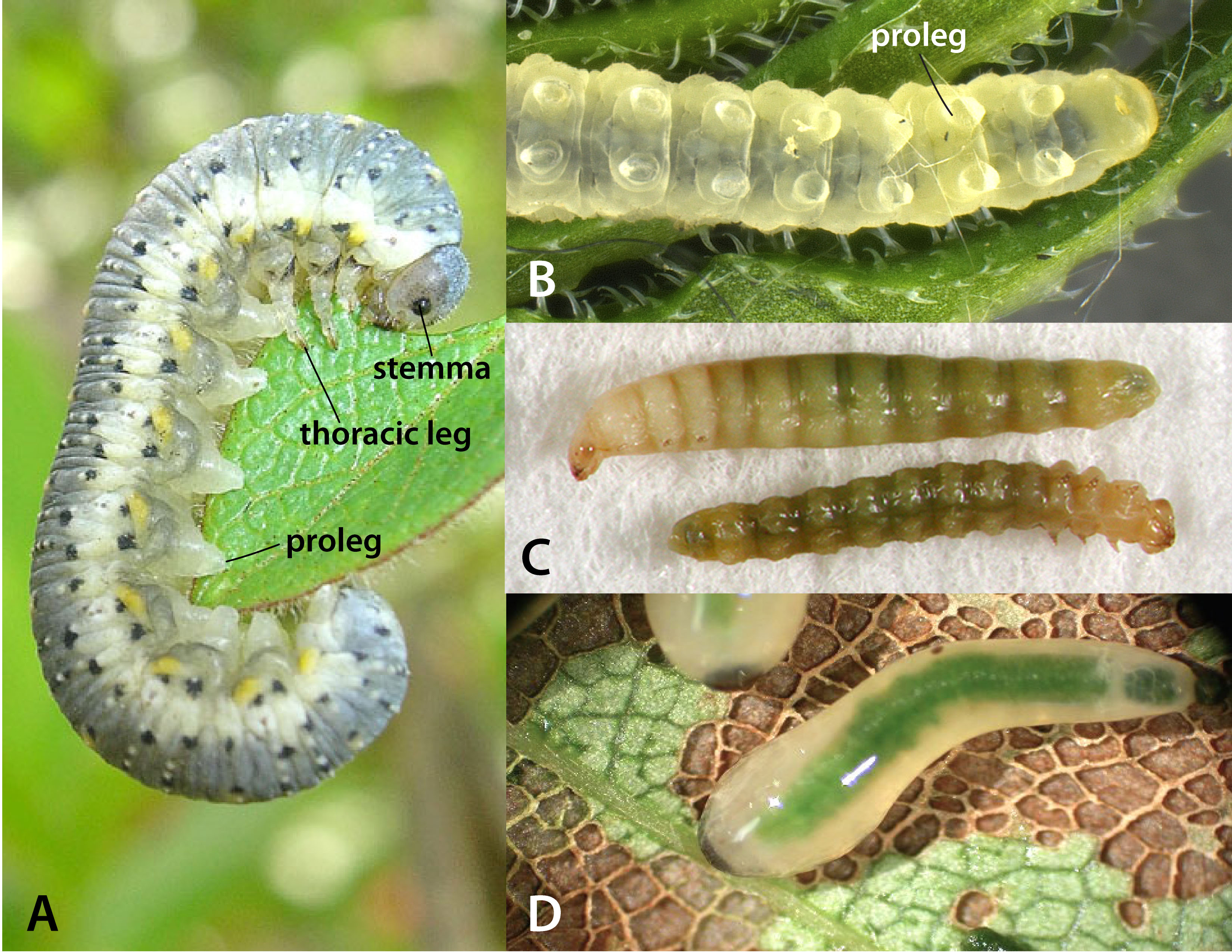 feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Johnson 1930Johnson 1930:
feed on the fungus, and in the process bore galleries through the wood (Johnson 1930Johnson 1930:
Johnson CW. 1930. On the variation and abundance of Sirex nitidus Harris. Psyche 37 (3): 281-282. https://doi.org/10.1155/1930/62786, Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.). The mycangia of S. nitidus individuals harbor either Amylostereum areolatum or A. chailletii fungus (Hajek et al. 2013Hajek et al. 2013:
Hajek AE, Nielsen C, Kepler RM, Long SJ, and Castrillo L. 2013. Fidelity among Sirex woodwasps and their fungal symbionts. Microbial Ecology 65: 753-762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0218-z).
Larvae are creamy white and grub-like in appearance with a dark head capsule. As with adults, larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 possess a short dorsaldorsal:
possess a short dorsaldorsal:
of or on the top surface of the body or structure
horn on the posterior end of the body. The larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
bore galleries into wood, feeding until pupation and subsequent emergence. Throughout this process, the larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
use their horn to pack the tunnel behind them with sawdust. Emergence holes are perfectly circular. The fungal symbiont is carried in specialized organs in female larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
that develop into the mycangia after metamorphosis (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
The documented flight period of S. nitidus is early July through early October, with most collections in September (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.). There is some evidence that trees with sustained damage, either from drought-related stress, weather, or other insect infestations, are preferred as hosts (Burnip et al. 2010Burnip et al. 2010:
Burnip GM, Voice D, and Brockerhoff EG. 2010. Interceptions and incursions of exotic Sirex species and other siricids (Hymenoptera: Siricidae). New Zealand Journal of Forestry Science 40: 133-140.).
One rearing record includes emergence of a parasitoid, Ibalia ensiger (Johnson 1930Johnson 1930:
Johnson CW. 1930. On the variation and abundance of Sirex nitidus Harris. Psyche 37 (3): 281-282. https://doi.org/10.1155/1930/62786).
World: North America. Interceptions have been made in New Zealand (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
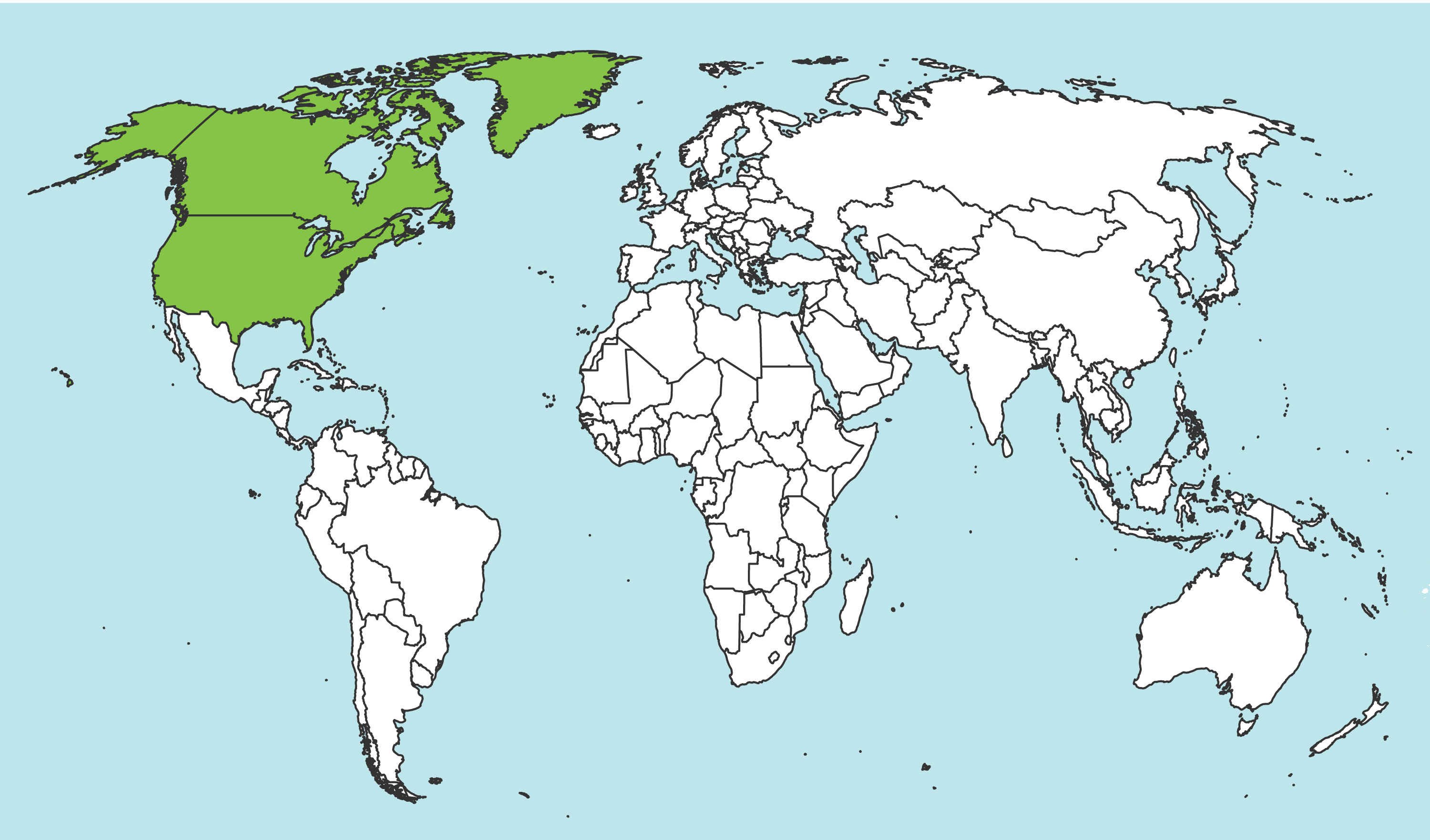
North America: The range of S. nitidus extends through northwest regions of the United States and forested regions of Canada, from as far north as Newfoundland in the east, and Alaska in the west. The southernmost part of the range of this species includes the Rocky Mountains in the western United States (Schiff et al. 2012Schiff et al. 2012:
Schiff NM, Goulet H, Smith DR, Boudreault C, Wilson AD, and Scheffler BE. 2012. Siricidae (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Siricoidea) of the Western Hemisphere. Canadian Journal of Arthropod Identification 21: 1-305.).
Map data from Washington State Department of Agriculture Entomology Collection.
Details about data used for maps can be found here.