Body length: 7–28 mm.
Eyes: eye interommatidial setaeseta:
a sclerotized hair-like projection of the cuticle
absent, eye deeply emarginateemarginate:
notched at the margin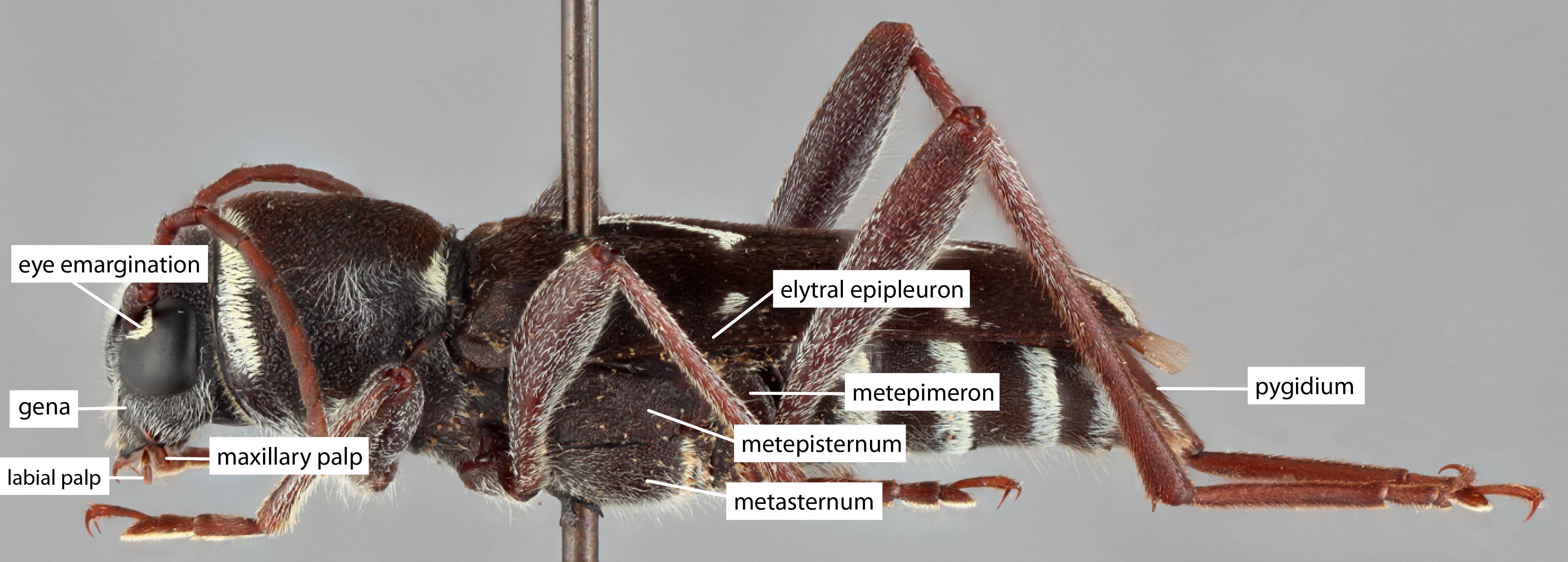 > half width, eye ommatidial density fine.
> half width, eye ommatidial density fine.
Antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
: antennal length reaching/surpassing end of body, antennal flagellar segments elongateelongate:
much longer than wide , scapescape:
, scapescape:
the first proximal segment of the antenna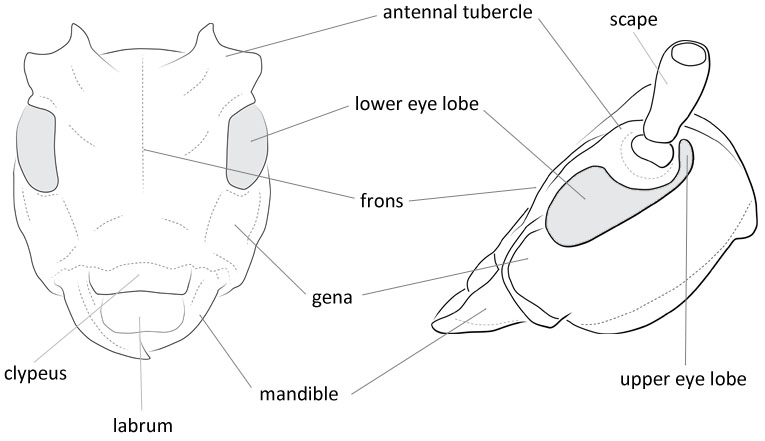 smooth/punctate at apexapex:
smooth/punctate at apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base , antennal segment 3 > scapescape:
, antennal segment 3 > scapescape:
the first proximal segment of the antenna .
.
Pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax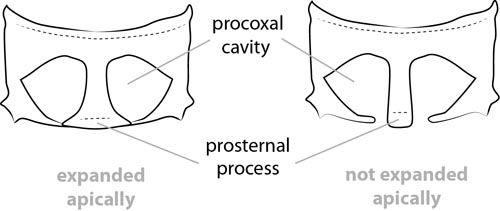 : pronotumpronotum:
: pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax shape transversetransverse:
shape transversetransverse:
broader than long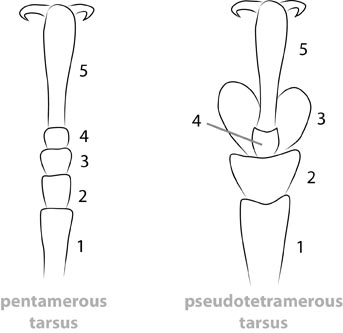 , pronotumpronotum:
, pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax lateral armature acute spinespine:
lateral armature acute spinespine:
a protuberance with an acute (sharp) distal end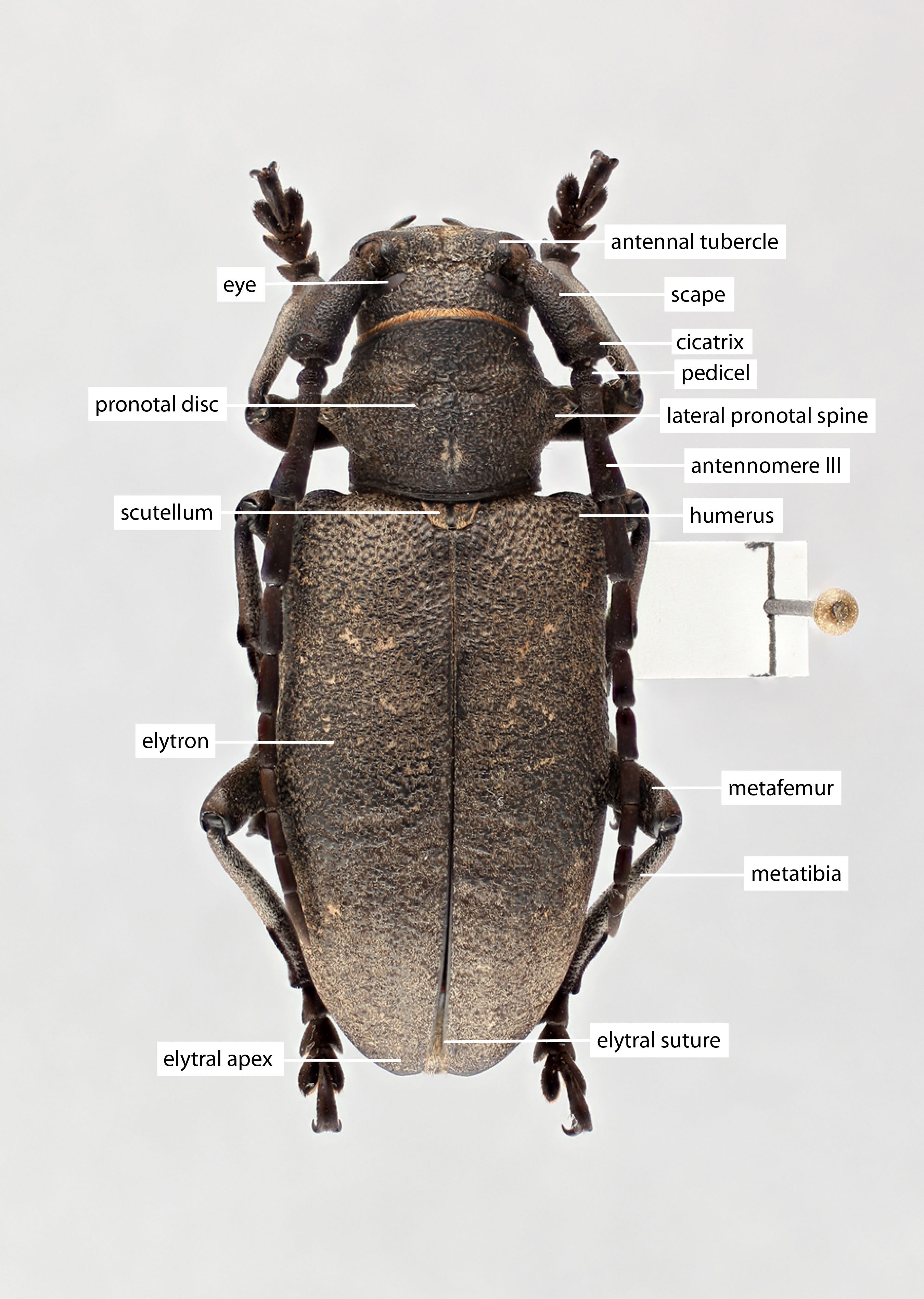 .
.
Prosternum: prosternal processprosternal process:
a posterior extension of the prosternum between the coxae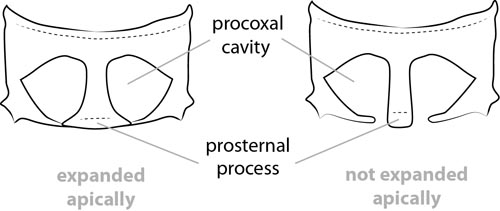 dilated at apexapex:
dilated at apexapex:
end of any structure distad to the base , procoxal cavities closed posteriorly.
, procoxal cavities closed posteriorly.
Elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
: elytral length reaching or close to end of abdomen, elytral apicesapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
rounded or truncatetruncate:
cut off squarely at the tip , elytral color pattern present.
, elytral color pattern present.
Legs: visible tarsomerestarsomere:
subdivision or article of the tarsus, usually numbering from two to five : 4, femora clavateclavate:
: 4, femora clavateclavate:
thickening gradually toward the tip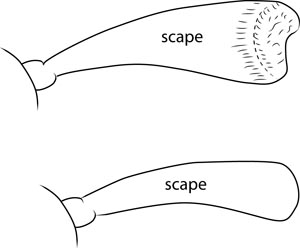 , protibial spursprotibial spur:
, protibial spursprotibial spur:
sclerotized spine(s) located at the distal tibia; can be single, double, or absent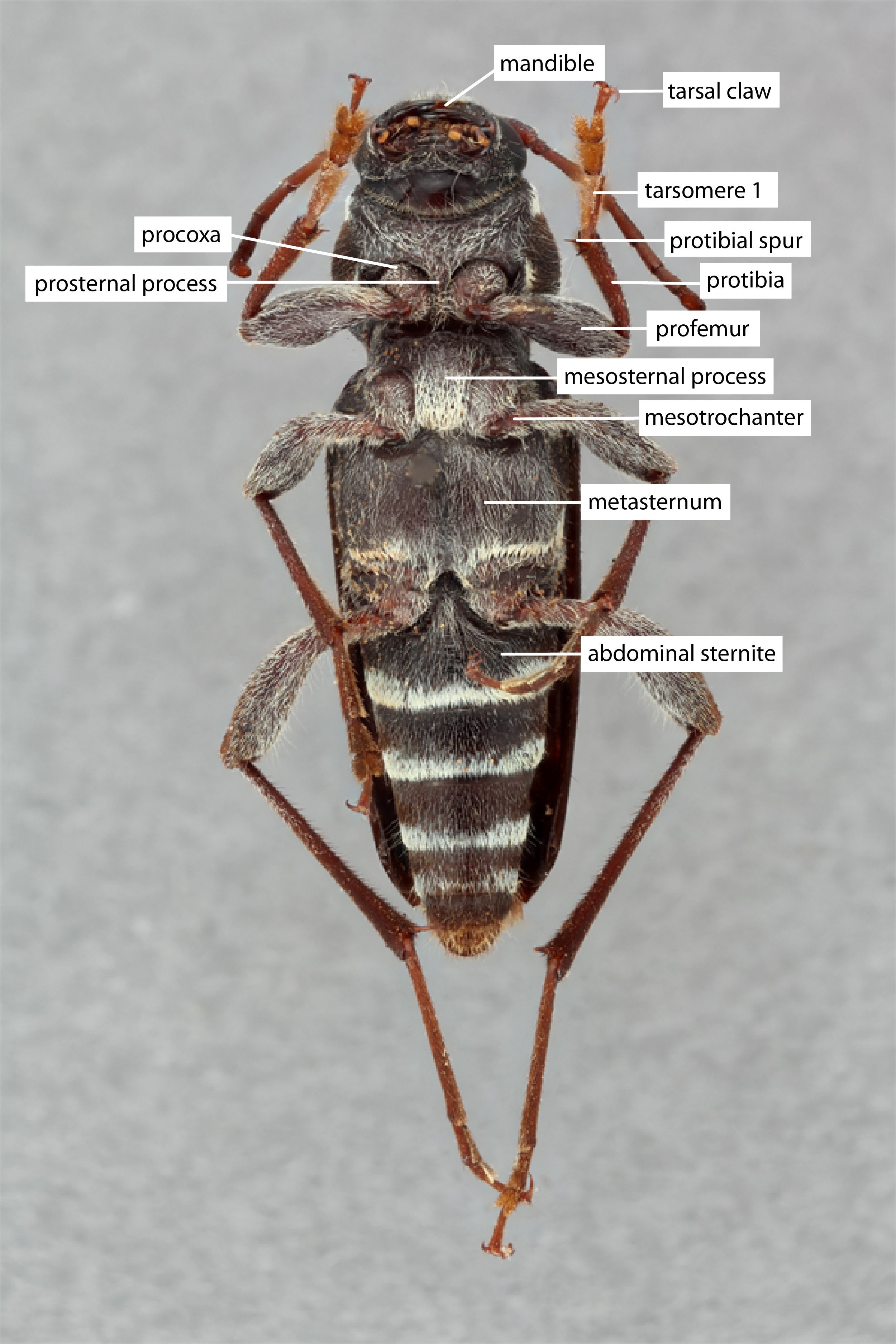 : 2, tarsal clawstarsal claw:
: 2, tarsal clawstarsal claw:
usually paired claws of the pretarsus, at the distal end of the leg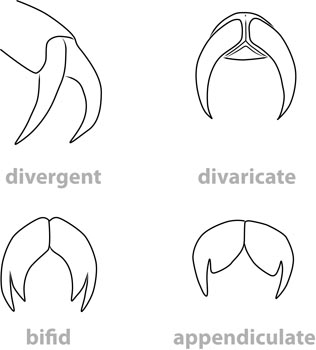 simple.
simple.
Form moderate-sized to large, somewhat depressed. Head with front rather short, quadrate, slightly convex; clypeusclypeus:
that part of the insect head below the frons, to which the labrum is attached anteriorly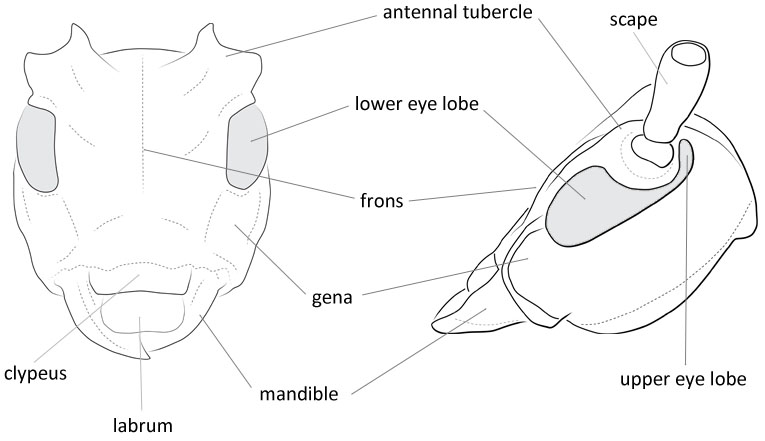 narrowly margined apically; eyes with lower lobes oblongoblong:
narrowly margined apically; eyes with lower lobes oblongoblong:
longer than broad
 , usually longer than genaegena:
, usually longer than genaegena:
the part of the cranium on each side below the eye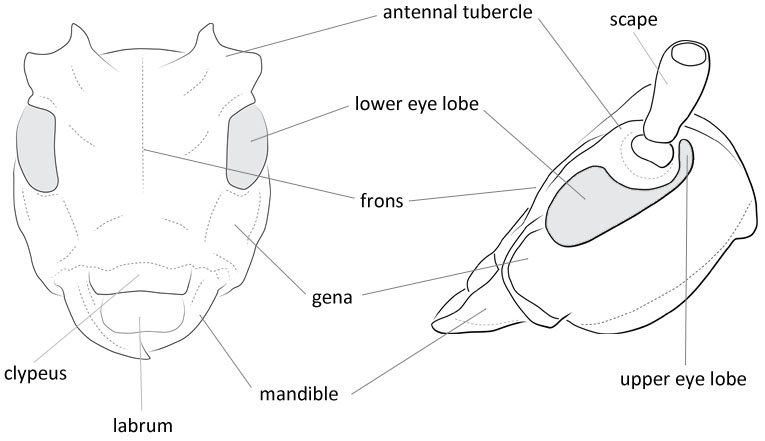 , upper lobes widely separated above; genaegena:
, upper lobes widely separated above; genaegena:
the part of the cranium on each side below the eye subparallel; antennal tubercles prominent, divergentdivergent:
subparallel; antennal tubercles prominent, divergentdivergent:
spreading out from a common base , bases contiguouscontiguous:
, bases contiguouscontiguous:
so near together as to touch ; antennaeantenna:
; antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
slender, 2-1/2 to four times longer than body in males, 1-1/2 to twice as long in females, segments four and/or five usually apically produced in males, segments three to at least five densely fimbriatefimbriate:
fringed with hairs of irregular length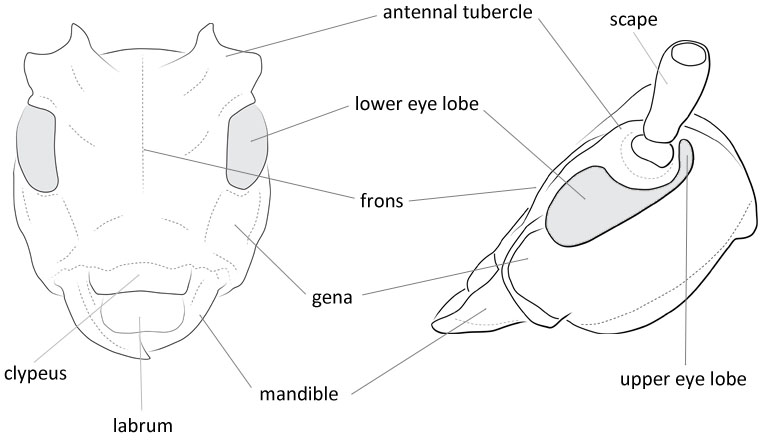 beneath, scapescape:
beneath, scapescape:
the first proximal segment of the antenna usually extending to lateral tubercles of pronotumpronotum:
usually extending to lateral tubercles of pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax , third segment longer than first, fourth subequal to third. Pronotumpronotum:
, third segment longer than first, fourth subequal to third. Pronotumpronotum:
the upper and dorsal part of the prothorax broader than long, sides moderately to strongly tuberculate behind middle, tubercles acutely spined at basal one-third; basal sulcussulcus:
broader than long, sides moderately to strongly tuberculate behind middle, tubercles acutely spined at basal one-third; basal sulcussulcus:
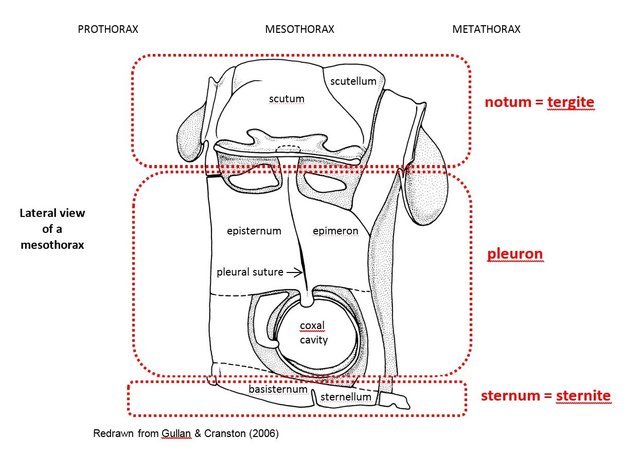
groove with a purely functional origin extending onto sides; disk bicallused behind apical margin; prosternum narrow, shallowly excavated, intercoxal process narrow, less than one-fourth as broad as coxal cavities; mesosternummesosternum:
extending onto sides; disk bicallused behind apical margin; prosternum narrow, shallowly excavated, intercoxal process narrow, less than one-fourth as broad as coxal cavities; mesosternummesosternum:
sternum of the mesothorax
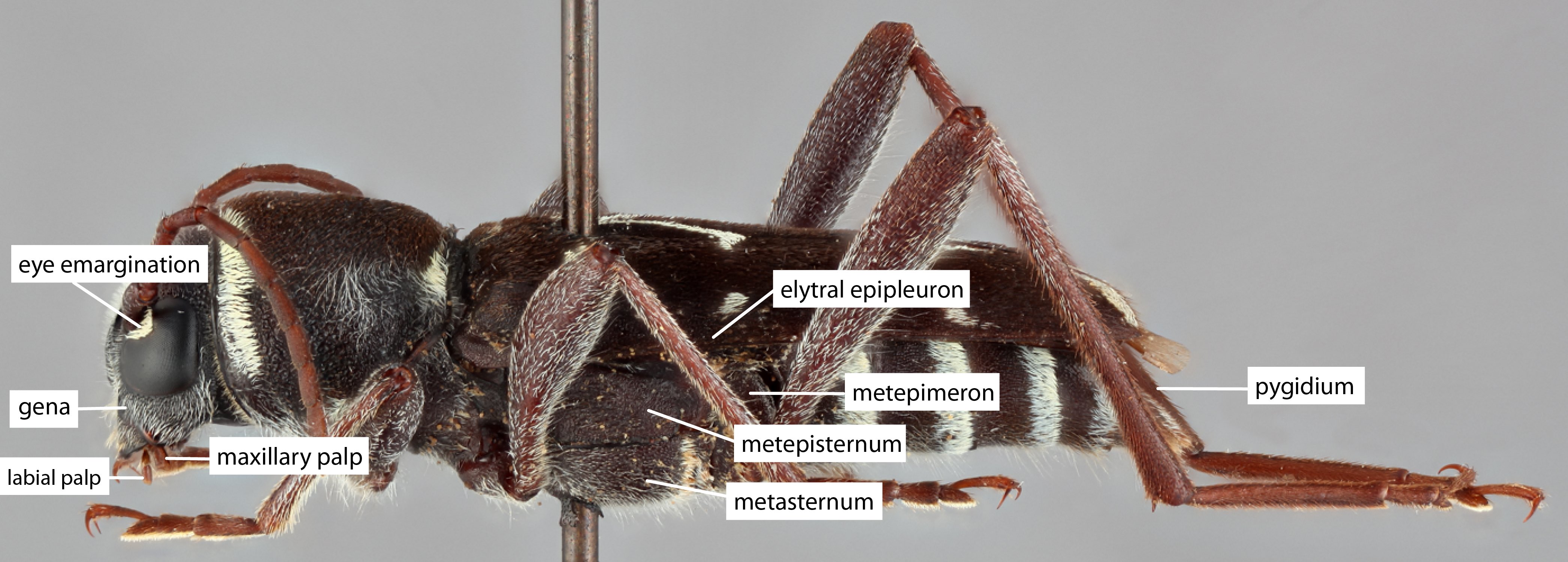 with intercoxal process about one-third as broad as coxal cavities, at least twice as broad as procoxal process; meta sternum with episternumepisternum:
with intercoxal process about one-third as broad as coxal cavities, at least twice as broad as procoxal process; meta sternum with episternumepisternum:
the aspect of a thoracic pleuron dorsal to the coxal cavity and anterior to the pleural suture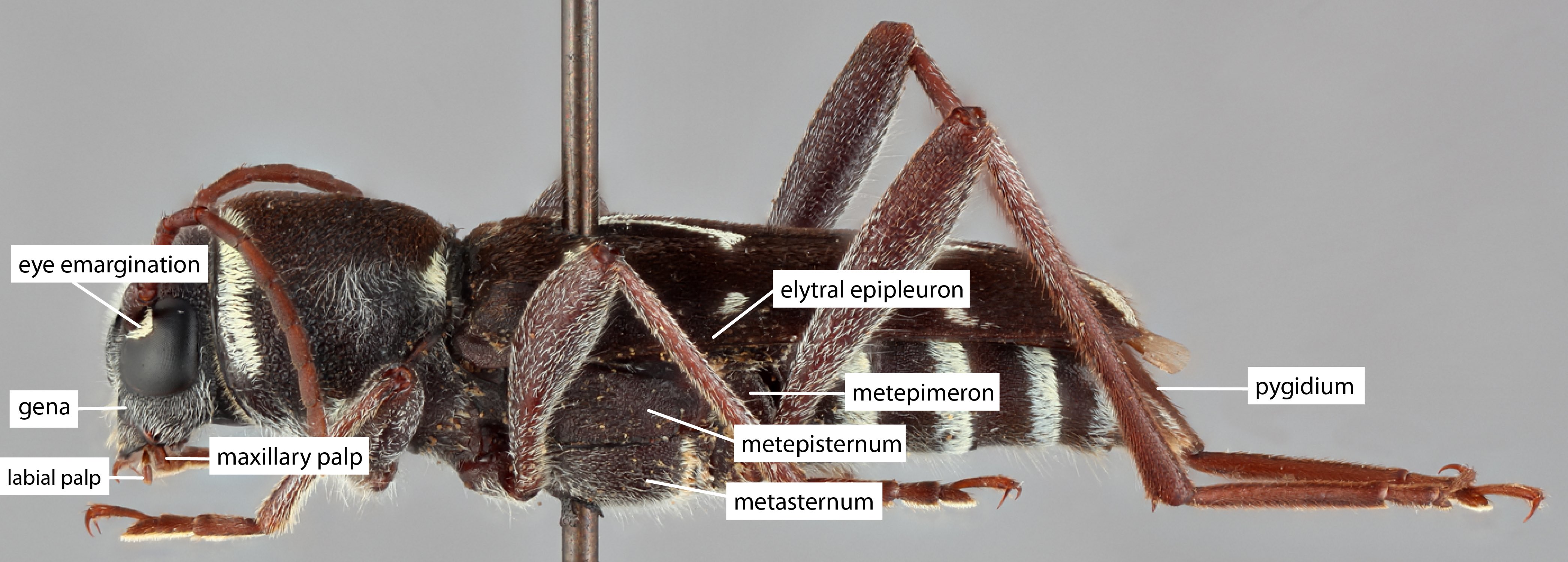 subparallel, abruptly tapering posteriorly. Elytraelytron:
subparallel, abruptly tapering posteriorly. Elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
more than twice as long as broad, slighty tapering posteriorly to subparallel; disk vaguely to strongly tricostate, basebase:
the part of any appendage or structure that is nearest the body feebly bigibbose; pubescence depressed, dense, often condensed into spots or vittaevitta:
feebly bigibbose; pubescence depressed, dense, often condensed into spots or vittaevitta:
a broad longitudinal stripe
along costae, erect hairs absent; apicesapex:
end of any structure distad to the base
rounded to subtruncatesubtruncate:
not quite cut off squarely at the tip . Legs robust; femora clavateclavate:
. Legs robust; femora clavateclavate:
thickening gradually toward the tip , lacking erect hairs; tarsitarsus:
, lacking erect hairs; tarsitarsus:
the leg segment distal to the apex of the tibia, bearing the pretarsus; consists of one to five tarsomeres (including pretarsus)
with first segment of hind pair longer than two following segments together, third segment cleft to basebase:
the part of any appendage or structure that is nearest the body . Abdomen normally segmented in males, last segment elongateelongate:
. Abdomen normally segmented in males, last segment elongateelongate:
much longer than wide in females, terminated by a long, visible ovipositor (Linsley and Chemsak 1995Linsley and Chemsak 1995:
in females, terminated by a long, visible ovipositor (Linsley and Chemsak 1995Linsley and Chemsak 1995:
Linsley EG and Chemsak JA. 1995. The Cerambycidae of North America. Part VII, No. 2. Taxonomy and Classification of the Subfamily Lamiinae, Tribes Acanthocinini Through Hemilophini. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles. 292 pp.).
Members of Acanthocinus are easily recognized by the > 1.5x body length antennaeantenna:
in larval and adult insects, paired segmented appendages, borne one on each side of the head, functioning as sense organs and bearing a large number of sensilla
, fimbriated antennal segments 3–5, lack of erect hairs on the elytraelytron:
the leathery forewing of beetles, serving as a covering for the hind wings, commonly meeting opposite elytron in a straight line down the middle of the dorsum in repose
, and by the elongateelongate:
much longer than wide
ovipositor of the females. The terminal abdominal segment in males notched.
Holarctic, Indomalaya
Old World: Pinaceae, Fagus sylvatica (A. xanthoneurus), Carpinus (A. elegans)
New World: Pinaceae
25 spp. + 1 ssp. (Acanthocinus), 1 sp. (Acanthobatesianus). Almost all species are conifer feeders.
Astynomus Dejean, 1835
Aedilis Audinet-Serville, 1835
Graphisurus (Canonura) Casey, 1913
Graphisurus (Tylocerina) Casey, 1913
Neacanthocinus Dillon, 1956
Subgenus Acanthocinus Dejean, 1821
Subgenus Acanthobatesianus Wallin, Kvamme & Lin, 2012