Phytophthora brassicae
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 8b: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. brassicae Ex-type CBS 179.87 = S&T BL 8. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 8b: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. brassicae Ex-type CBS 179.87 = S&T BL 8. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
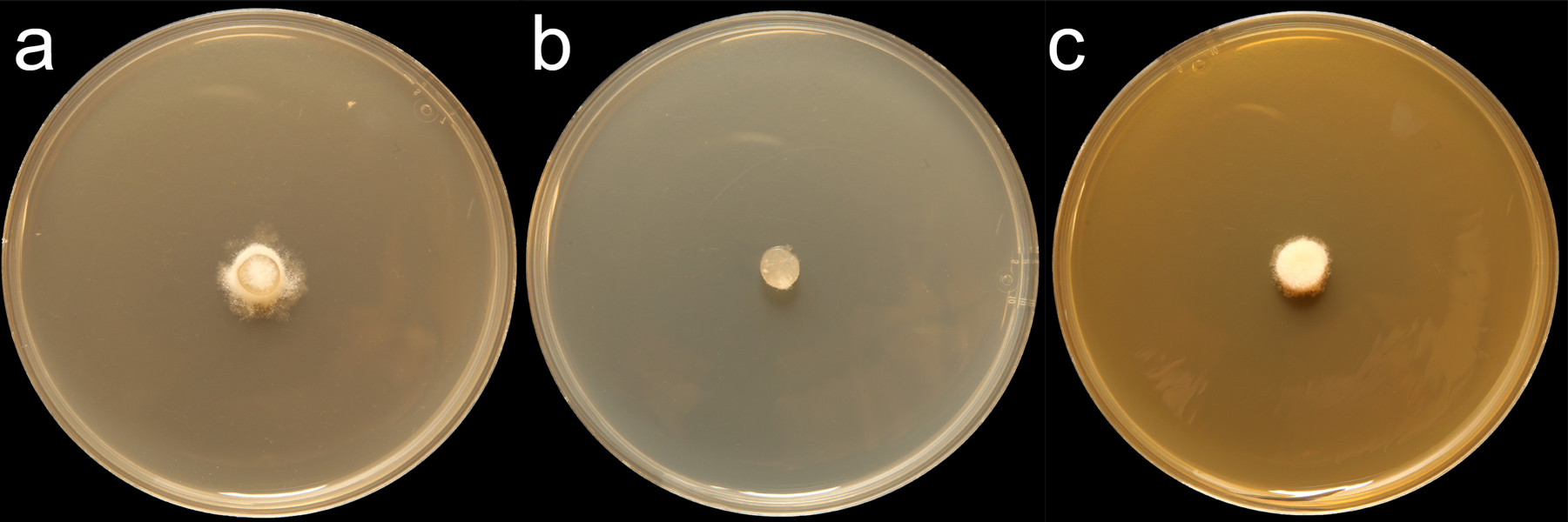
Phytophthora brassicae (CPHST BL 8) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
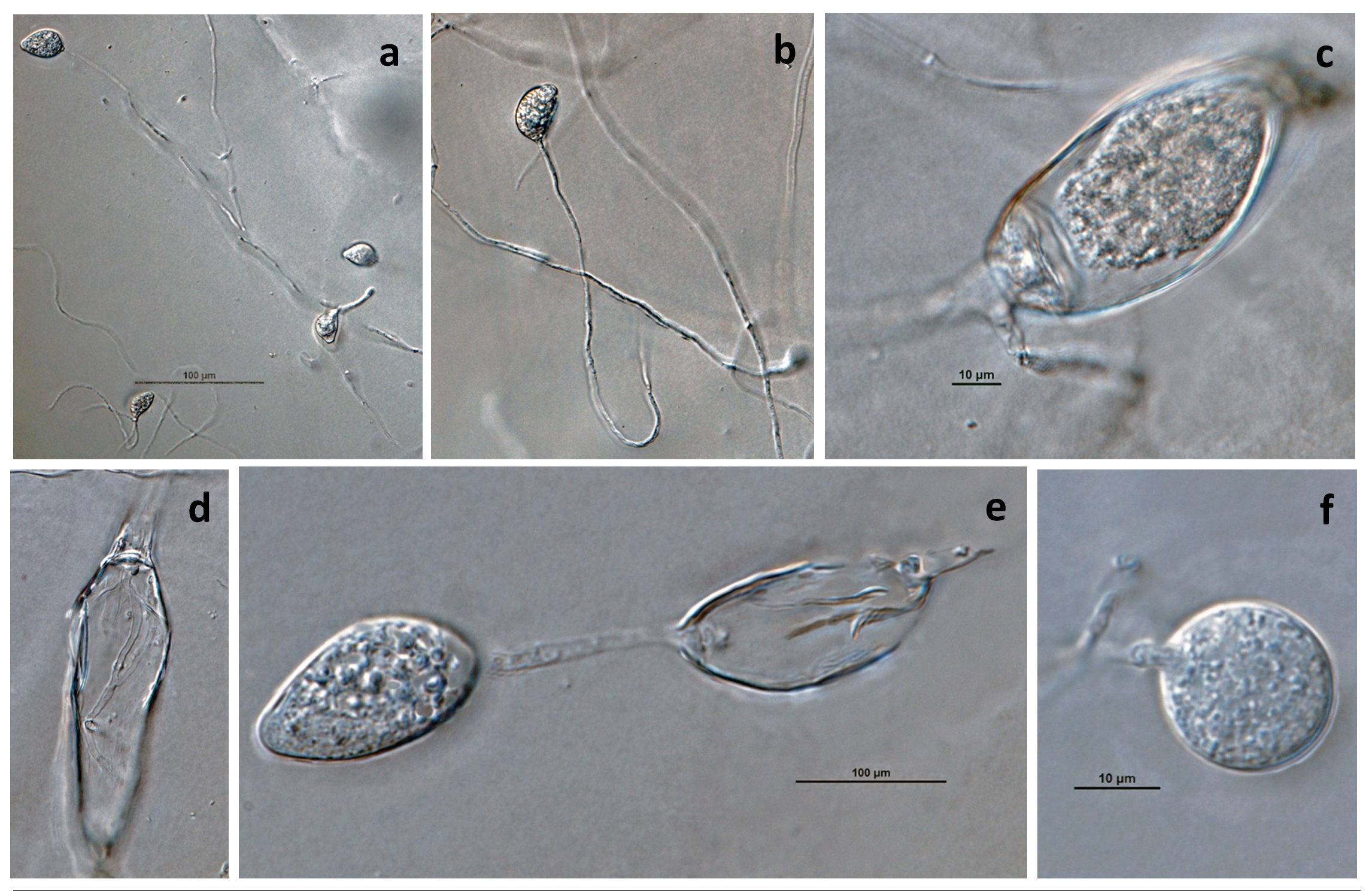
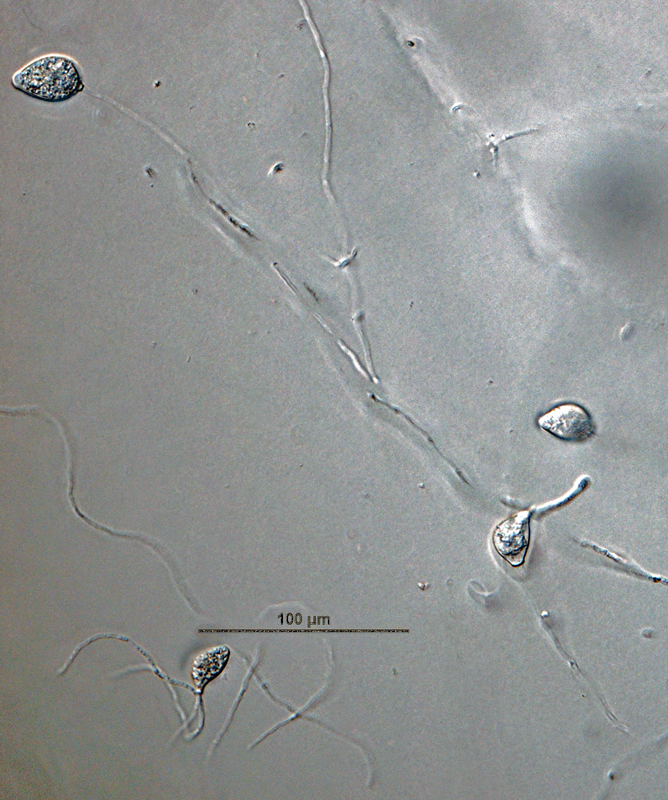
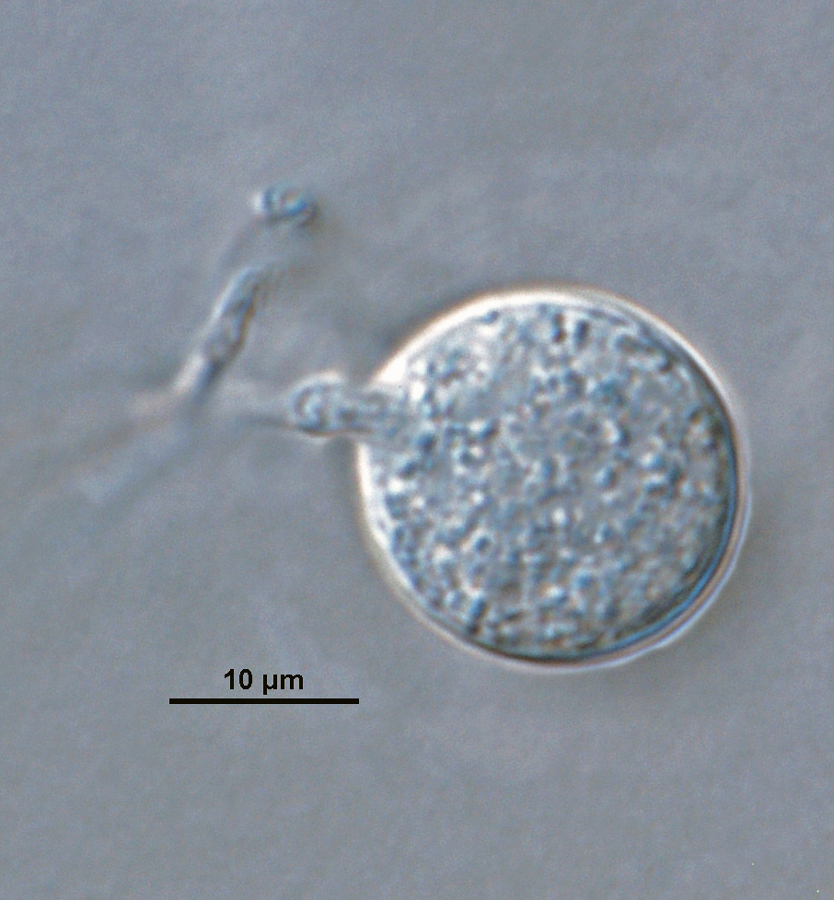
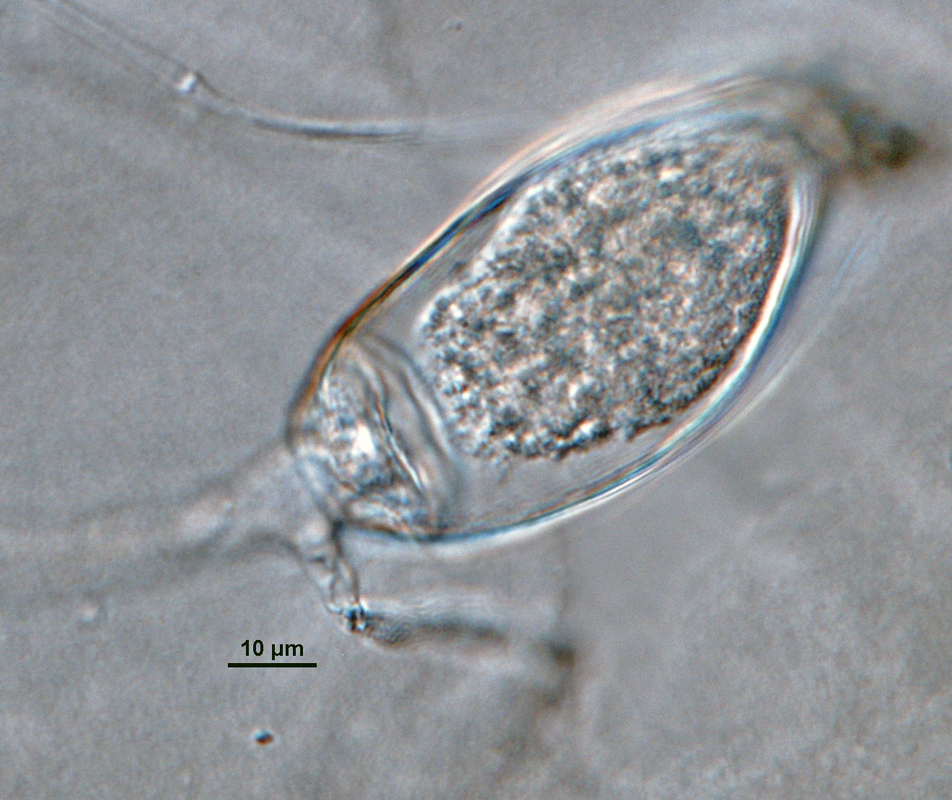
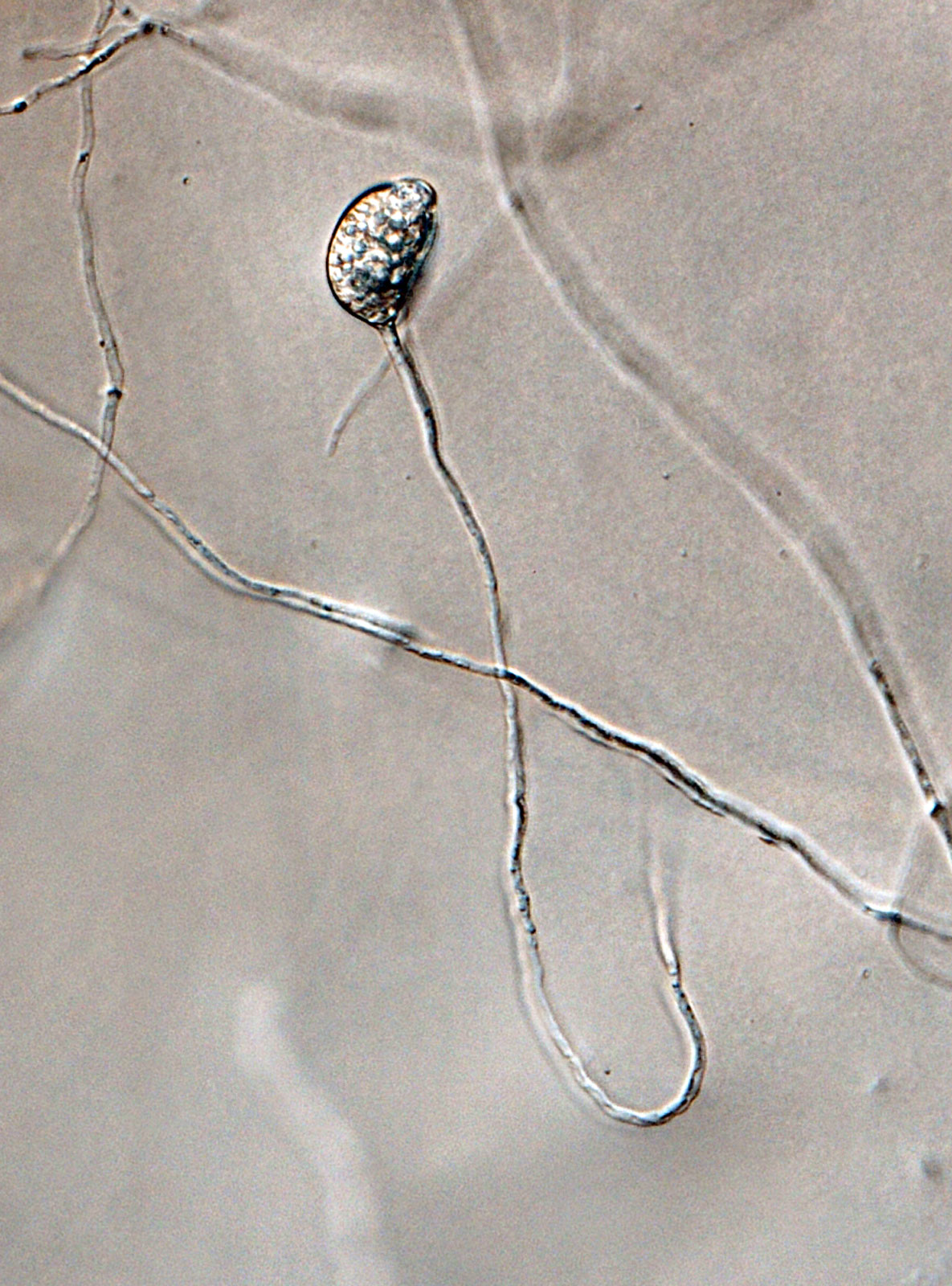
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase (a-f): (a, b) sporangia produced in sporangiophores, (c) sporangium showing internal plug, (d) sporangium with internal proliferation, (e) sporangium with external proliferation, (f) globose sporangium; photos by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: sporangium with internal proliferation. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
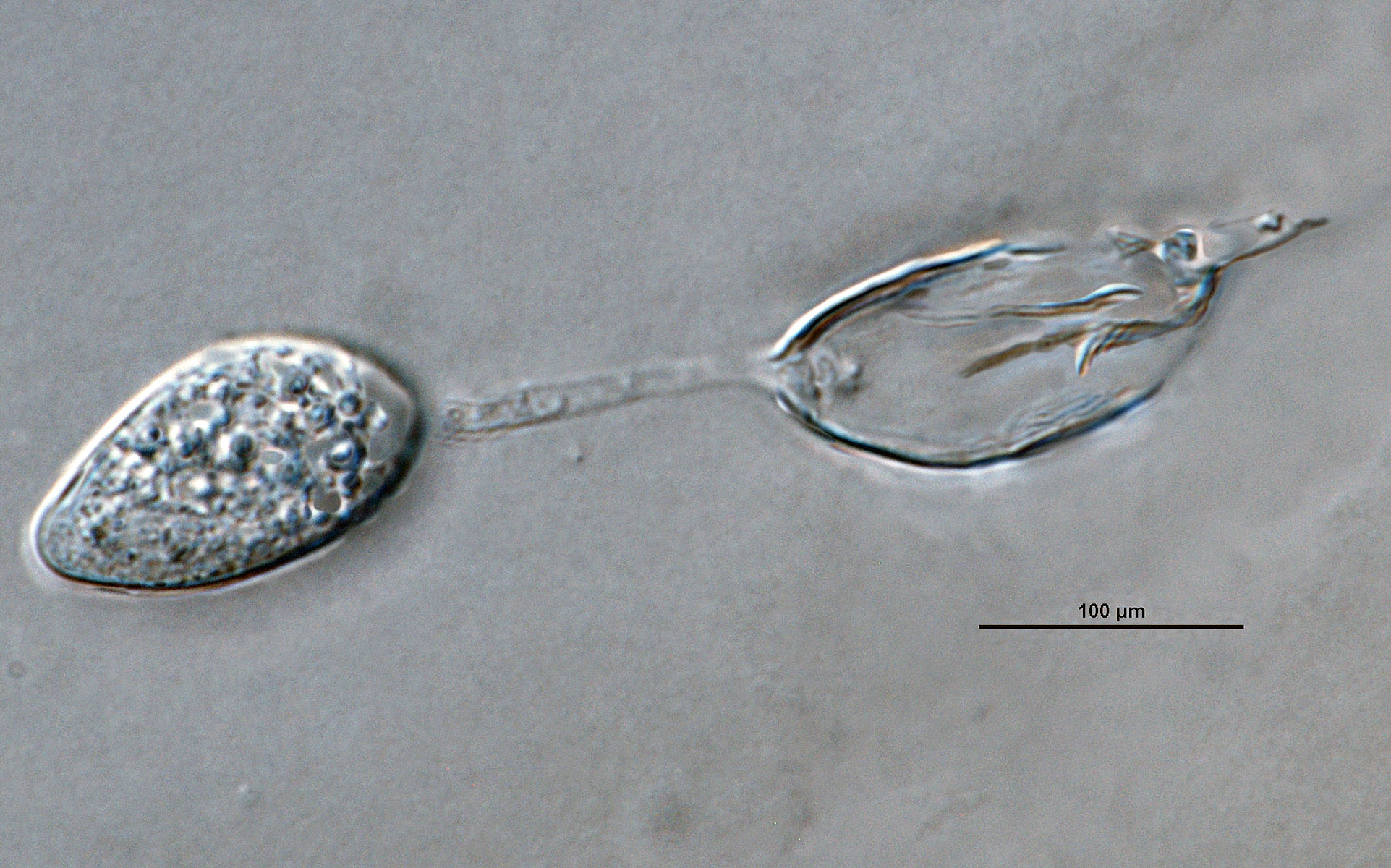
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: sporangium with external proliferation. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: sporangia produced in sporangiophores. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: globose sporangium (chlamydospores absent in species). Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
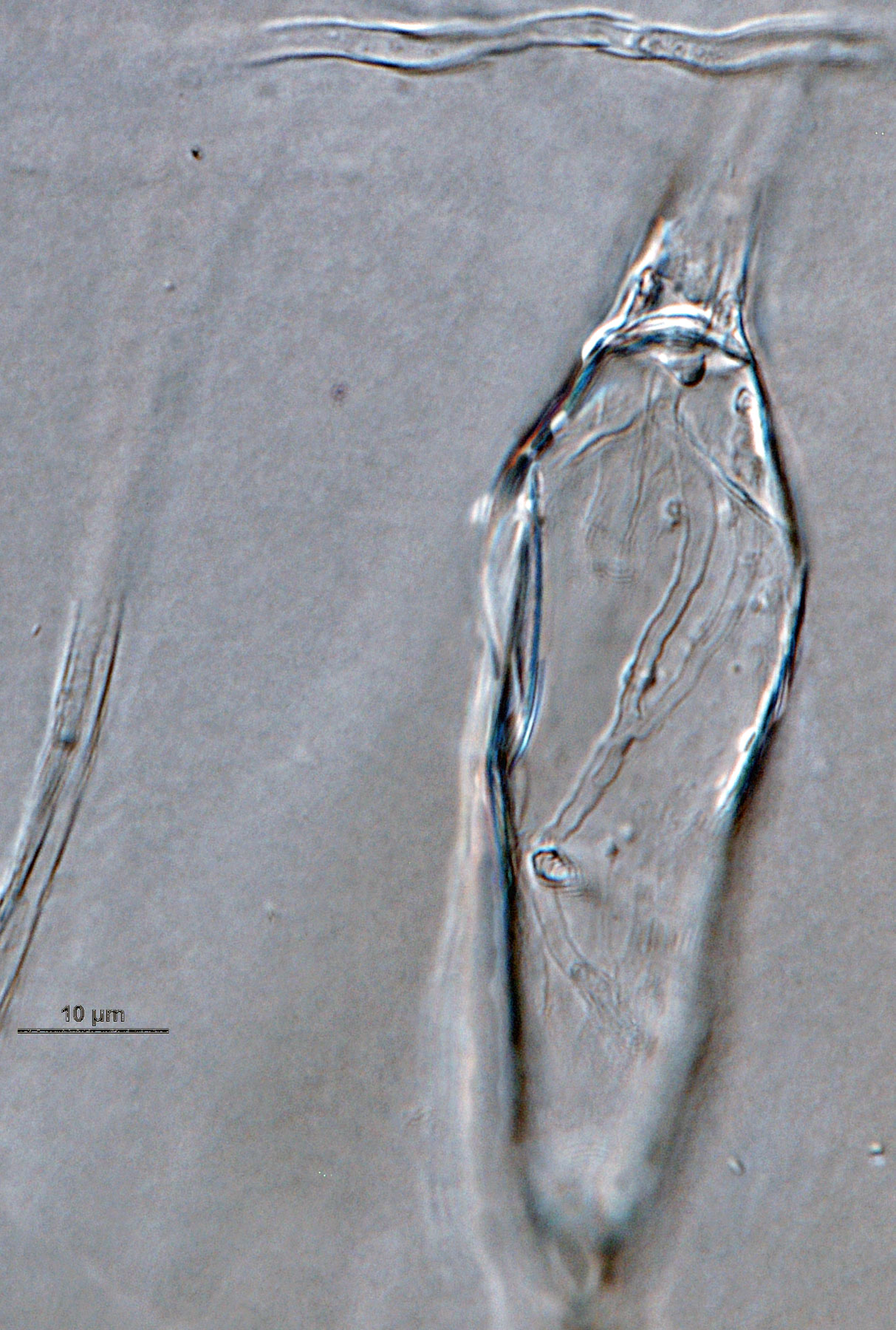
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: sporangium showing internal plug. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora brassicae ex-type CPHST BL 8, asexual phase: sporangia produced in sporangiophore. Photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora brassicae De Cock & Man in ’t Veld (2002)
Man in 't Veld WA, de Cock AWAM, Ilieva E, and Lévesque CA. 2002. Gene flow analysis of Phytophthora porri reveals a new species: Phytophthora brassicae sp. nov. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 108: 51–62.
Corresponding author: w.a.man.in.’t.veld@pd.agro.nl
Nomenclature
from Man in 't Veld et al. (2002)
Mycobank
Typification
Type: THE NETHERLANDS, from Brassica oleracea, CBS 179.87-H, in herb. dried culture
Ex-type: CBS 179.87
Sequences for ex-type in original manuscript: Phytophhtora brassicae CBS 179.87 = ITS rDNA AF380148
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 179.87, WPC P7517, S&T BL 8 (Abad), 61J8 (Hong)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora brassicae isolate CPHST BL 8 (= P7517 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG783384, COI MH136857
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora brassicae CPHST BL 8
- NCBI: Phytophthora brassicae CBS 179.87
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora brassicae CBS 179.87
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora brassicae (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
8b
Morphological identification
adapted from Man in 't Veld et al. (2002)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colonies on V8-A, PDA, and MEA with no distinct growth pattern, on PDA with slow growth. Cardinal temperatures for growth: minimum below 3°C, optimum 21°C, maximum 27°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Sporangia abundantly produced in and on cornmeal agar as well as on hemp seeds in soil extract. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
developed on cornmeal agar and V8 agar, only during a short period after isolation.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
or semipapillatesemipapillate:
pertaining to the production of shallow having papilla that are not well developed, shallow and less nipple-like than fully papillate structures
, persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
or caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with short pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
, globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
to ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, sometimes distorted shapes, 25–48 × 40–74 μm, borne singly or in sympodial sporangiophoresporangiophore:
the hyphal strand on which the sporangium is formed; may be branched or unbranched to form compound sympodia or simple sympodia
, occasionally laterally attached or intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
. Hyphal swellings present in hemp-seed/water cultures, intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
, often in chains and/or provided with radiating hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
, occasionally terminal, (sub-) globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, 10–40 (–53) μm diam. Chlamydospores absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallichomothallic:
pertaining to sexual reproduction that can take place within a single thallus (i.e. self-fertile, non-outcrossing) (cf. heterothallic).
. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
terminal, wall smooth, inner side of the wall undulate, colorless to pale yellow, up to 2 μm thick (in some other isolates also dark yellow and up to 6 μm thick). AntheridiaAntheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
1–2 per oogoniumoogonium:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
, mostly amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
, occasionally paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
, variable in shape, 16–20 μm diam. OosporesOospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
, wall up to 2 μm thick.
Most typical characters
Phytophthora brassicae is characterized by low cardinal temperatures for growth, the presence of semi- to nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
sporangia, and caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
sporangia with short pedicels.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora brassicae CPHST BL 8 (Abad) = P7517 [World Phytophthora Collection (WPC) California, USA]
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Europe (UK, Germany), North America (USA: WI)
Substrate: leaves?
Disease note: storage rot (see Erwin & Ribeiro as Phytophthora porri)
Hosts: Brassica oleracea and Brassica sinensis (Brassicaceae)
Retrieved January 29, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora brassicae
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora brassicae
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora brassicae
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora brassicae
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora brassicae
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora brassicae
- Google All Phytophthora brassicae
- Google Images Phytophthora brassicae
- Google Scholar Phytophthora brassicae
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.