Phytophthora emzansi
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 2c: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. emzansi Ex-type CBS 147464 = S&T BL 210. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 2c: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. emzansi Ex-type CBS 147464 = S&T BL 210. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
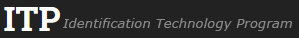
persistent, semi-papillate, predominantly ovoid sporangia, usually solitary but sometime is loose sympodia; scale bar = 25µm |
|
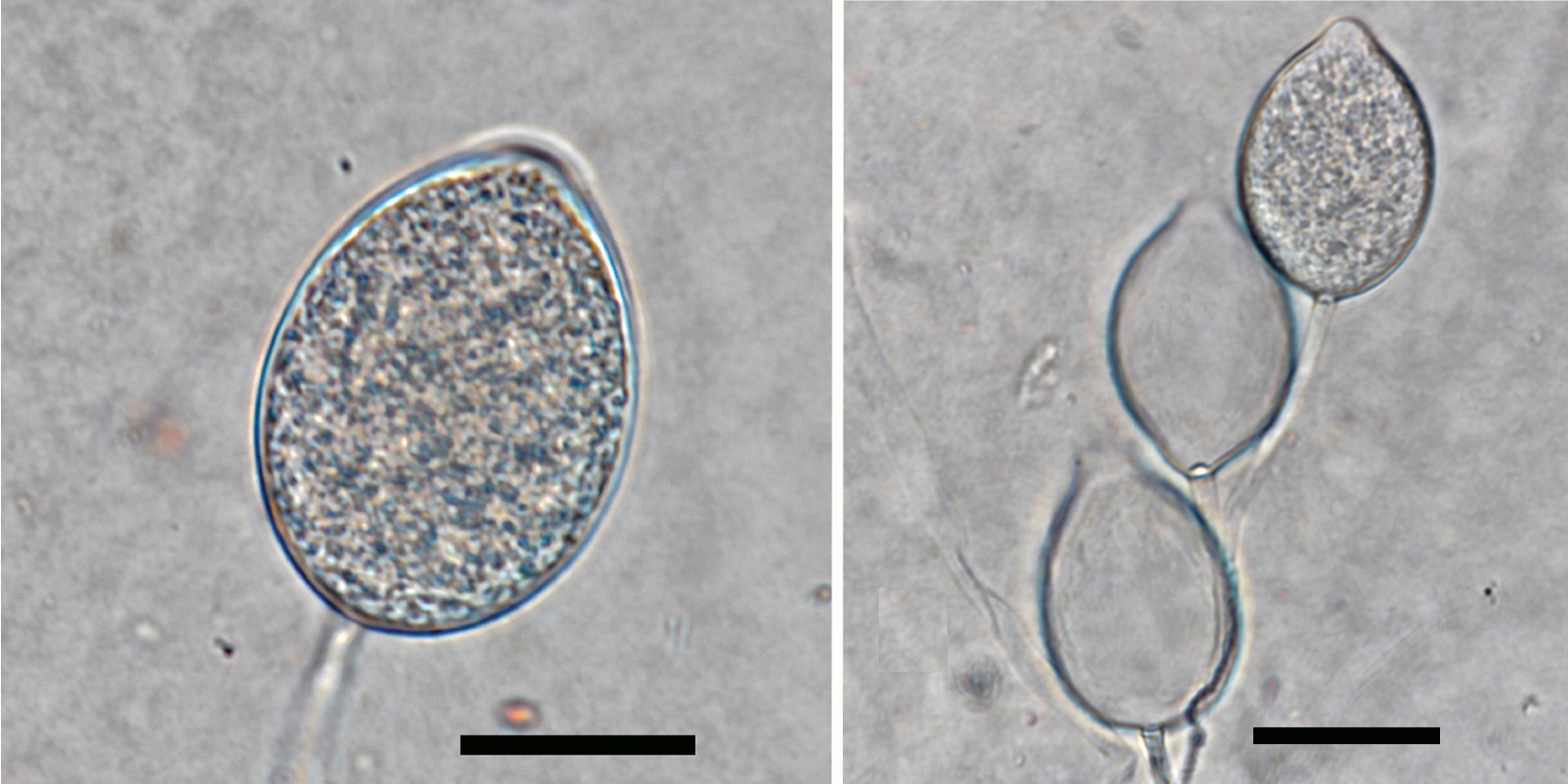
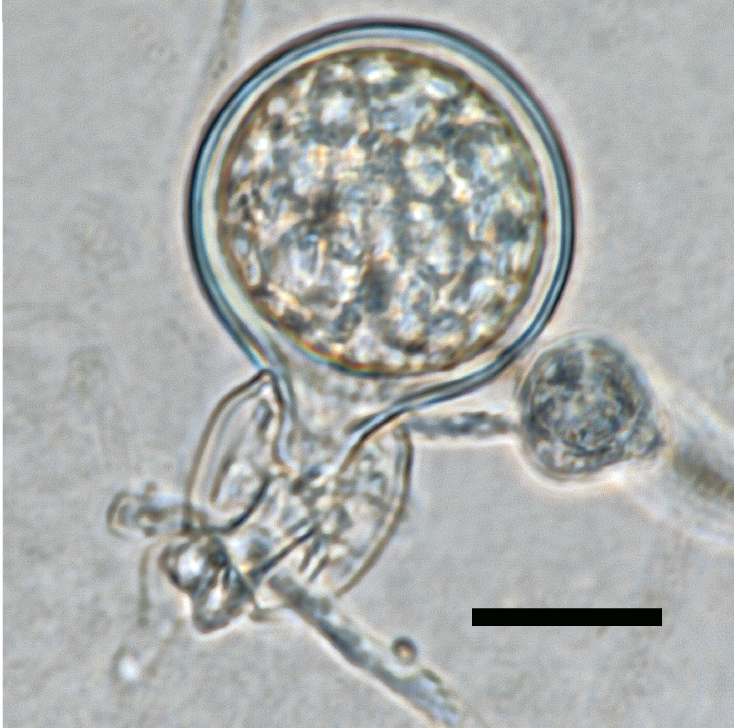
oogonia with smooth walls containing plerotic oospores; antheridia were exclusively amphigynous; scale bar = 20µm |
Name and publication
Phytophthora emzansi T. Bose, T. Paap, and J.M. Hulbert (2021)
Bose T, Hulbert JM, Burgess TI, Paap T, Roets F, Wingfield MJ. 2021. Two novel Phytophthora species from the southern tip of Africa. Mycological Progress 20 (6): 755–767.
Corresponding author: Tanay Bose Tanay.Bose@fabi.up.ac.za
Nomenclature
Mycobank
Etymology
name derived from the Zulu word for south or from the south
Typification
Type: SOUTH AFRICA, Knysna Forest, Western Cape Province, from rhizosphere soil of Afrocarpus falcatus (− 33.93149201, 22.62277904), November 2017, JM Hulbert, holotype PREM63081
Ex-type: culture PPRI 28451 = CMW 54354 = CBS 147464
Sequences of ex-type in manuscript: ITS MT762301, ß-tubulin MT762318, HSP90 MT762327, coxI MT762309
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 147464, NRRL 64318, PPRI28451, CMW54354, S&T BL 210 (Abad)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora emzansi ITS rDNA, COI
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora emzansi
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora emzansi
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora emzansi
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
2c
Morphological identification
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology cottony with no distinct pattern on MEA, CA, V8A and PDA. Minimum growth temperature 4°C, optimum 20°C, and maximum 30°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
are produced in water cultures (soil extract or river water) and not observed in solid media. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
are formed readily in single-strain culture on CA and V8 after about 14 d.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
were semi-papillate, persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
, and predominantly ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
in shape with no proliferationproliferation:
formation of a sporangium within an empty sporangium that has previously emitted zoospores (internal or nested) or after the sporangiophore has emerged from the empty sporangium (external)
. SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
averaged 26.7 x 23.9 µm (overall range 25–68.3 x 17.5–41.5 µm); Sporangiophores simple or loose sympodiasympodia:
a type of sporangiophore which appears simple, but where each successive sporangium develops on a branch behind and to one side of the previous apex, where growth has already ceased
. Hyphal swellings present. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
had smooth walls and size ranged from 18.8–49.9 µm. OosporesOospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
pleroticplerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
, globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
often with a tapering base and light golden brown on maturity, size ranged 18.2–46.7 µm. OosporesOospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
often aborted after formation of the walls. AntheridiaAntheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
.
Most typical characters
Phytophthora emzansi is a sister species to P. capansis but differs mainly by the high abortion rate of oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
and in having amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
antheridia.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
South Africa, Knysna Forest, Western Cape Province, from rhizosphere soil of Afrocarpus falcatus, 2017, JM Hulbert, CBS 147464; CBS 147466; 2019, CMW 54569; Eerste River, 2016, CBS 147465; from rhizosphere soil of Rapanea melanophloeos, 2019, CMW 54577; Western Cape Province, from rhizosphere soil of Podocarpus elongata, 2016, T Paap – CMW50975; Agathosma betulina, 2005, K Lubbe, STE-U 6269 (= WPC P15619, CMW 56071); STE-U 6272 (= WPC P19574, CMW 56072)
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: South Africa
Substrate: roots
Disease note: no diseases recorded
Hosts: Agathosma betulina, asymptomatically from rhizosphere soil in natural vegetation
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora emzansi
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora emzansi
- Forest Phytophthoras of the World: Phytophthora emzansi
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora emzansi
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora emzansi
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora emzansi
Fact sheet author
Treena Burgess, Ph.D., Phytophthora Science and Management, Harry Butler Institute, Murdoch University, Australia
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.