Phytophthora boehmeriae
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 10a: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. boehmeriae Ex-type CBS 291.29 = S&T BL 32G. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 10a: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. boehmeriae Ex-type CBS 291.29 = S&T BL 32G. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
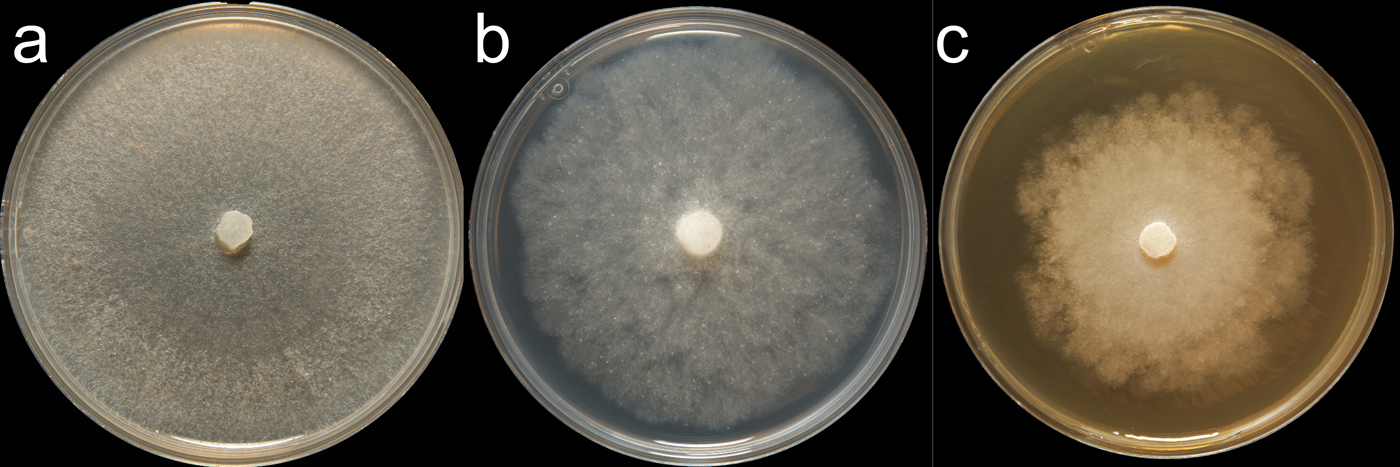
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 79) colony of a selected specimen grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
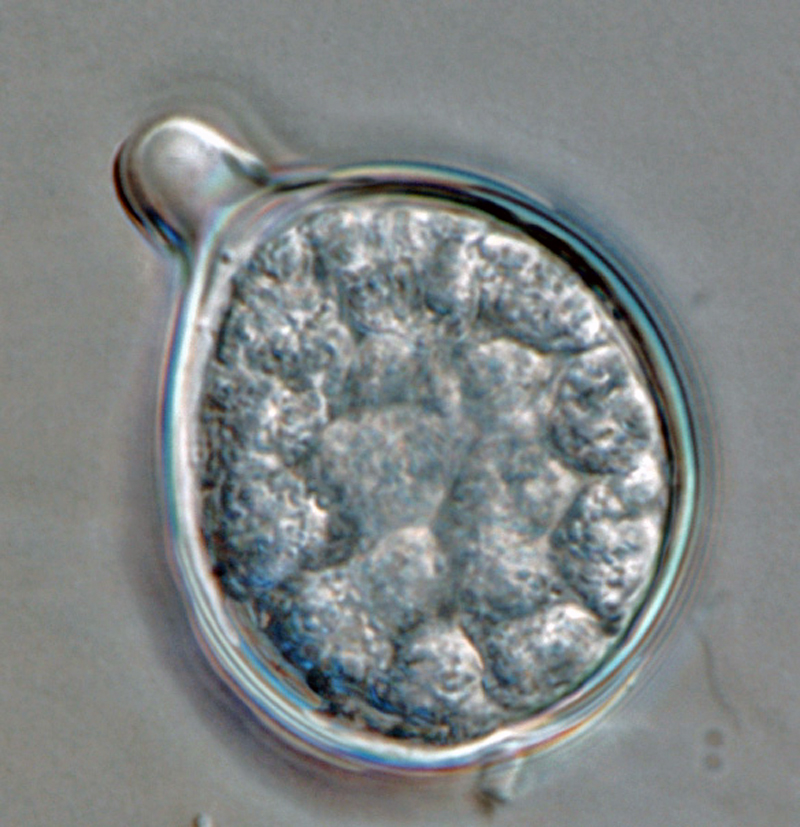
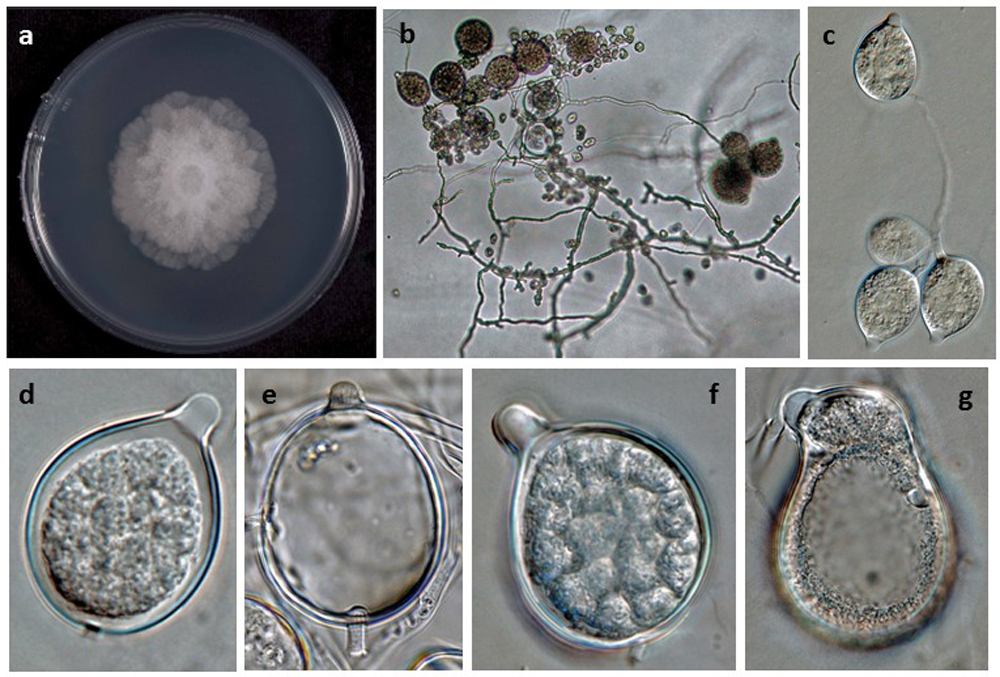
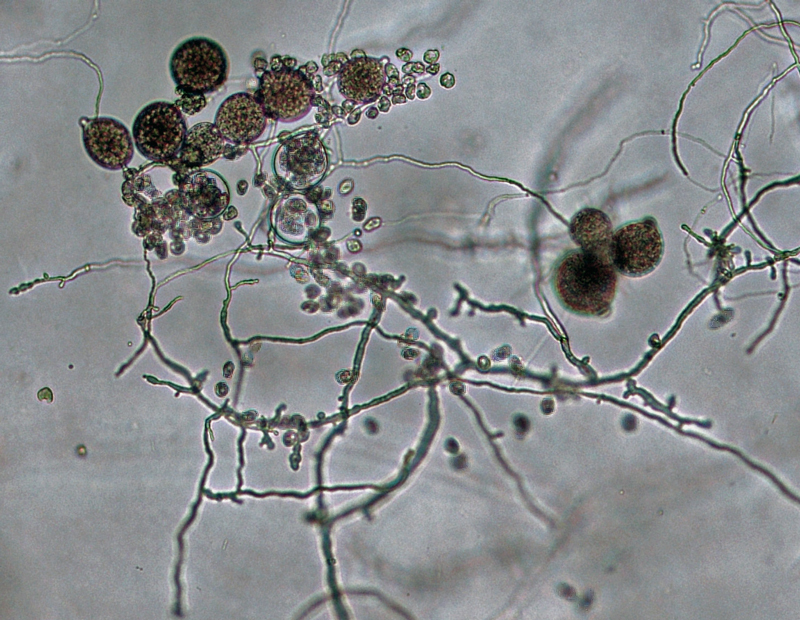
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) (a) colony morphology on potato dextrose agar, (b-g) asexual phase; (a-c) sporangia originated in unbranched or sympodially branching sporangiophores, (d-g) sporangia papillated caducous with short pedicels, (d-f) sporangia globose, (g) sporangium with irregular shape; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
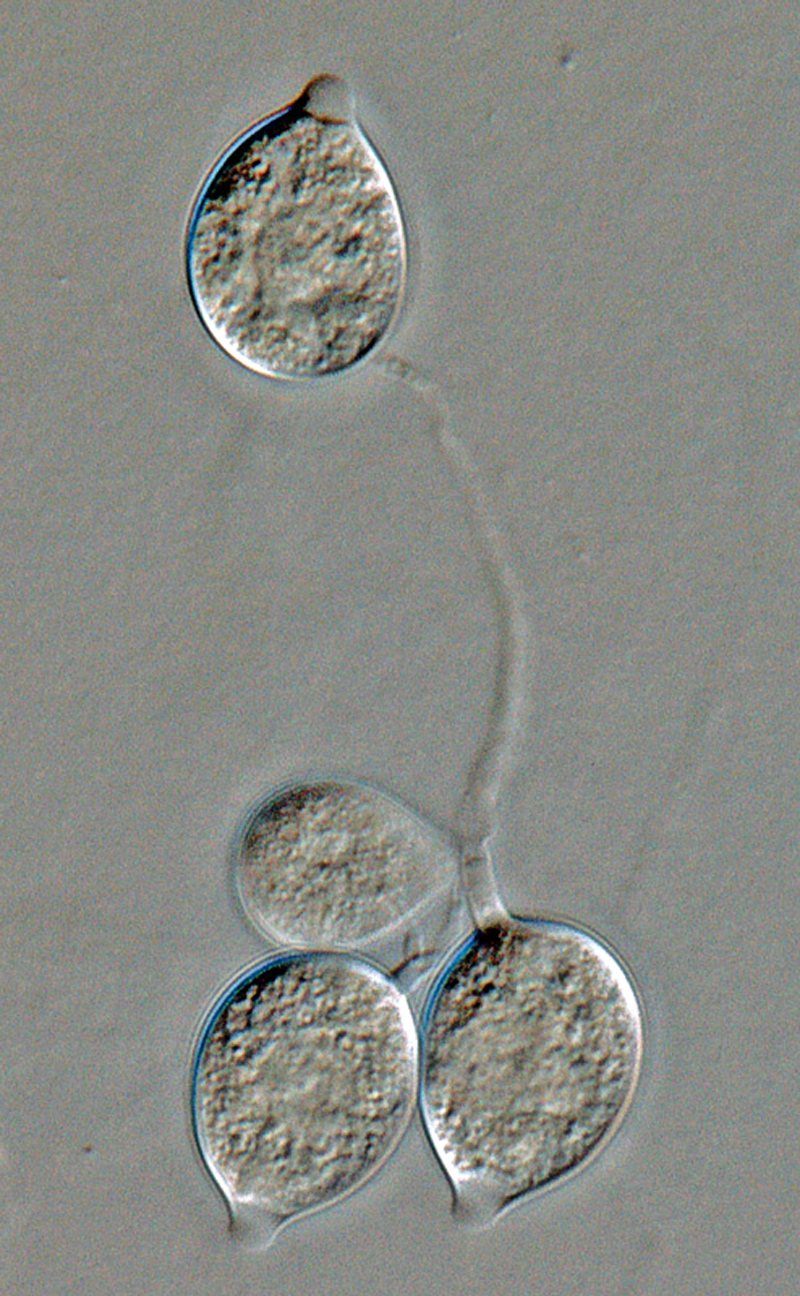
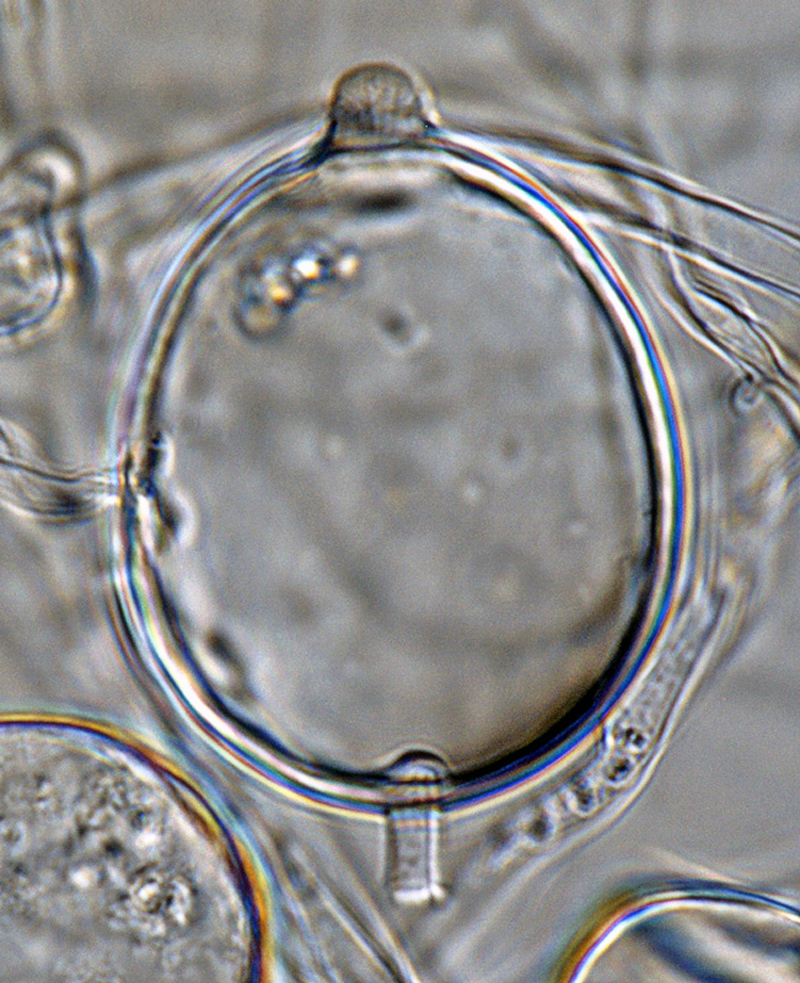
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) sexual phase: (a-d) oogonia smooth-walled with amphigynous antheridia almost spherical in shape and plerotic oospores, (b, c) antheridia with digitated projections; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree with 1000 bp based on the ITS rDNA region of Phytophthora species in Clade 10 showing the position of Phytophthora boehmeriae ex-type (in red) and the cluster of the "sensu stricto". Other clusters correspond to P. gondwanenwsis (2017) and putative new species in P. like boehmeriae "complex". Phythophthora parvispora in Clade 9 is the outgroup. |
|
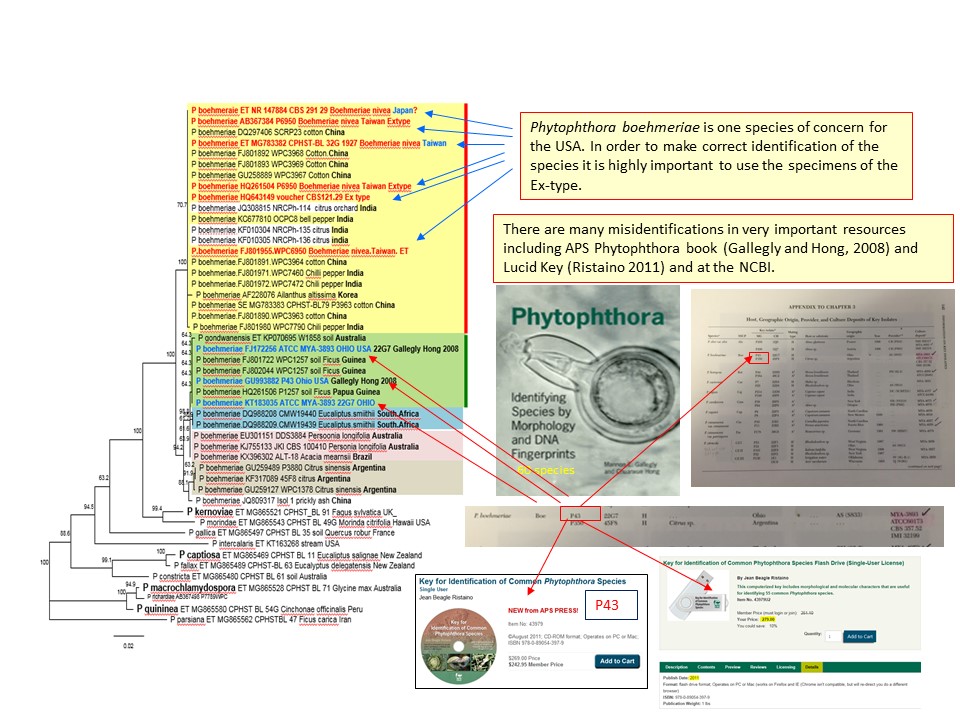
Phytophthora species in Clade 10 (ITS rDNA). Notice the position of the cluster of the "sensu stricto" of P. boehmeriae, in relation of the position of P. gondwanensis and other related clusters. Blue arrows point the position of sequences from the the ex-type and red arrows show the position of misidentifications. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sympodially branching sporangiophores. Sporangia papillate, caducous, with short pedicels. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sympodially branching sporangiophores. Sporangia papillate, caducous, with short pedicels. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sporangium globose, papillate, caducous, with short pedicel. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sporangium globose, papillate, caducous, with short pedicel. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sporangium papillate, caducous, with short pedicel. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) asexual phase: sporangium with irregular shape, papillate, caducous. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
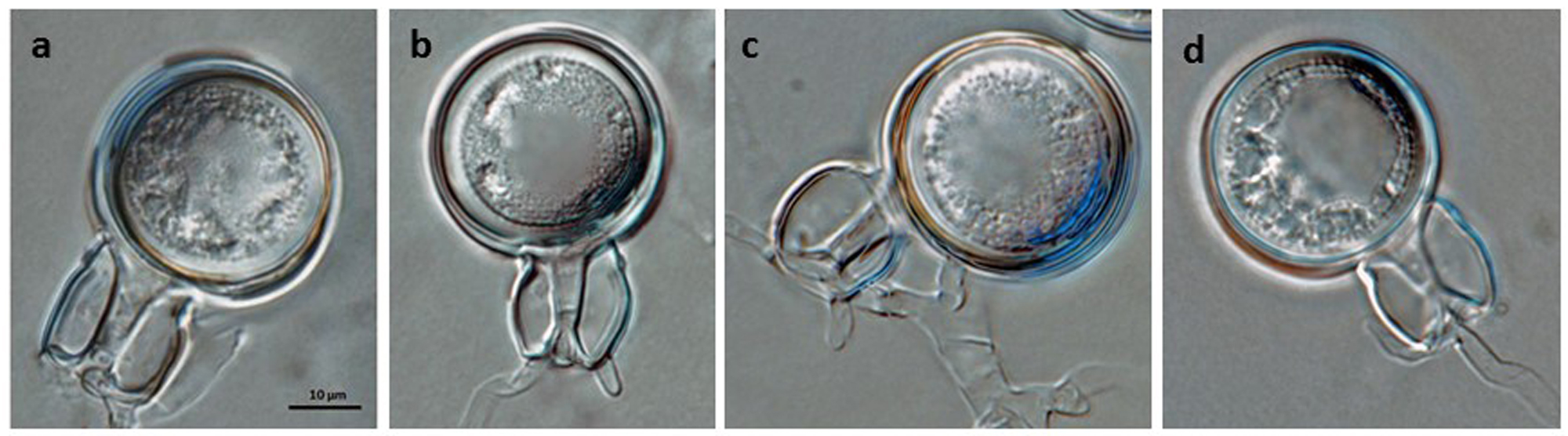
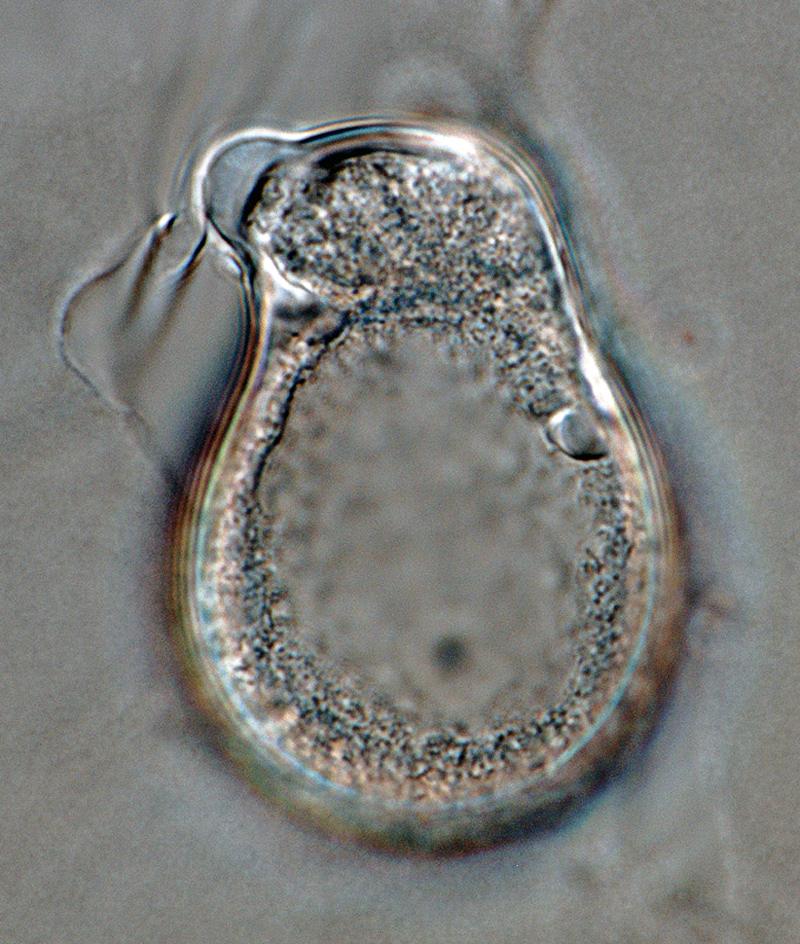
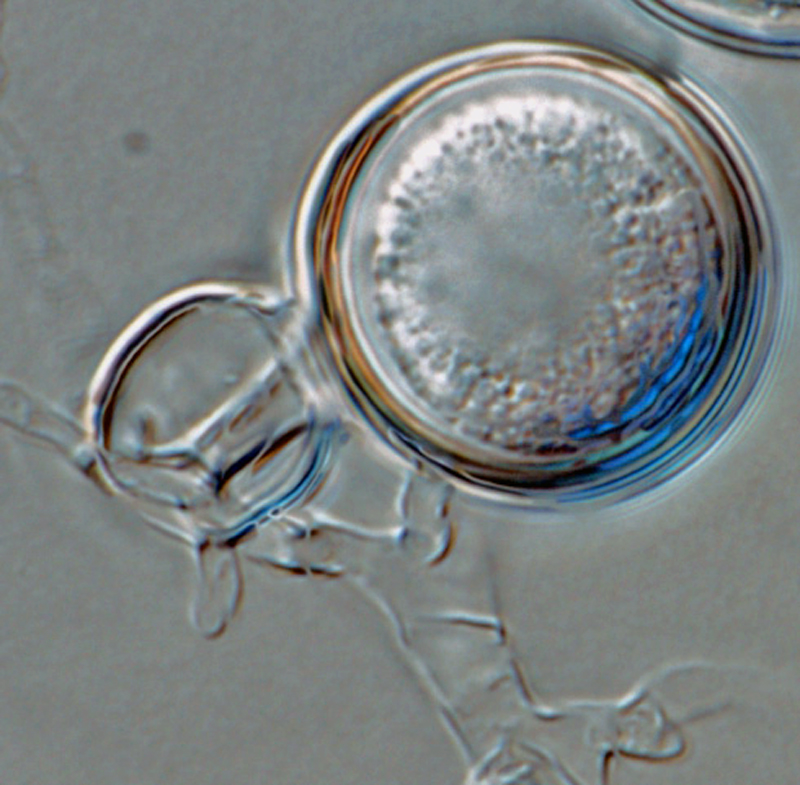
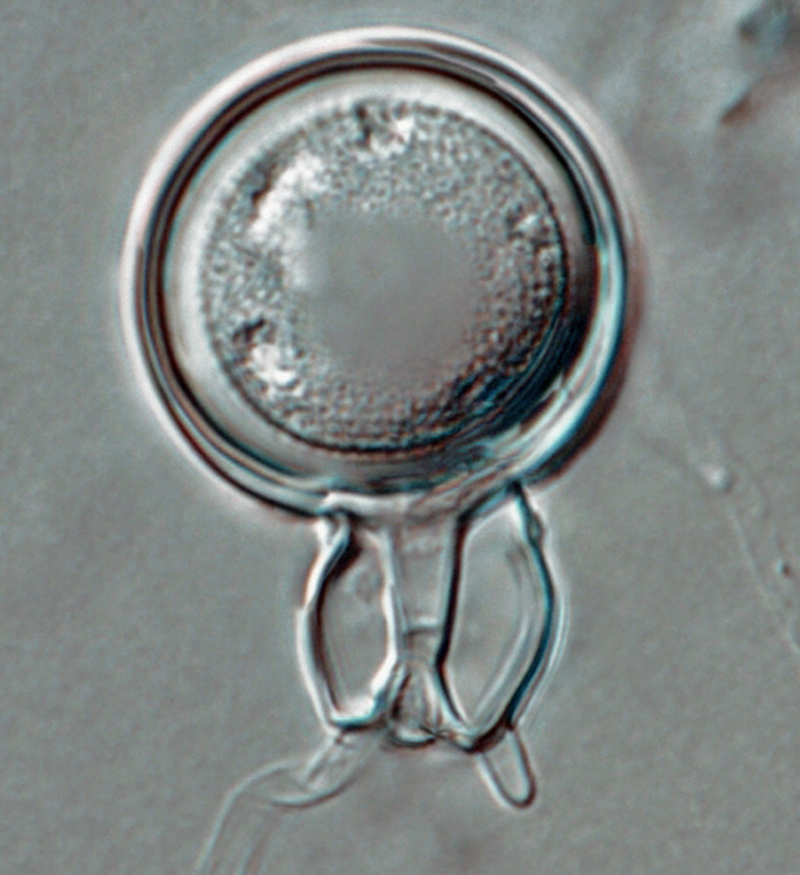
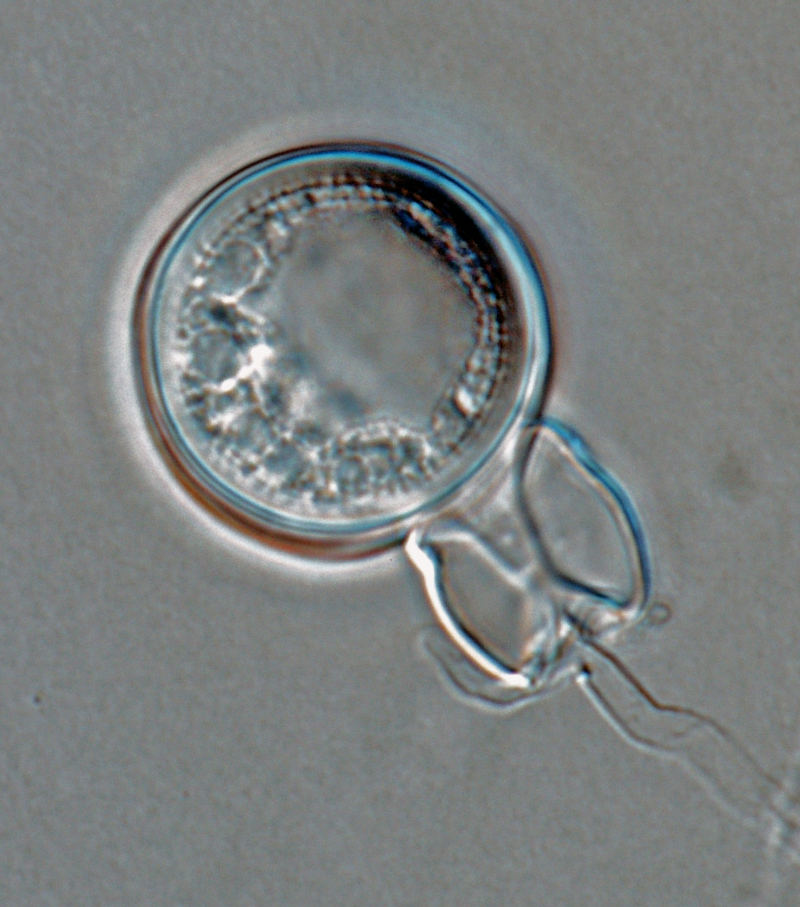
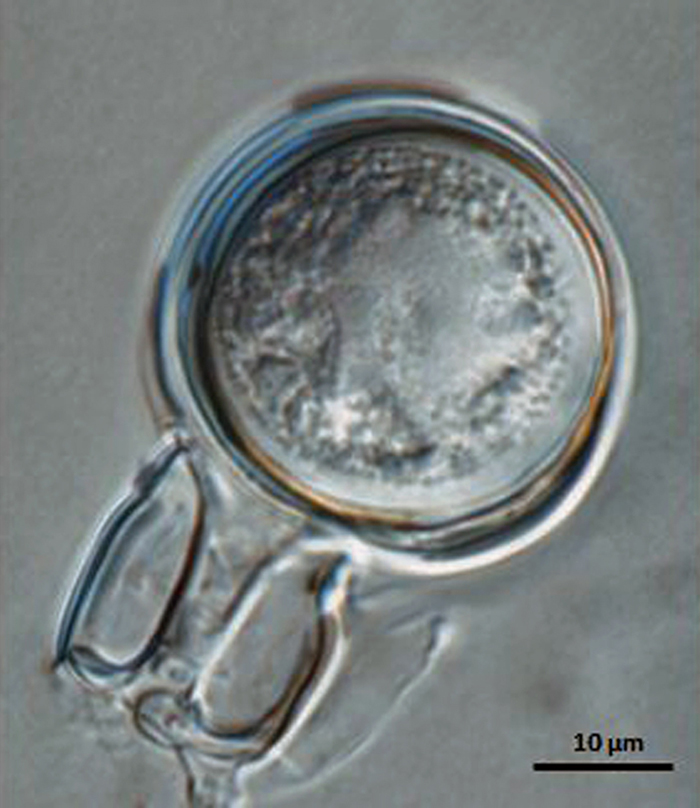
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled with amphigynous antheridium almost spherical in shape with plerotic oospore. Note digitated projection on antheridium. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled with amphigynous antheridium almost spherical in shape with plerotic oospore. Note digitated projection on antheridium. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled with amphigynous antheridium almost spherical in shape with plerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora boehmeriae (CPHST BL 32G ex-type) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled with amphigynous antheridium almost spherical in shape with plerotic oospore. Photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora boehmeriae Sawada (1927)
Sawada K. 1927. Descriptive catalogue of the Formosan fungi III. Report of the Department of Agriculture, Government Research Institute of Formosa 27: 1–62.
Nomenclature
from Sawada (1927)
Mycobank
Etymology
named for the association with the host Boehmeria nivea
Typification
Type: TAIWAN from leaf of Boehmeria nivea (Chinese silk tree, Ramie), 1929, Sawada, IMI 180614
Ex-type: CBS 291.29
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 291.29, WPC P6950, CABI IMI180614 (PL), ATCC 60238, S&T BL 32G (Abad), 45F9 (Hong)
Note about the ex-type: Although HerbIMI cites that a culture of IMI 180614 is available from CABI, specimen IMI 180614 is not available from CABI (search 11.5.2017). In this collection the only specimen available for P. boehmeriae is IMI 403470 from USA, Schmittener's Ohio S833. Isolate IMI 403470 corresponds to ATCC MYA-3893 = P43 (S833, 22G7) cited in ATCC as "key isolate of the species" in Gallegly and Hong 2008. However sequences of MYA-3893 FJ172256, KT183035 (ITS rDNA) don't align with sequences of the duplicate of the ex-type P6950 FJ801955 (ITS rDNA).
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora boehmeriae isolate CPHST BL 32G (= P6950 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG783382, COI MH136852
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Selected specimens
Phytophthora boehmeriae isolate CPHST BL 79 (= P3963 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG783383, COI MH136853
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora boehmeriae CPHST BL 32G
- NCBI: Phytophthora boehmeriae P6950
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora boehmeriae CBS 291.29
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora boehmeriae PHYTO211-10 = P6950 (barcoding COI & ITS)
NOTE: P. boehmeriae CBS 100410 is a P. like boehmeriae.
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
10a
Morphological identification
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
on V8-A is uniform, on PDA and MEA with light chrysanthemum pattern. Minimum temperature for growth is 5°C, optimum is 25°C, and maximum is 33°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Oospores, chlamydosporeschlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
, and sporangiasporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
form abundantly in an agar medium in 7 to 10 days.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
papillatepapillate:
pertaining to the production of a distinct papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. nonpapillate and semipapillate)
, sometimes bipapillate; caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with short pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
up to 3 µm long; globose, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, obturbinate, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
, and distorted shapes (50–70 L x 35–45 W µm); originated in unbranched or sympodiallysympodially:
at the foot of; referring to a sporangiophore that emerges externally from the base of the previous sporangium
branching sporangiophores; laterally displaced attachment of sporangiophoresporangiophore:
the hyphal strand on which the sporangium is formed; may be branched or unbranched to form compound sympodia or simple sympodia
is observed. Hyphal swellings absent. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
are produced infrequently (40–50 µm diam).
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
are smooth-walled and hyaline to yellow, antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
and almost spherical in shape, frequently with digitated projection, often with a residual oil globule; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
pleroticplerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
rarely apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
, wall is 2 μm or less in thickness.
Most typical characters
P. boehmeriae can be recognized by the production of abundant oogoniaoogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
and oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
in single culture, amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
antheridia, sporangiasporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
broadly ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
to subspherical and conspicuously papillatepapillate:
pertaining to the production of a distinct papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. nonpapillate and semipapillate)
, and caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with short pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
.
Specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora boehmeriae CPHST BL 32G duplicate of ex-type P6950 (World Phytophthora Collection, California, USA)
Additional isolates: CPHST BL 79 (Abad) selected specimen duplicate of P3963 from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) in China
Hosts and distribution
Distribution*: Japan, China, Australia, India (Karnataka and Tamil Nadu states), Argentina, Brazil, Greece, and Papua New Guinea
Substrate: fruits, leaves, roots, bolls
Disease note: causes foliar blight, brown rot of citrus fruit, root rot of Pinus spp., cotton boll blight, basal rot of Gerald ton wax plant (Chamaelauciun uncinatum Schauer.), and gummosis on black wattle (Acacia mearnsii)
Hosts: Citrus spp. (Rutaceae) and various other plant families; Boehmeria nivea (Urticaceae); Gossypium sp. (Malvaceae) cotton
Retrieved January 29, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
*NOTE: The distribution of Phytophthora boehmeriae is in Asia. The distribution of the species in other areas of the world is incorrectly cited in several online sources (including the above).
Quarantine status
USA: This species was listed as a species of concern during the 2009 Phytophthora prioritization project conducted by USDA APHIS PPQ CPHST PERAL (Schwartzburg et al.).
Phytophthora boehmeriae is listed in the U.S. Regulated Plant Pest Table (last modified Nov. 15, 2017).
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora boehmeriae
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora boehmeriae (incorrectly cites occurrence in other parts of the world)
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Google All Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Google Images Phytophthora boehmeriae
- Google Scholar Phytophthora boehmeriae
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.