Phytophthora hedraiandra
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 1a: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. hedraiandra Ex-type CBS 111725 = S&T BL 4. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 1a: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. hedraiandra Ex-type CBS 111725 = S&T BL 4. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
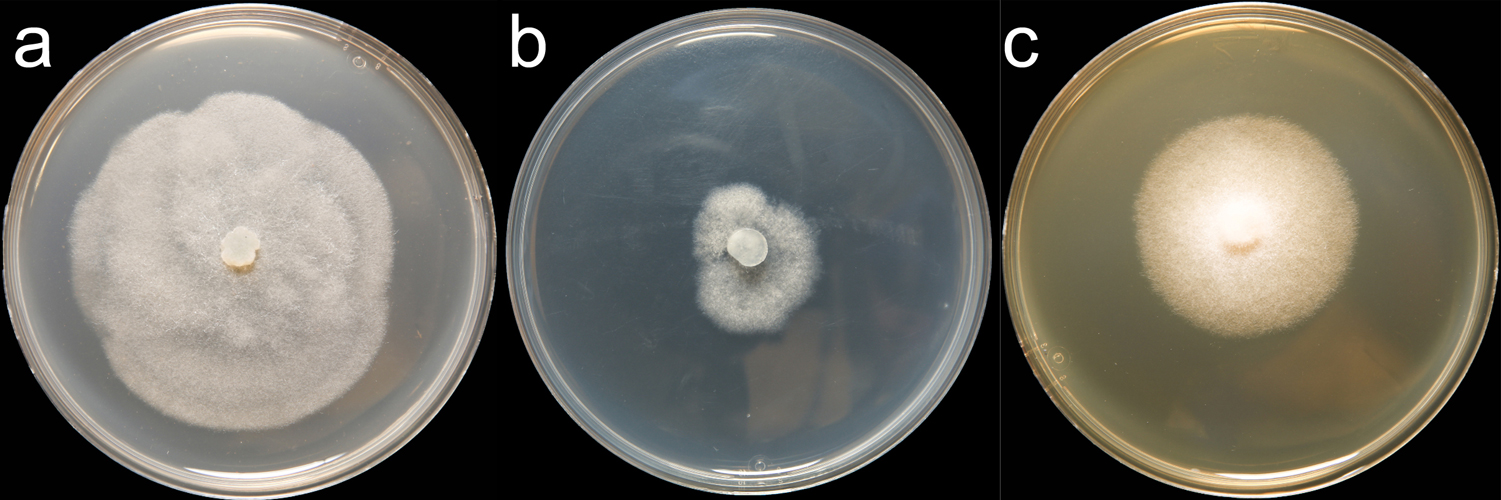
Phytophthora hedraiandra (CPHST BL 4) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
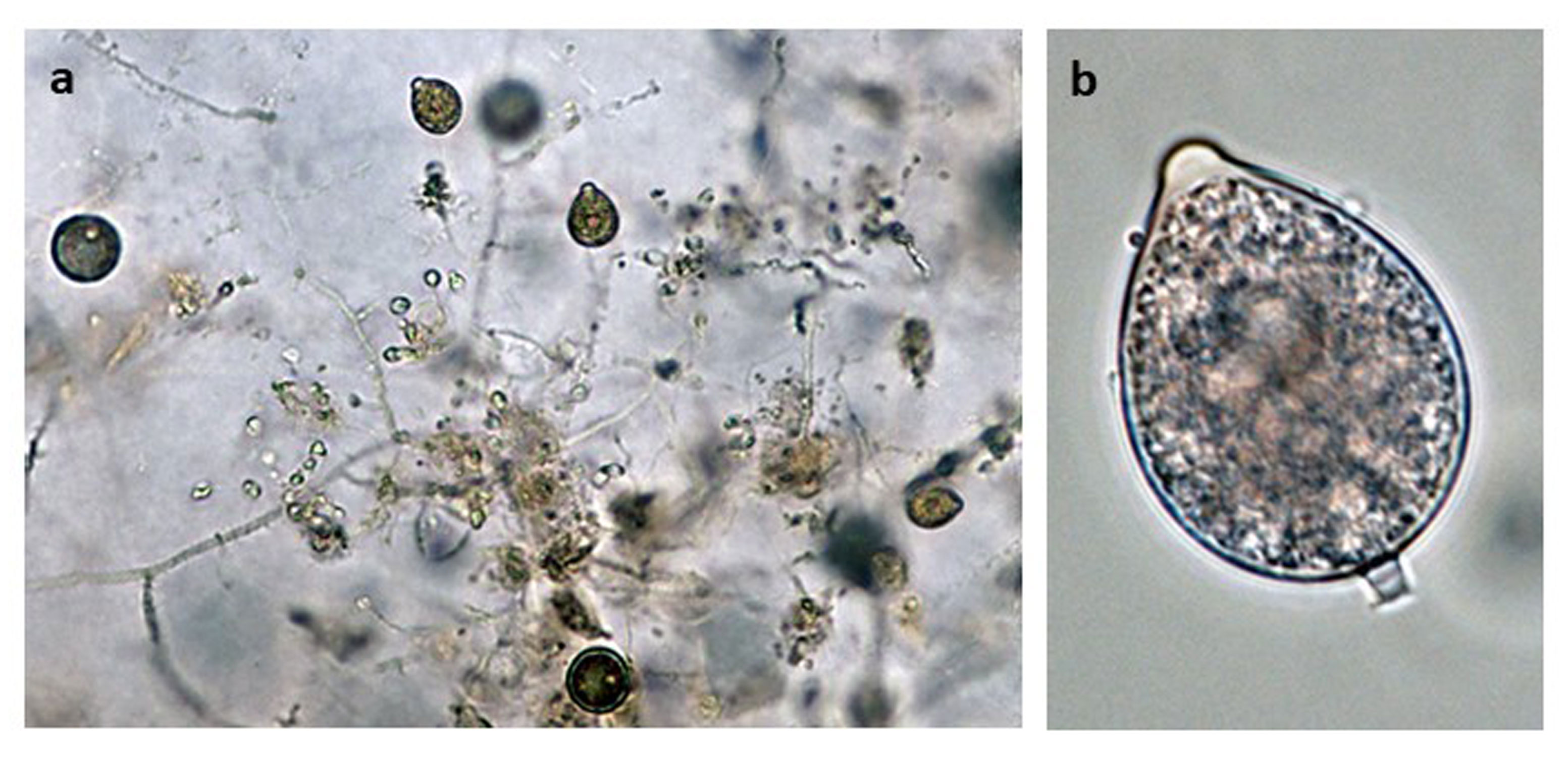
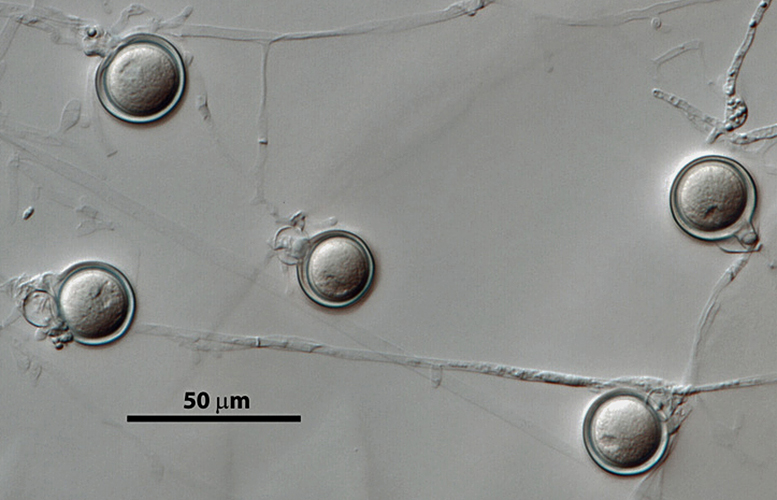
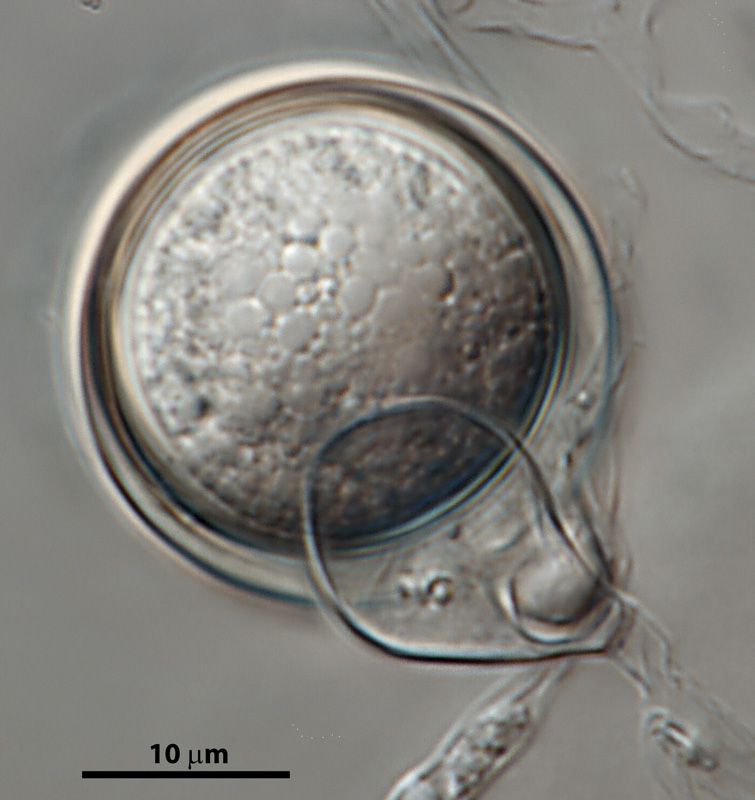
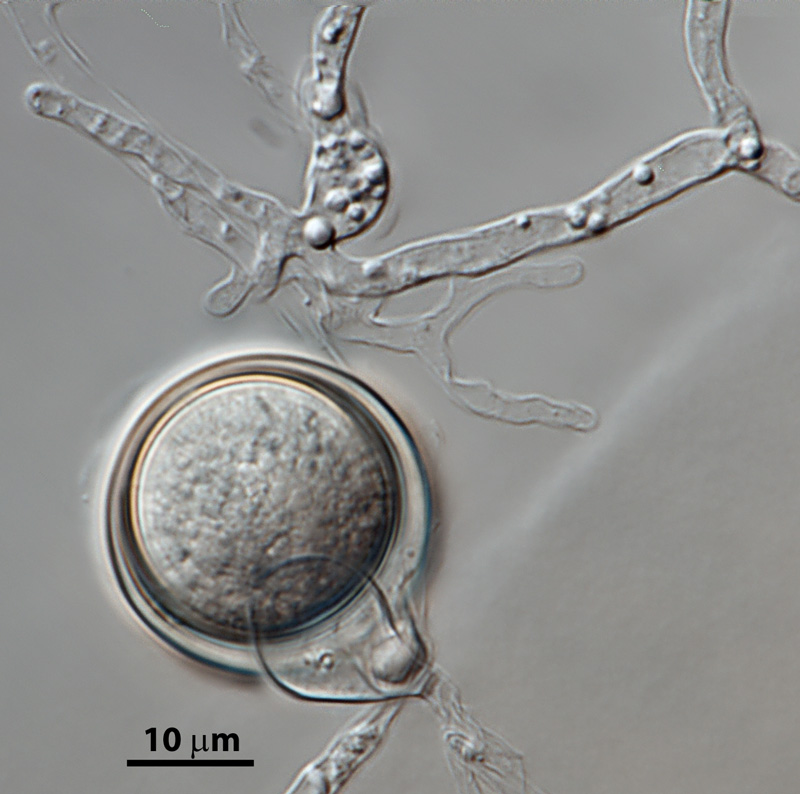
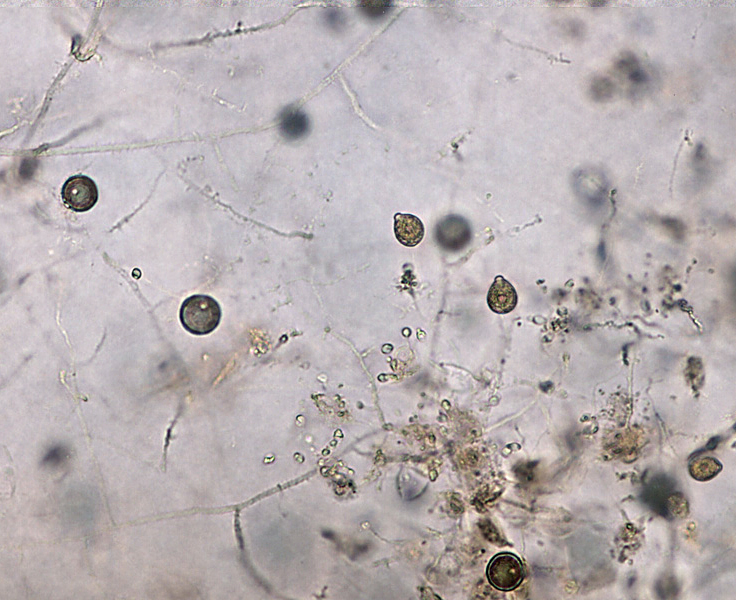
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) asexual phase of the ex-type: (a) sporangia and oospores, (b) sporangium papillate with caducous short pedicel; photos by Gloria Abad USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
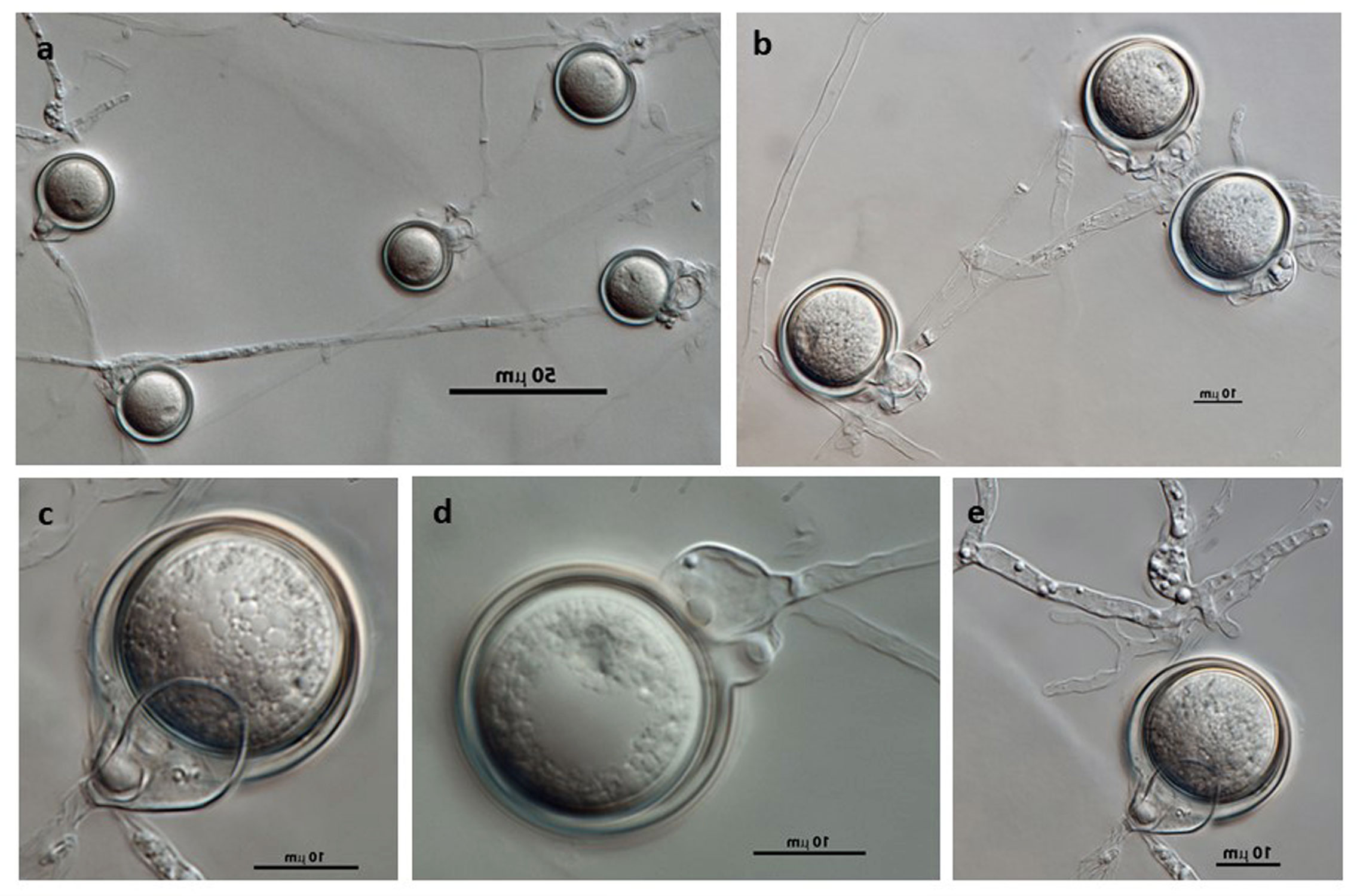
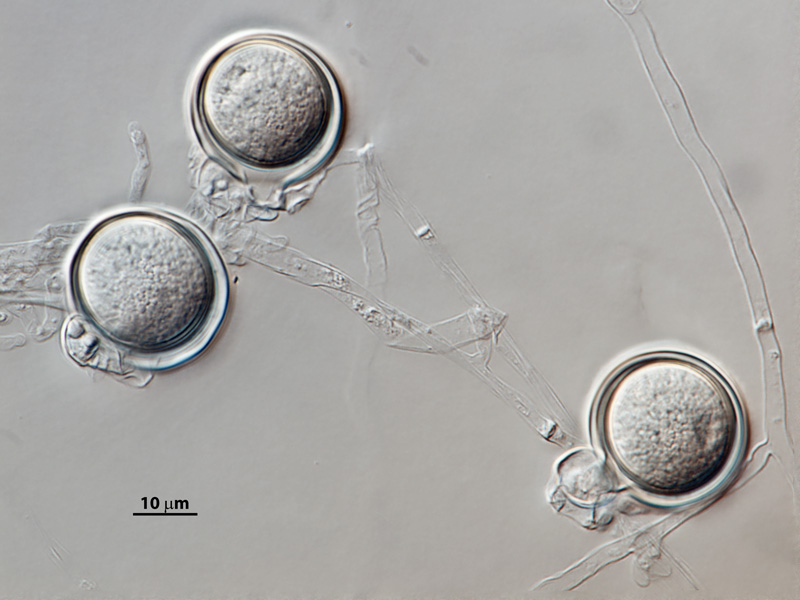
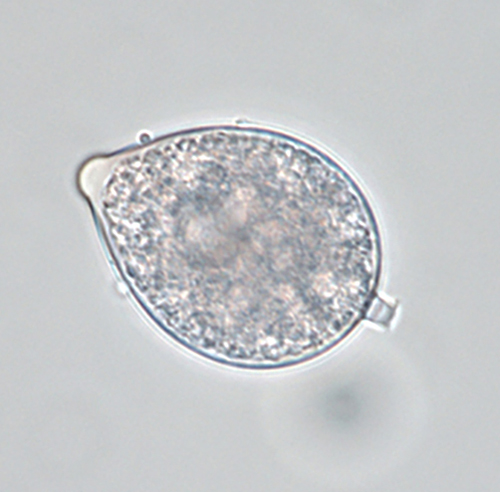
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: (a–e) smooth oogonia with paragynous antheridia and aplerotic, some plerotic (d) oospores; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: smooth oogonia with paragynous antheridia and aplerotic, some plerotic oospores; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: smooth oogonia with paragynous antheridia and aplerotic, some plerotic oospores; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
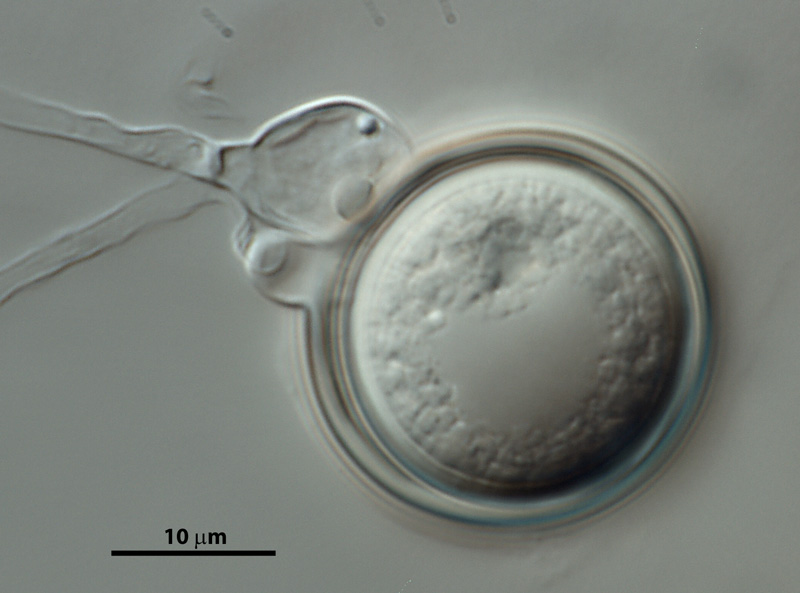
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: smooth oogonium with paragynous antheridium and plerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: smooth oogonium with paragynous antheridium and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) sexual phase of the ex-type: smooth oogonium with paragynous antheridium and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) asexual phase of the ex-type: sporangia and oospores; photo by Gloria Abad USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora hedriandra (CPHST BL 4) asexual phase of the ex-type: sporangium papillate with caducous short pedicel; photos by Gloria Abad USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora hedraiandra De Cock & Man in 't Veld (2004)
De Cock AWAM, Lévesque A, 2004. New species of Pythium and Phytophthora. Studies in Mycology 50: 481–488.
Corresponding author: Arthur W.A.M. de Cock, decock@cbs.knaw.nl
Nomenclature
from De Cock and Lévesque (2004)
Mycobank
Etymology
refers to the mainly sessile and short-stalked antheridia
Typification
Type: THE NETHERLANDS, isolated from leaves of Viburnus sp. CBS H-12856, deposited in herb. CBS
Ex-type: CBS 111725
Sequences for ex-type in original manuscript: CBS 111725 = ITS AY707987 , Cox1 AY769115
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 111725, NRRL 66991, WPC P19523, S&T BL 4 (Abad), 62A5 (Hong), PD 20017520, TJ0069 (Jung)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora hedraiandra isolate CPHST BL 4 (= P19523 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG865504, COI MH136898
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora hedraiandra CPHST BL 4
- NCBI: Phytophthora hedraiandra CBS 111725
- Q-bank: Phytophthora hedraiandra CBS 111725
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora hedraiandra (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
1a
Morphological identification
adapted from De Cock and Lévesque (2004)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures:
Colonies on V8-A with light chrysanthemum pattern, on PDA and MEA with non-distinctive pattern. Minimum temperature for growth 6°C, optimum 22–24°C, and maximum 30°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Sporangia produced on solid media and water cultures, and chlamydosporeschlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
mostly observed in old CMA cultures.
Asexual phase
Sporangia papillate; caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with a very short pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
(2–5 μm); globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
to broadly ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
or oval, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
(26–47 L x 21–37 W μm); occasionally single, terminal, or laterally sessile and with lateral displaced attachment; grown mostly on simple sympodial sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings absent. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
and subglobose, positioned terminally or intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
.
Sexual phase
Homothallichomothallic:
pertaining to sexual reproduction that can take place within a single thallus (i.e. self-fertile, non-outcrossing) (cf. heterothallic).
. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled, globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
(24–36 μm diam), sometimes with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
, stalk often bent or coiled; antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
mostly paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
, occasionally amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
, diclinousdiclinous:
the hypha bearing the antheridium originated from a different hypha than that of the oogonium (cf. monoclinous)
, rarely monoclinousmonoclinous:
the hypha bearing the antheridium originated from the same hypha as the oogonium (cf. diclinous)
, spherical, irregular, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
or ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, club-shaped (8–20 L x 7–14 W μm), mostly laterally sessile, occasionally terminal, or unilaterally intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
, attached near the oogonial stalk, one per oogoniumoogonium:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
, but in some occasions 2 or more antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
are observed, some antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
with spine or digitate projections; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(20–30 μm diam), wall up to 2 μm thick.
Most typical characters
Phytophthora hedraiandra is characterized by the shape and position of the antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
including the diclinousdiclinous:
the hypha bearing the antheridium originated from a different hypha than that of the oogonium (cf. monoclinous)
origin.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora hedraiandra ex-type CPHST BL 4, duplicate of P19523 (World Phytophthora Collection), which is a duplicate of ex-type CBS 111725
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Europe (Hungary, Netherlands, UK), North America (USA: MN)
Substrate: leaves
Disease note: leaf spot, dieback, root rot, collar rot
Hosts: multiple hosts, foliage; Viburnum sp. (Adoxaceae), Rhododendron sp. (Ericaceae)
Retrieved January 30, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora hedraiandra
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora hedraiandra
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Google All Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Google Images Phytophthora hedraiandra
- Google Scholar Phytophthora hedraiandra
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.