Phytophthora gondwanensis
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 10a: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. gondwanensis Ex-type CBS 139336. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 10a: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. gondwanensis Ex-type CBS 139336. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
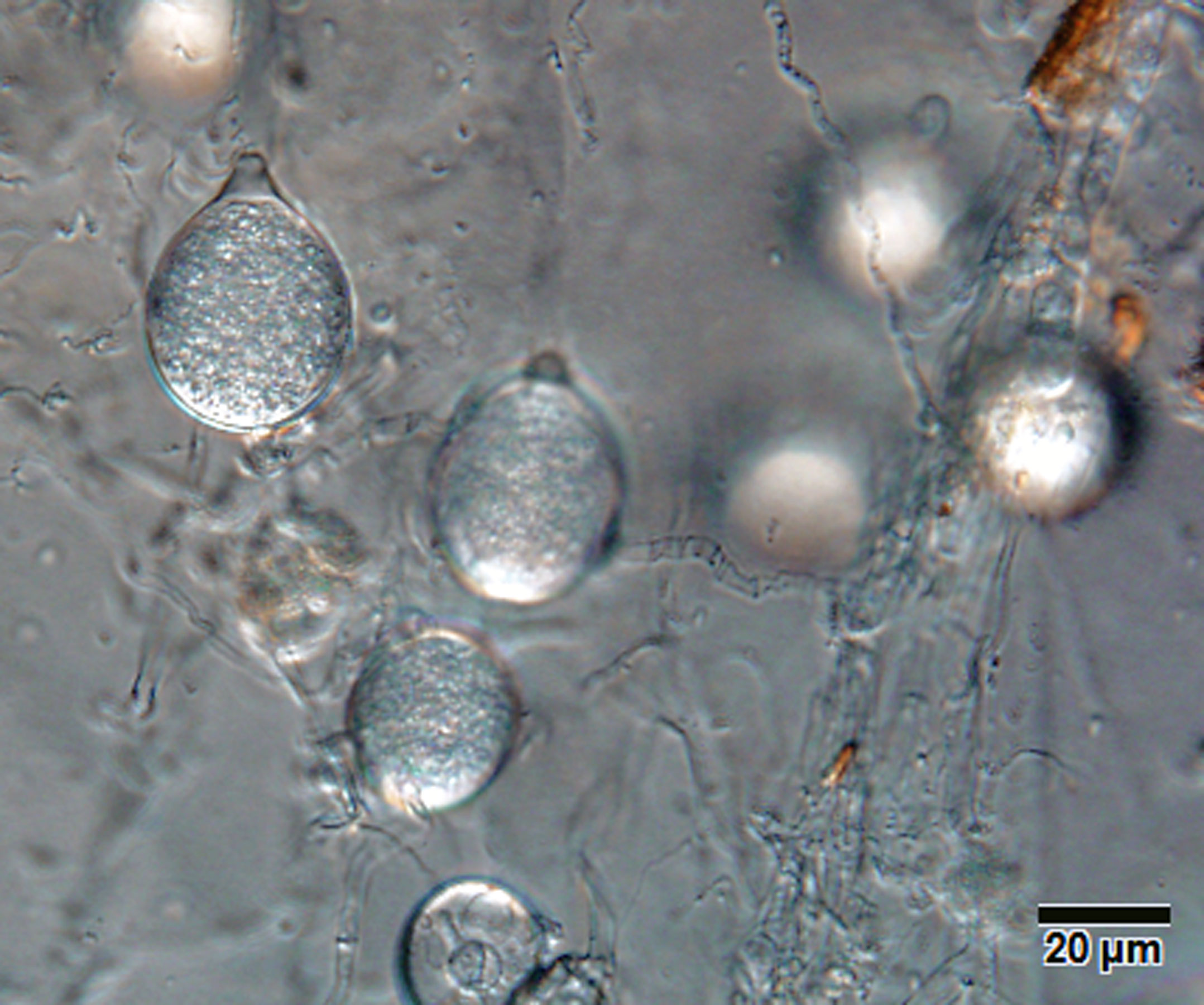
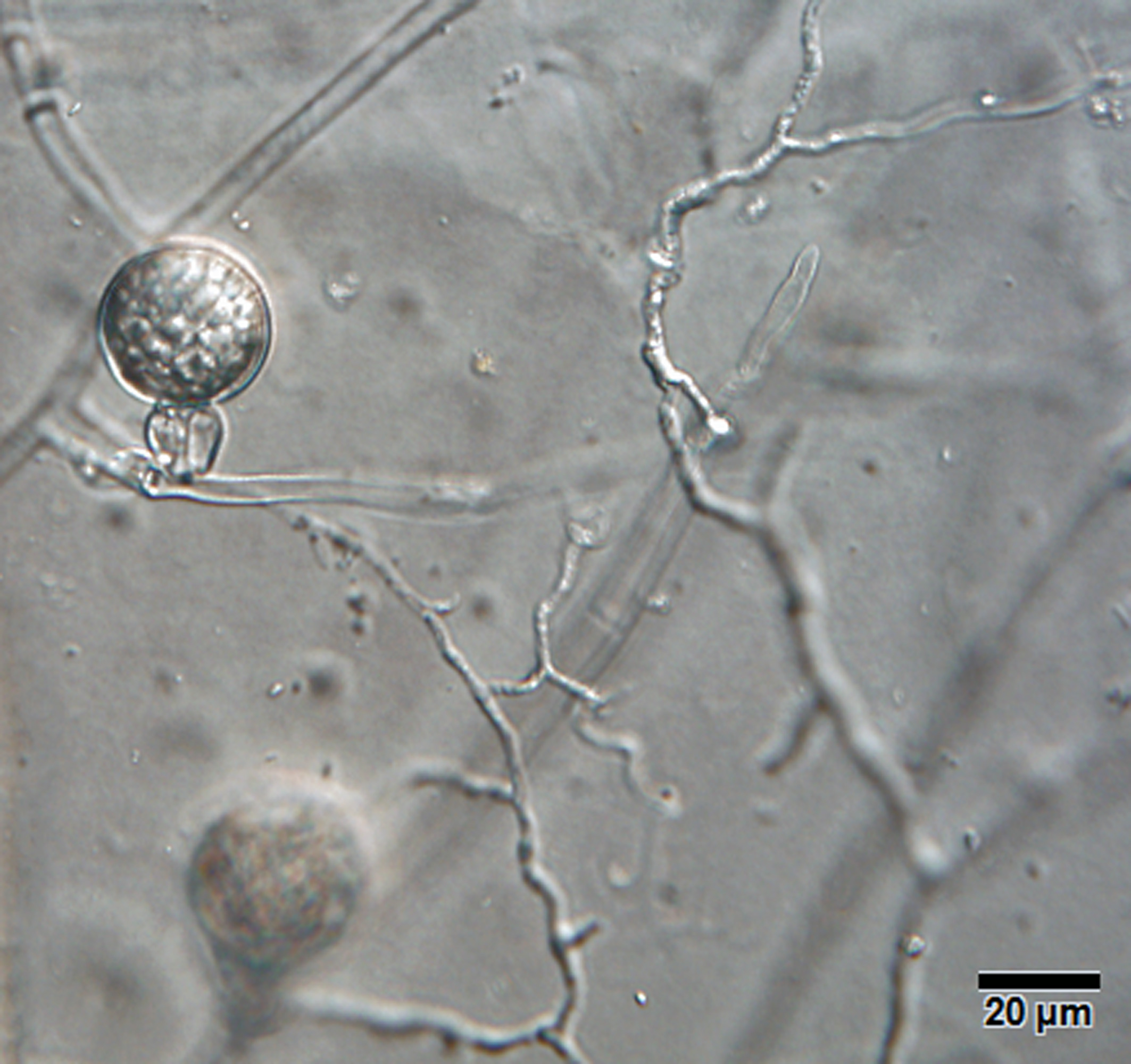
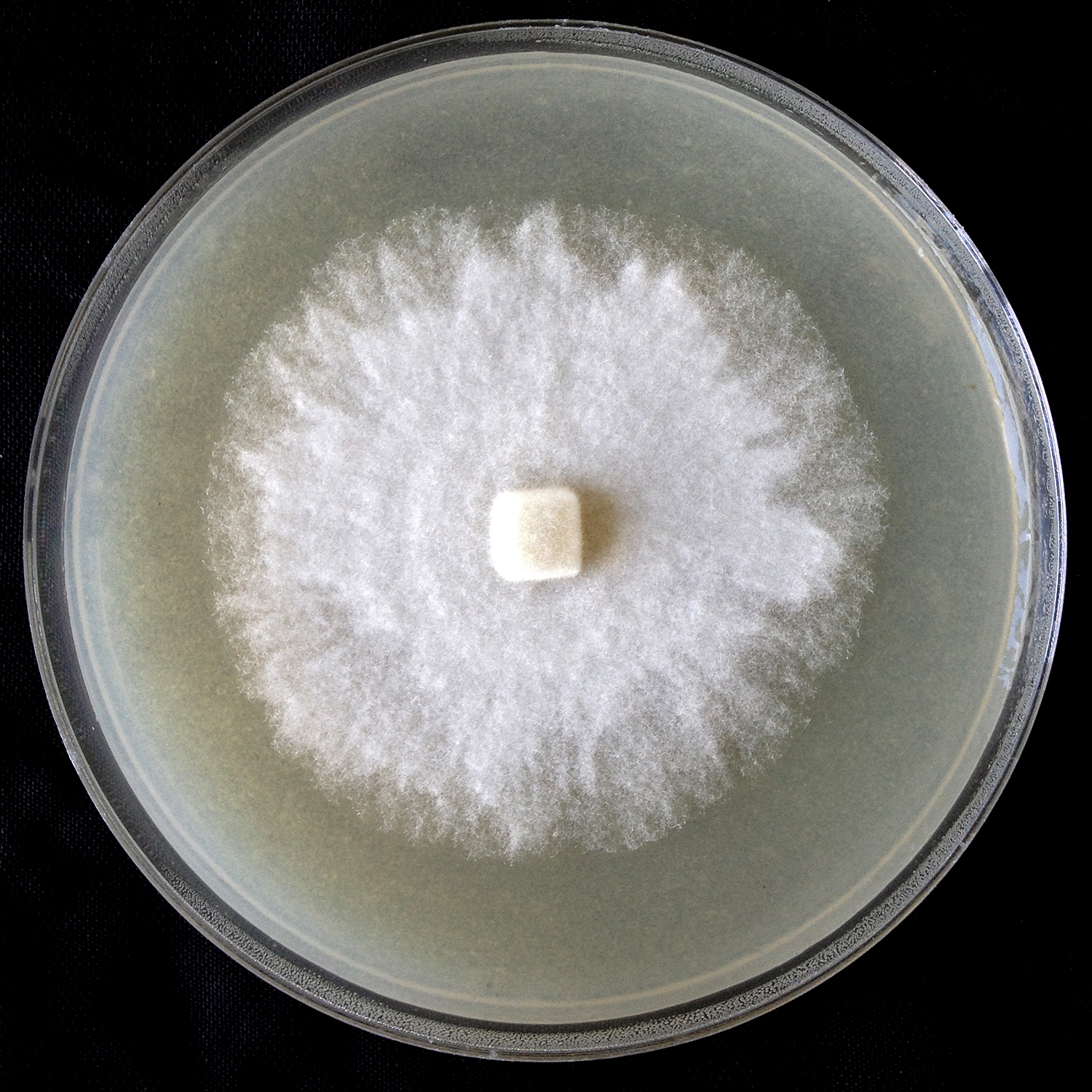
Phytophthora gondwanensis (ex-type CBS 139336) colony morphology, asexual and sexual phases: (a) sporangia papillated, with short pedicel (red arrow); (b) smooth-walled oogonium with amphigynous antheridium and plerotic oospore; (c) colony morphology in 10% V8 agar; photos by Lucas A. Shuttleworth, University of Sidney, Australia. |
|
Phytophthora gondwanensis (ex-type CBS 139336) asexual phase: sporangia papillated, with short pedicel; photo by Lucas A. Shuttleworth, University of Sidney, Australia. |
|
Phytophthora gondwanensis (ex-type CBS 139336) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with amphigynous antheridium and plerotic oospore; photo by Lucas A. Shuttleworth, University of Sidney, Australia. |
|
Phytophthora gondwanensis (ex-type CBS 139336) colony morphology in 10% V8 agar; photo by Lucas A. Shuttleworth, University of Sidney, Australia. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora gondwanensis L.A. Shuttlew., K. Scarlett, R. Daniel & D.I. Guest (2015)
Shuttleworth LA, Scarlett K, Daniel R, and Guest DI. 2016. Phytophthora gondwanensis. Persoonia 35: 298–299. In Crous P, et al. 2015. Fungal Planet description sheets: 371–399. Persoonia 35: 264–327.
Nomenclature
from Shuttleworth et al. (2016)
Mycobank
Etymology
refers to Gondwana Rainforests of Australia World Heritage Area where this species was collected
Typification
Type: AUSTRALIA, New South Wales, Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, collected from soil, coll. L.A. Shuttleworth & B.L. Freedman, 28 Nov. 2011, isol. K. Scarlett, Mar. 2014 (holotype a dried 10% V8 agar disc CBS H-22283)
Ex-type: W1858 = CBS 139336 = CMW 42633
Sequences for ex-type in original manuscript: Phytophthora sp. gondwanense isolate W1858 = ITSrDNA KP070695, β-tub KP070605, coxII KP070638
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 139336, CMW 42633, W1858
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora gondwanensis isolate W1858 ITS rDNA KP070695 as Phytophthora sp. gondwanense isolate W1858
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora sp. gondwanense W1858
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora gondwanensis
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora gondwanensis
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
10a
Morphological identification
adapted from Shuttleworth et al. (2016)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology after 7 days of growth on V8 agar, potato-dextrose agar, and malt extract with no distinct pattern. Minimum temperature for growth is 5 °C, optimum 25–30 °C, and maximum 32 °C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Sporangia initially abundant after isolation from soil, and on 10% V8 agar after 5 days, oogoniaoogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
abundant on V8 after 5 days.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
papillatepapillate:
pertaining to the production of a distinct papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. nonpapillate and semipapillate)
; caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with short pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
; globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, limoniform, obturbinate, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
(26–57 μm L × 22–39 μm W); originated in simple sympodial sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings absent. Chlamydospores absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, smooth-walled; antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
(10–20 μm diam.); oospores plerotic plerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
(24–32 μm diam.).
Most typical characters
Morphologically, P. gondwanensis has smaller sporangial dimensions and smaller antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
than Phytophthora boehmeriae.
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Australia
Substrate: isolated from soil
Retrieved January 30, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora gondwanensis
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora gondwanensis
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Google All Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Google Images Phytophthora gondwanensis
- Google Scholar Phytophthora gondwanensis
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.