Phytophthora acerina
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 2c: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. acerina Ex-type CBS 133931 = S&T BL114. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 2c: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. acerina Ex-type CBS 133931 = S&T BL114. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
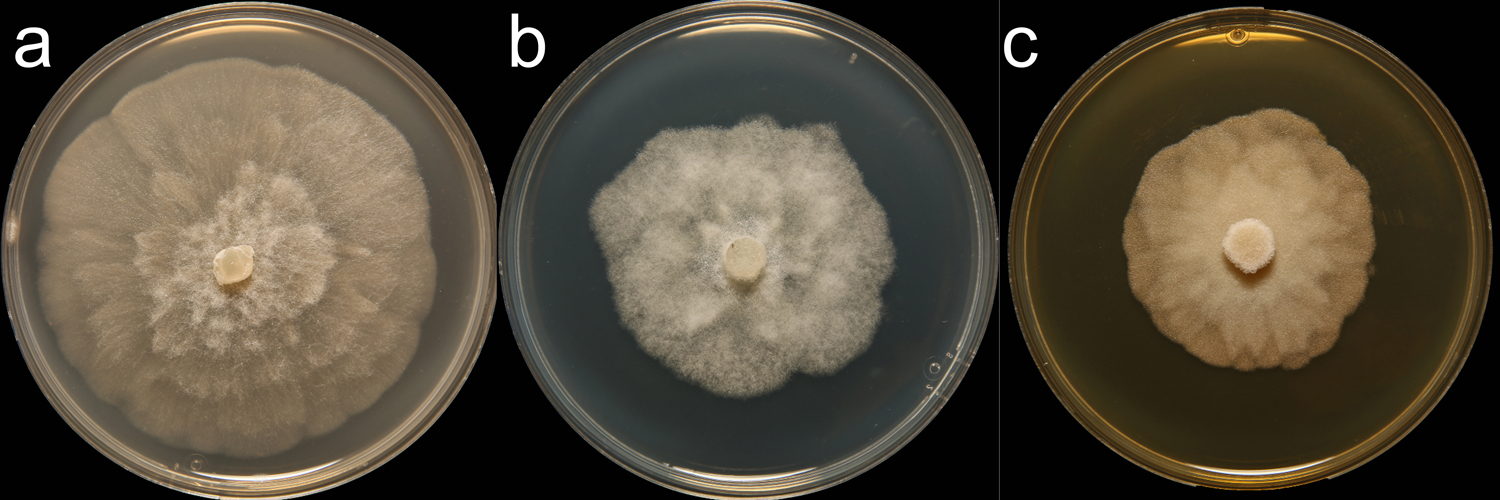
Phytophthora acerina (CPHST BL 114) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
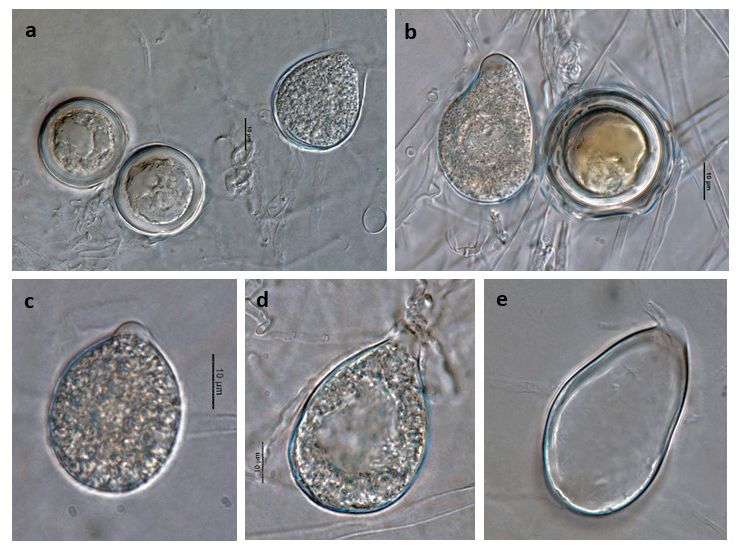
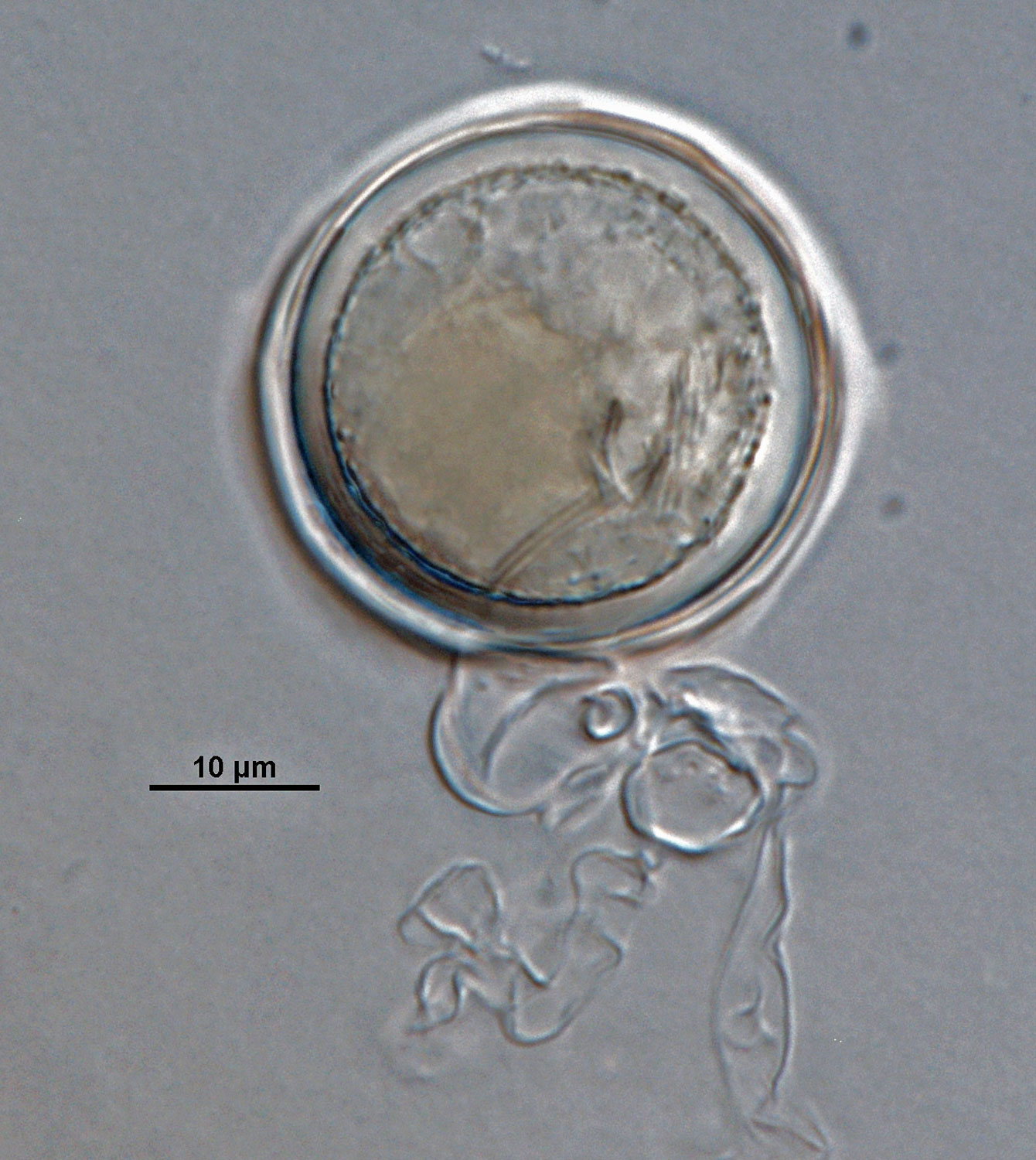
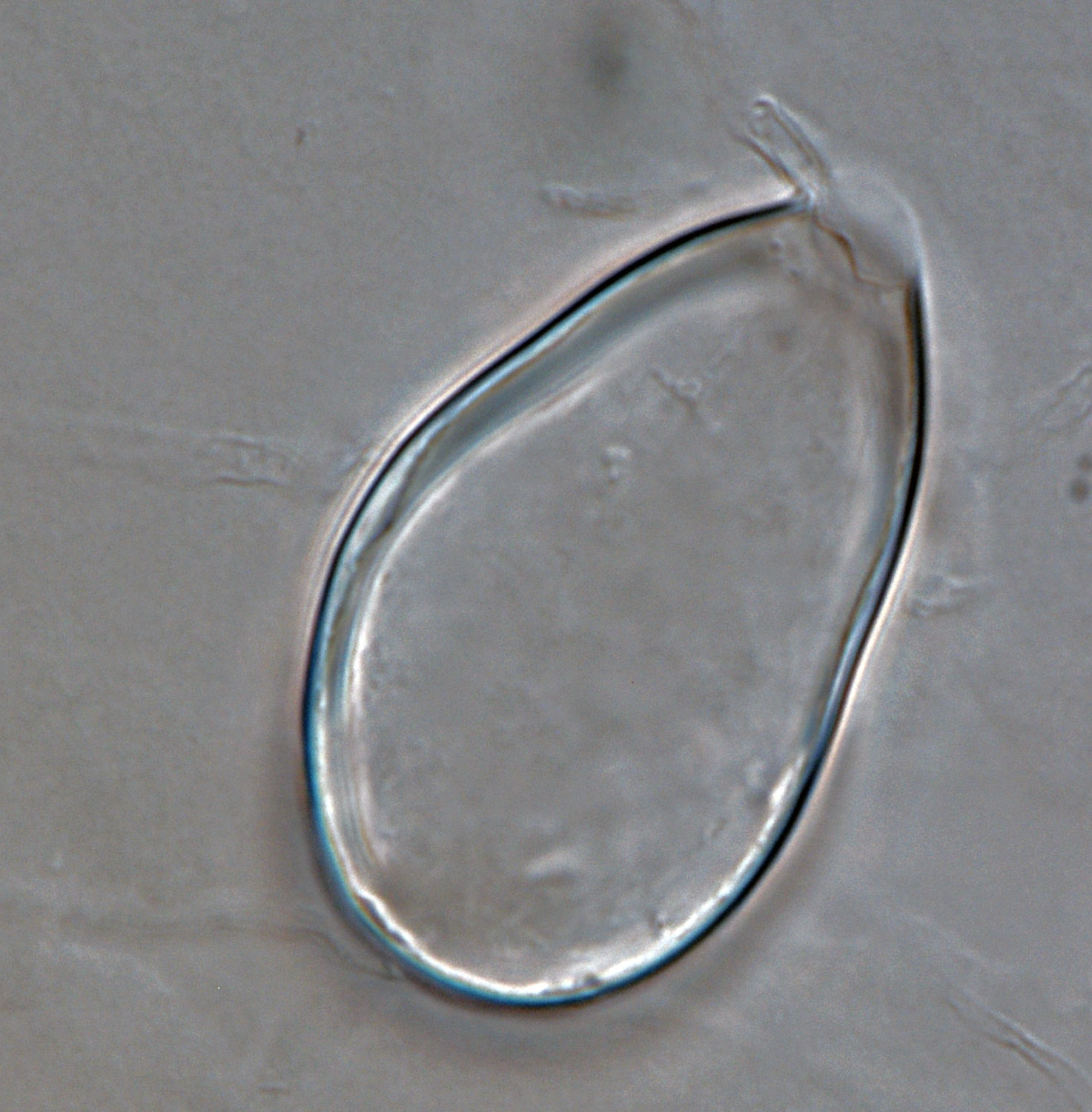
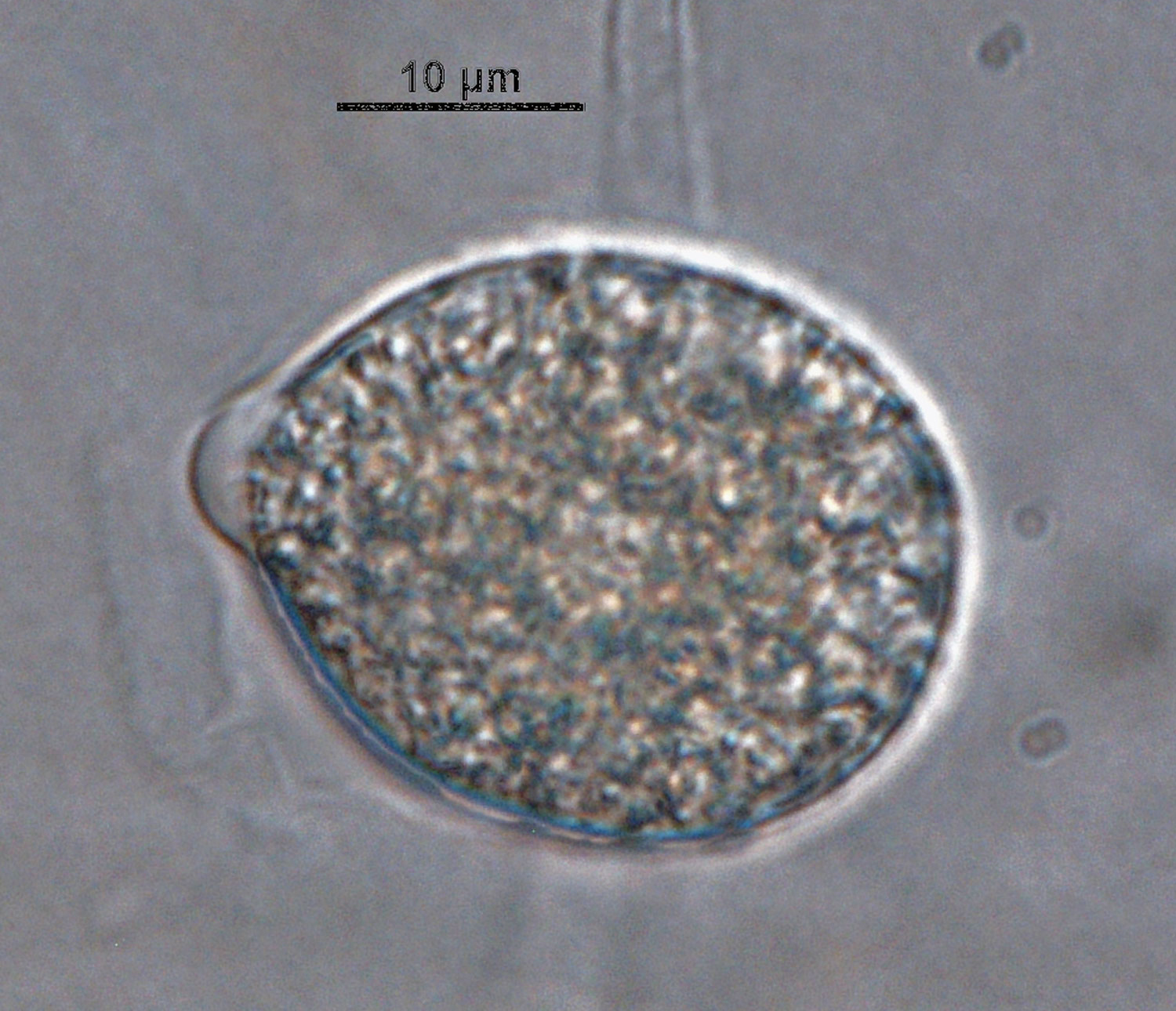
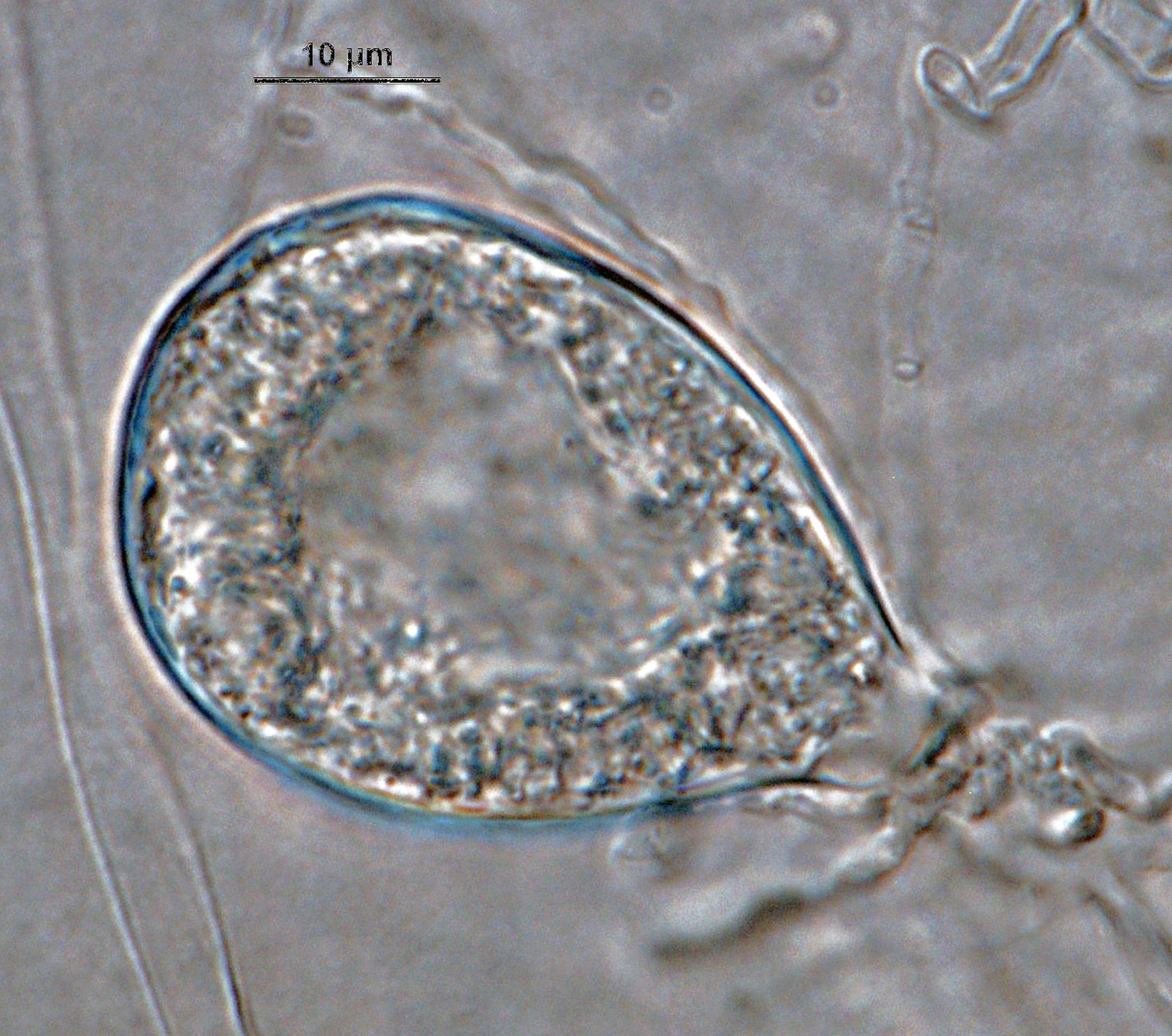
Phytophthora acerina (CPHST BL 114, ex-type) asexual phase and sexual phase (a-b); different shapes of semi-papillate persistent sporangia (a-e); photos by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
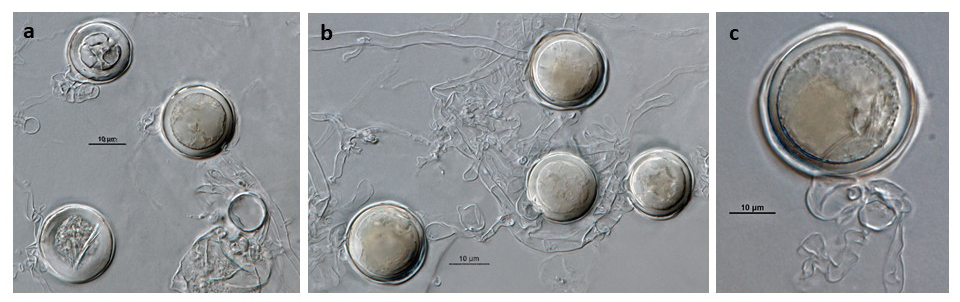
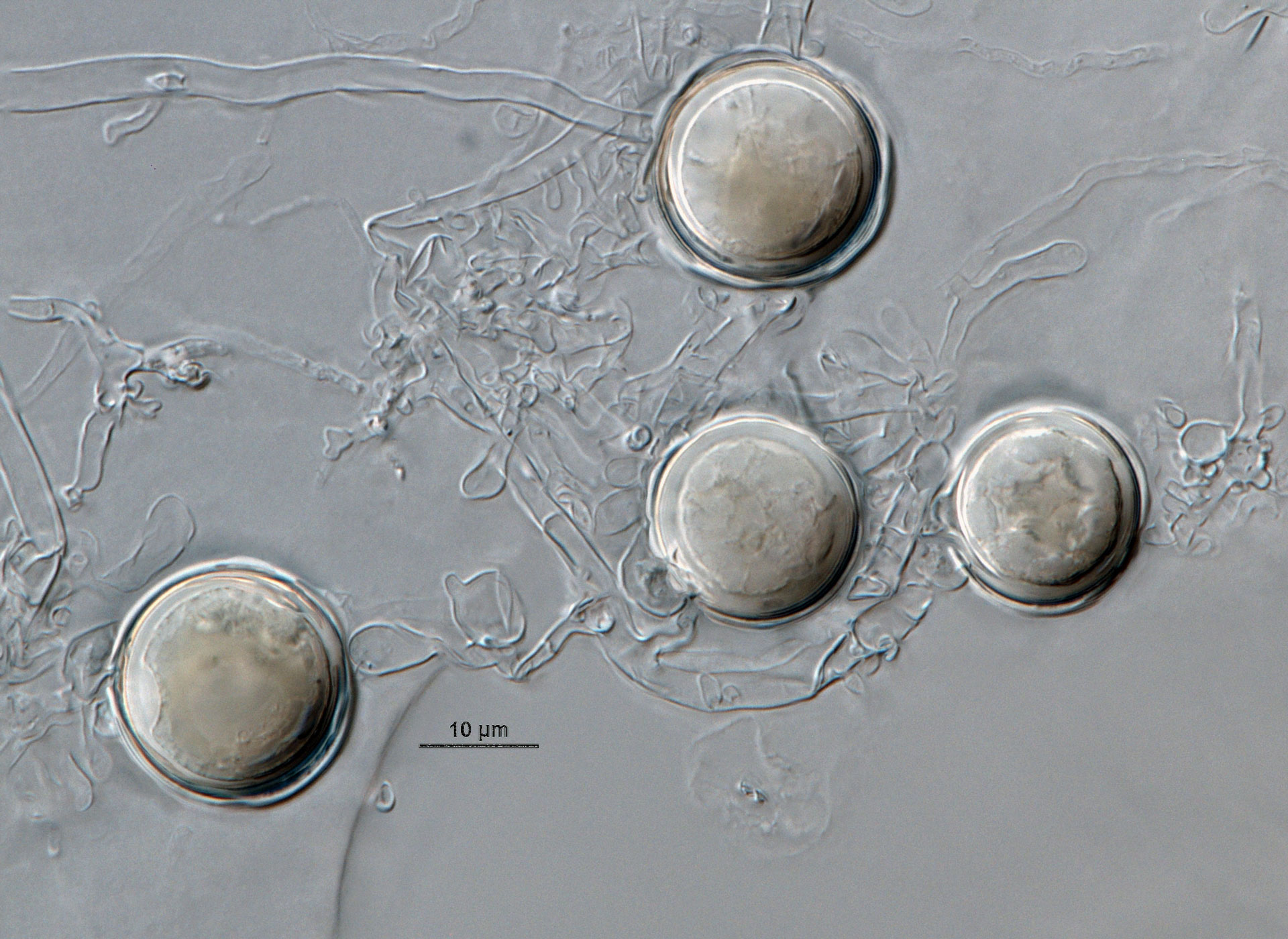
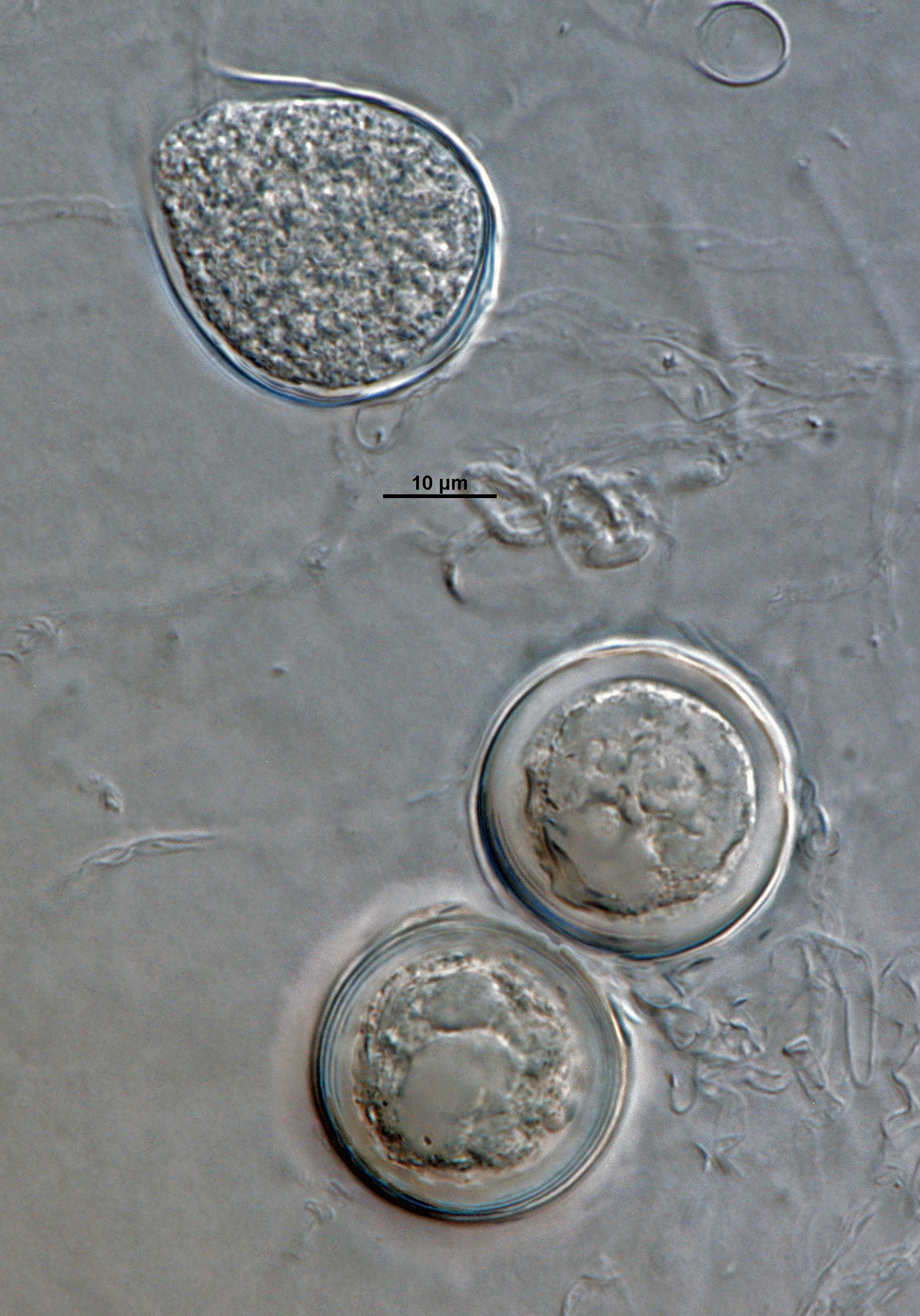
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) sexual phase formed on hemp seed agar (a-c): smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and plerotic oospores; photos by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) sexual phase formed on hemp seed agar. Smooth-walled oogonium with paragynous antheridium and plerotic oospore. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (CPHST BL 114, ex-type) asexual phase; semi-papillate persistent sporangium. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) sexual phase formed on hemp seed agar. Smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and plerotic oospores. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) sexual phase formed on hemp seed agar. Smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and plerotic oospores. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (CPHST BL 114, ex-type) asexual phase; semi-papillate persistent sporangium. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (CPHST BL 114, ex-type) asexual phase; semi-papillate persistent sporangium. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
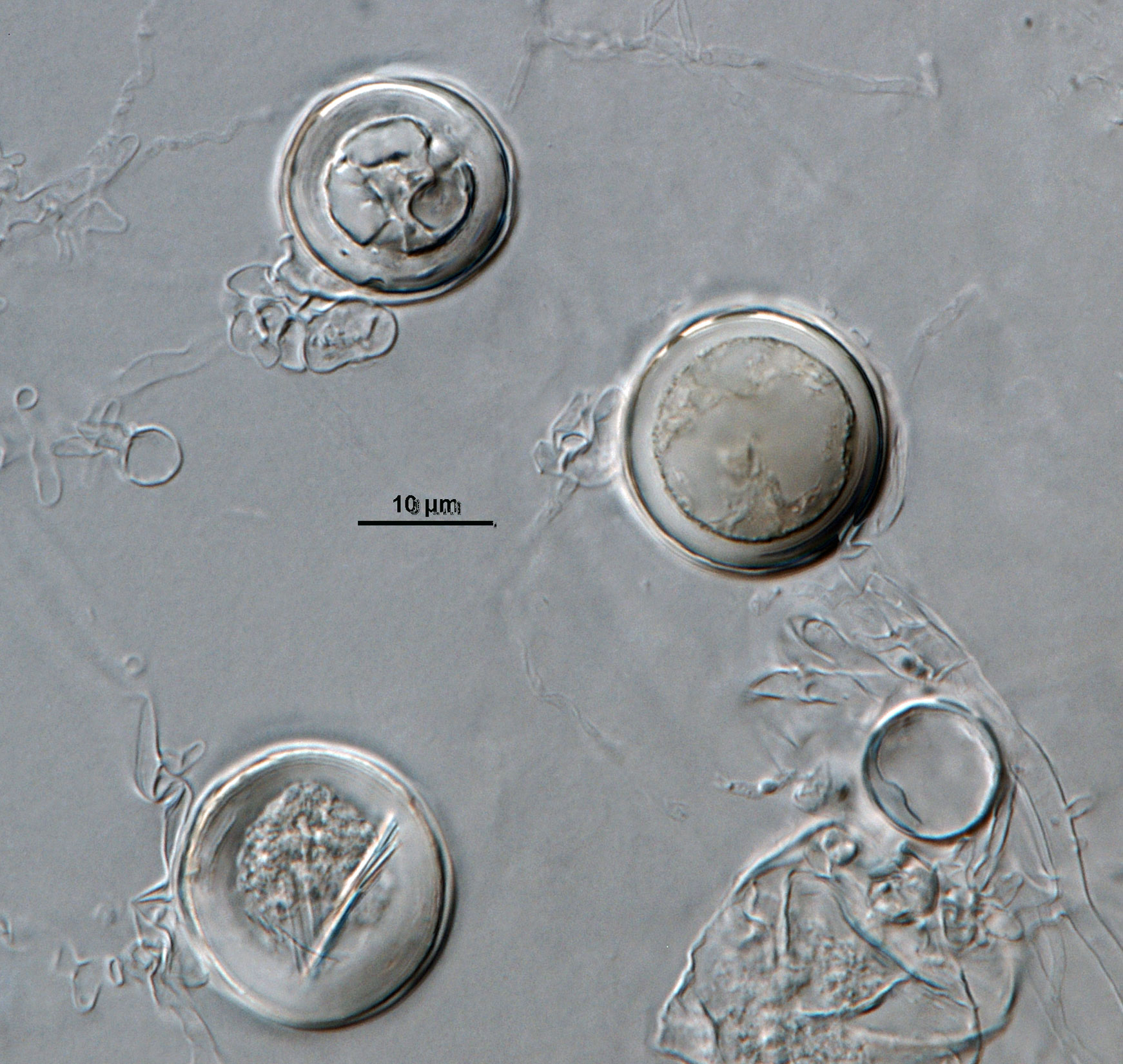
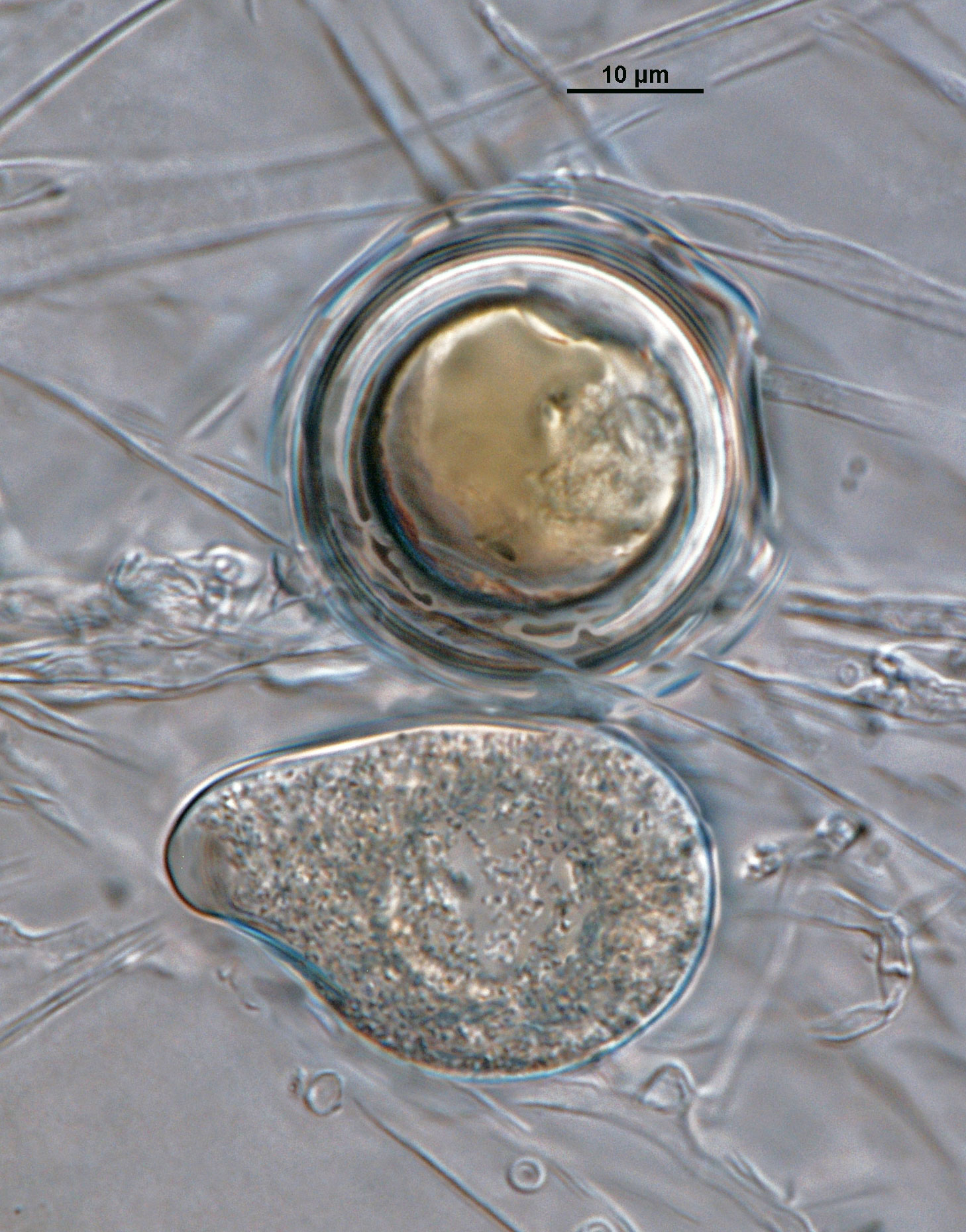
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) asexual and sexual phase. Smooth-walled oogonia and semi-papillate persistent sporangium. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora acerina (ex-type CPHST BL 114) asexual and sexual phase. Smooth-walled oogonium and semi-papillate persistent sporangium. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora acerina B. Ginetti, T. Jung, D.E.L. Cooke & S. Moricca (2014)
Ginetti B, Moricca S, Squires J, Cooke D, Ragazzi A, Jung T. 2014. Phytophthora acerina sp. nov., a new species causing bleeding cankers and dieback of Acer pseudoplatanus trees in planted forests in Northern Italy. Plant Pathology 63: 858–876.
Corresponding author: salvatore.moricca@unifi.it
Nomenclature
from Ginetti et al. (2014)
Mycobank
Etymology
refers to Acer pseudoplatanus from which all studied isolates had been isolated
Typification
Type: ITALY, Boscoincittà Park, Milan, isolated from bleeding bark canker of Acer pseudoplatanus, 2010, B. Ginetti (isolate B057) FI AGR 057 (dried culture on V8A at herbarium of the Museum of Natural History of the University of Florence, Italy)
Ex-type: cultures CBS 133931 = B057
Sequences for ex-type: Phytophthora acerina B057 = ITSrDNA JX951285, β-tubulin KC201283, COI KC156134
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 133931, NRRL 64028, B057, WPC P19934, S&T BL 114 (Abad), 61H1 (Hong), TJ 0469 (Jung)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora acerina isolate CPHST BL 114 (= P19934 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG518642, COI MH136845
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora acerina CPHST BL 114
- NCBI: Phytophthora acerina B057
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora acerina
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora acerina
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
2c
Morphological identification
adapted from Ginetti et al. (2014)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology after 7 days of growth in V8-A is a chrysanthemum pattern, on PDA rosette (petaloid), and on MEA stellate. Minimum growth temperature 6°C, maximum 32°C, and optimum 25°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Hyphal swellings produced in ageing cultures (3–6 weeks old) and in nonsterile pond water.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
semipapillatesemipapillate:
pertaining to the production of shallow having papilla that are not well developed, shallow and less nipple-like than fully papillate structures
, rarely bi- or tripapillate; persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
; ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, limoniform, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, elongated, obovoidobovoid:
inversely egg-shaped; ovoid, but with the widest part at the apex
, mouse-shaped, and with distorted shapes (20–105 L x 11–51 W μm); originated on unbranched sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings subglobose or irregular, sometimes catenulatecatenulate:
having a chain-like form
, infrequently formed on sporangiophores. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled; globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, subglobose, or elongated (28–36 μm diam); antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
; globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, obovoidobovoid:
inversely egg-shaped; ovoid, but with the widest part at the apex
, club-shaped or irregular, sometimes with a finger-like projection and usually attached close to the oogonial stalk; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
pleroticplerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
; globose or subglobose in elongated oogoniaoogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
(24–32 μm) with medium wall thickness (1.8–2.4 μm).
Most typical characters
Besides the characters mentioned above, the species is characterized by the presence of a high oosporeoospore:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
abortion rate of 40–96% and the abundant production of dense stromata-like hyphal aggregations.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora acerina CPHST BL 114 (Abad) = P19934 [World Phytophthora Collection (WPC) California, USA] duplicate of the ex-type CBS 133931
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Europe (Italy)
Substrate: collar, stems
Disease note: collar rot, bleeding canker, crown dieback, death
Host: Acer pseudoplatanus (Sapindaceae)
Retrieved January 17, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Quarantine status
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora acerina
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora acerina
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora acerina
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora acerina
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora acerina
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora acerina
- Google All Phytophthora acerina
- Google Images Phytophthora acerina
- Google Scholar Phytophthora acerina
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.