Phytophthora heveae
|
Phytophthora spp. in Clade 5: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. heveae Ex-type CBS 296.29 = S&T BL 67. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in Clade 5: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. heveae Ex-type CBS 296.29 = S&T BL 67. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
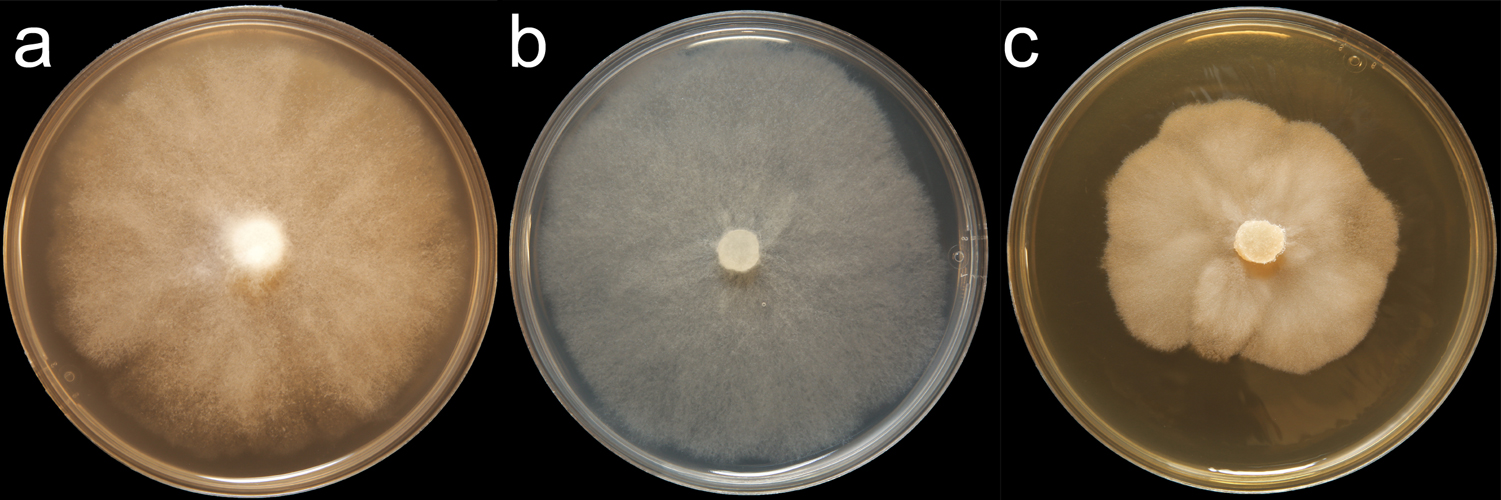
Phytophthora heveae (CPHST BL 67) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
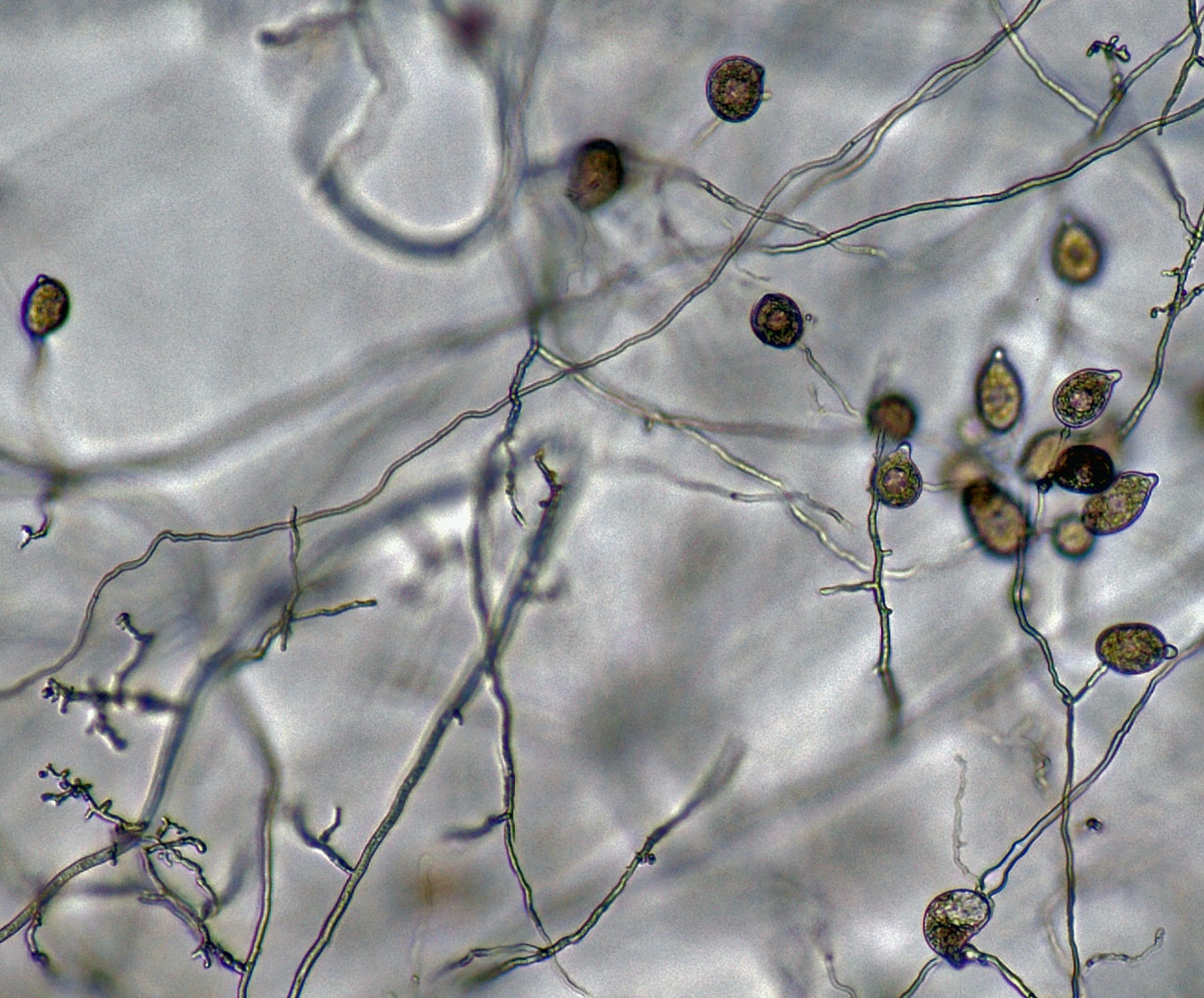
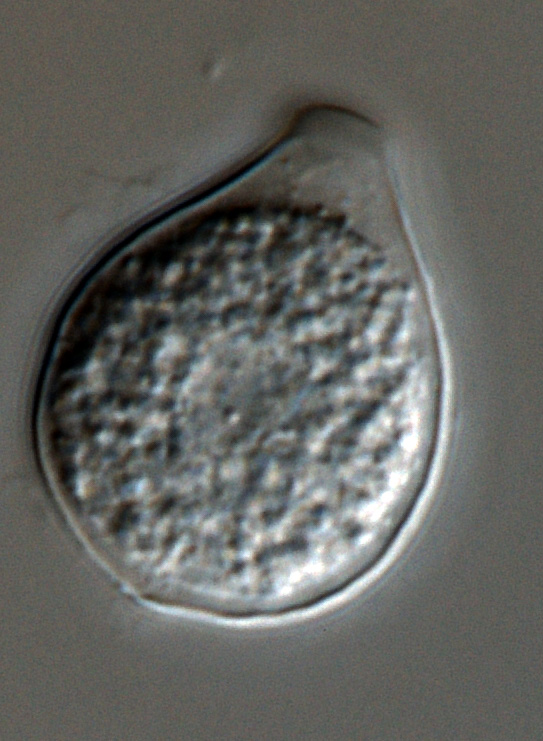
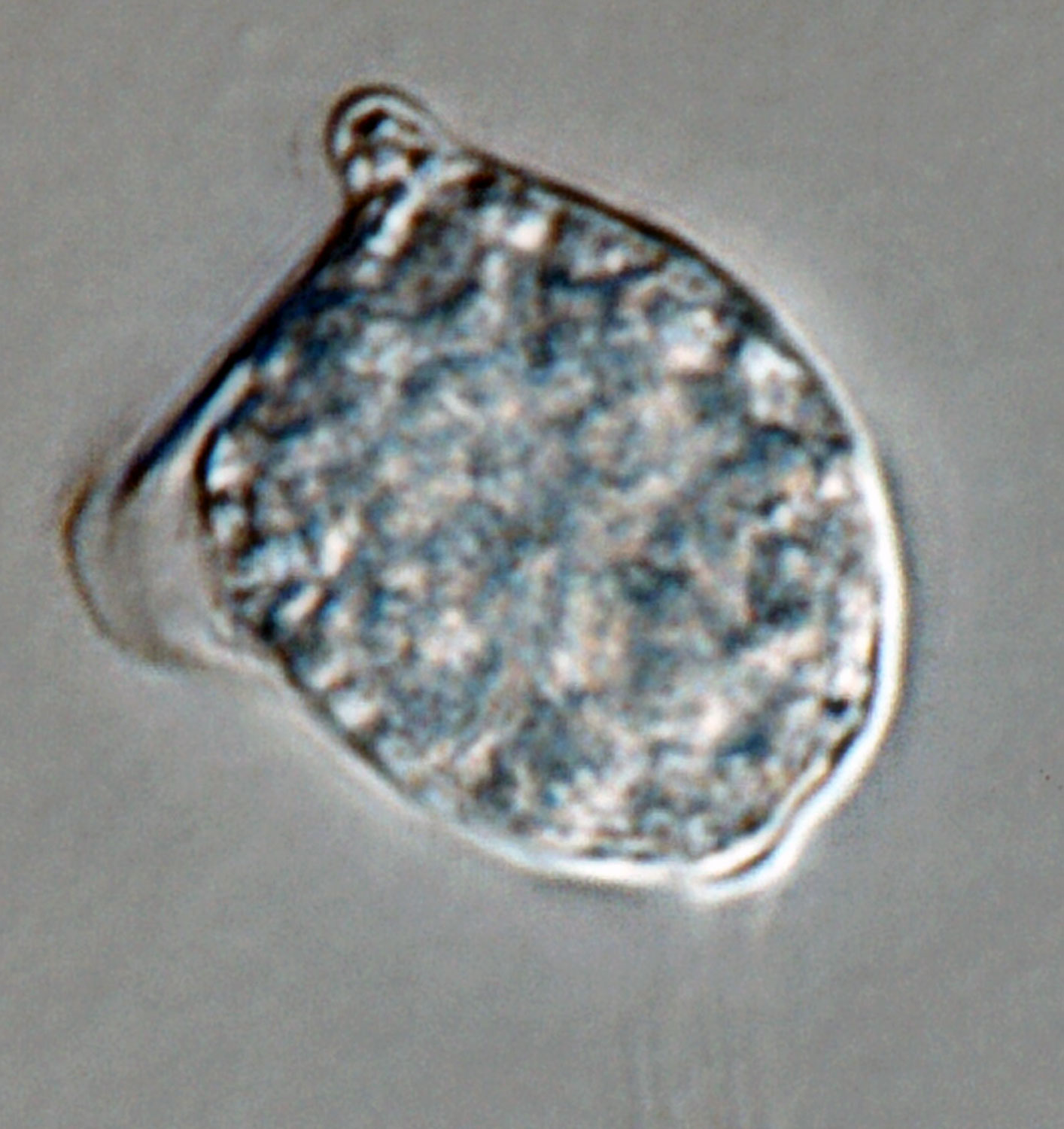
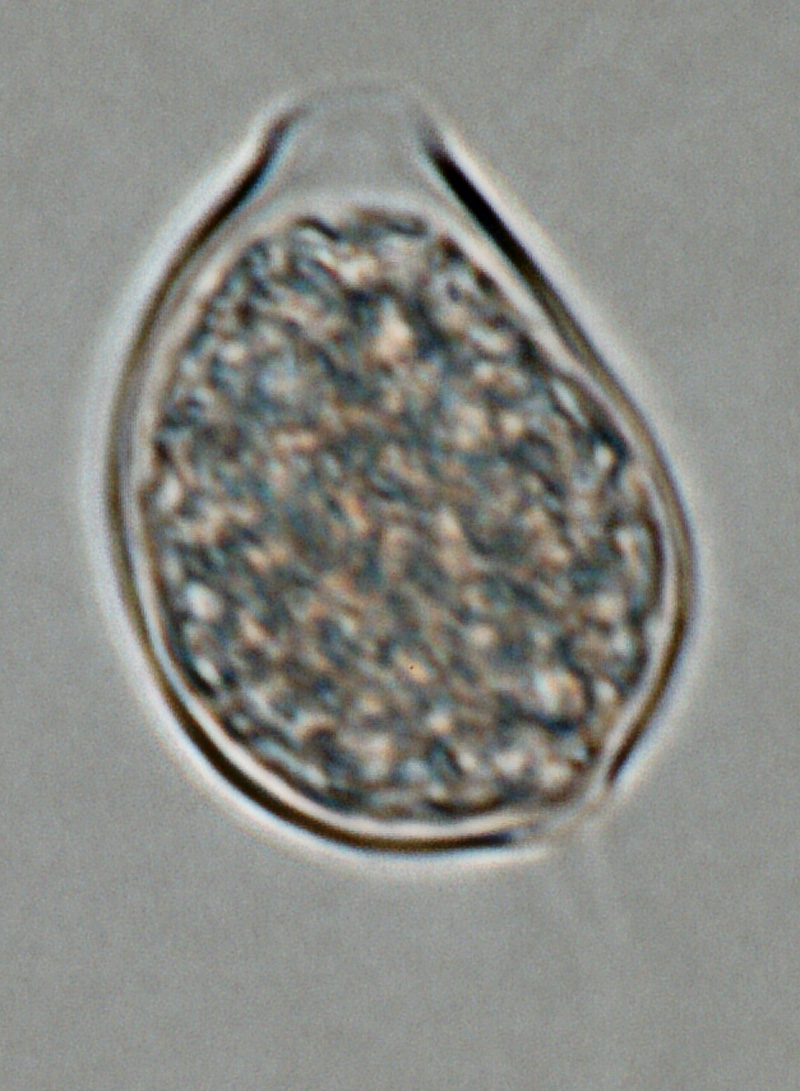
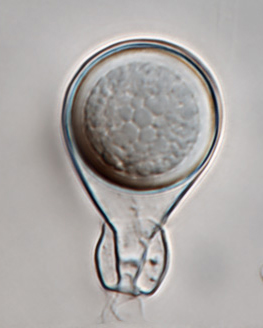
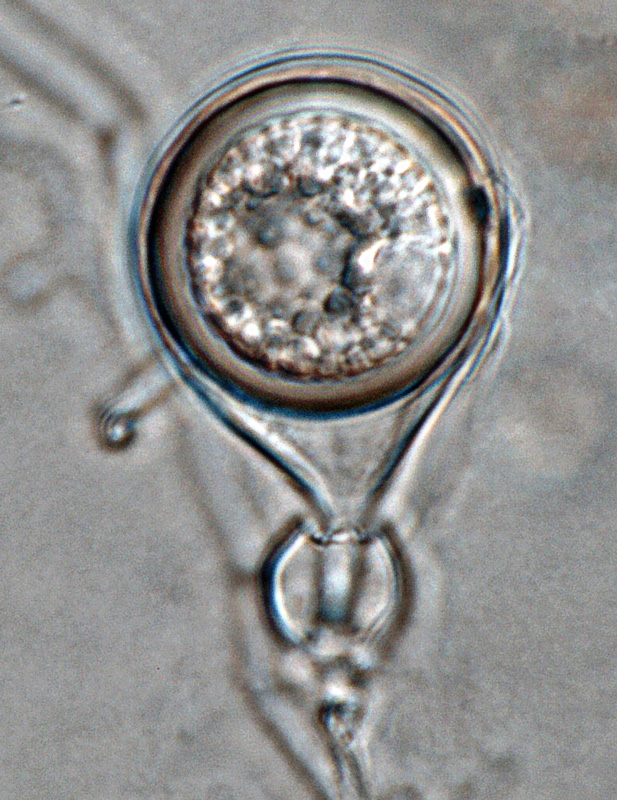
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: (a) sporangia in sporangiophores; (b–g) papillate sporangia, persistent and caducous - with pedicels (blue arrows); (f) bipapillate sporangium, (g) sporangium with external proliferation; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
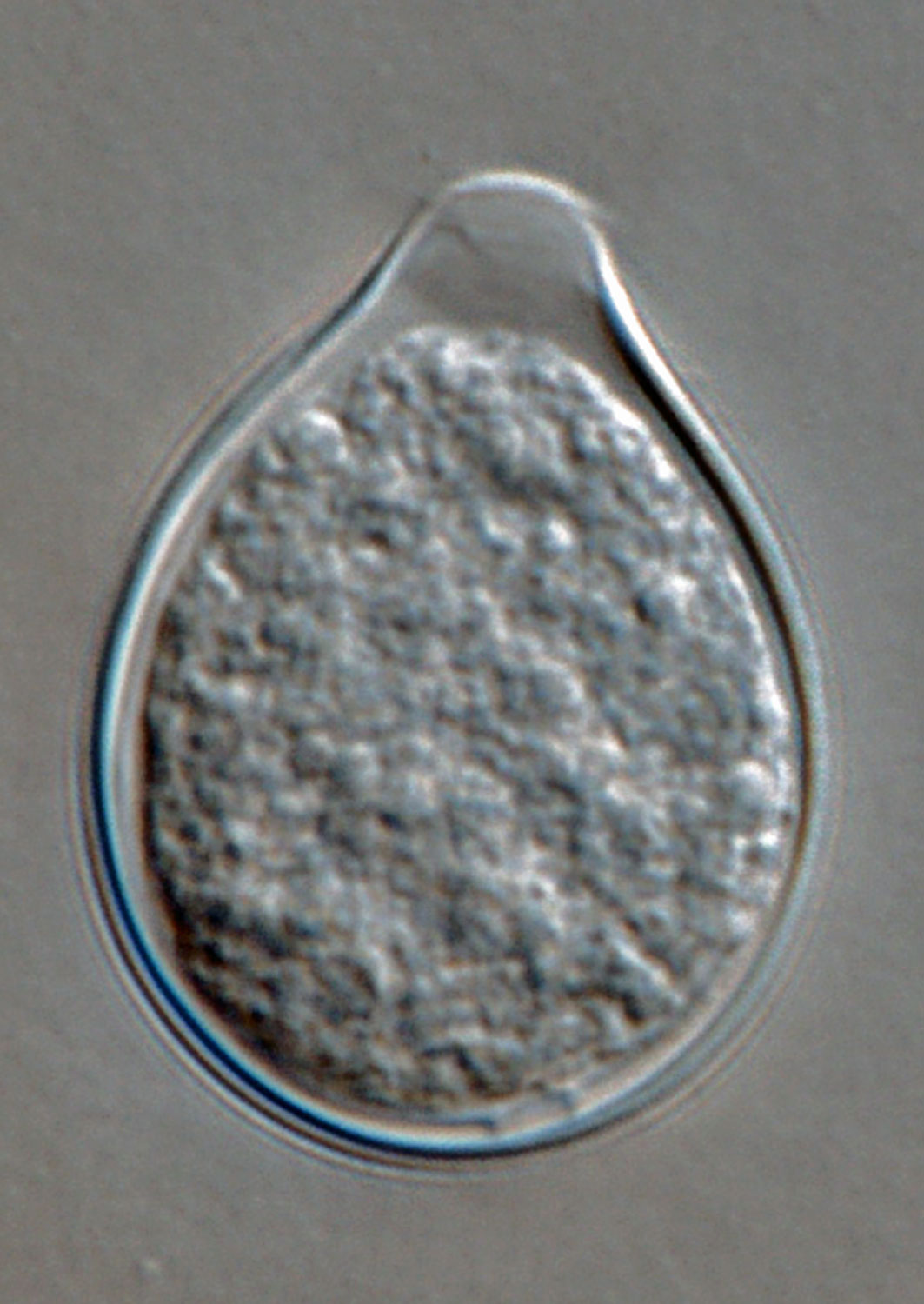
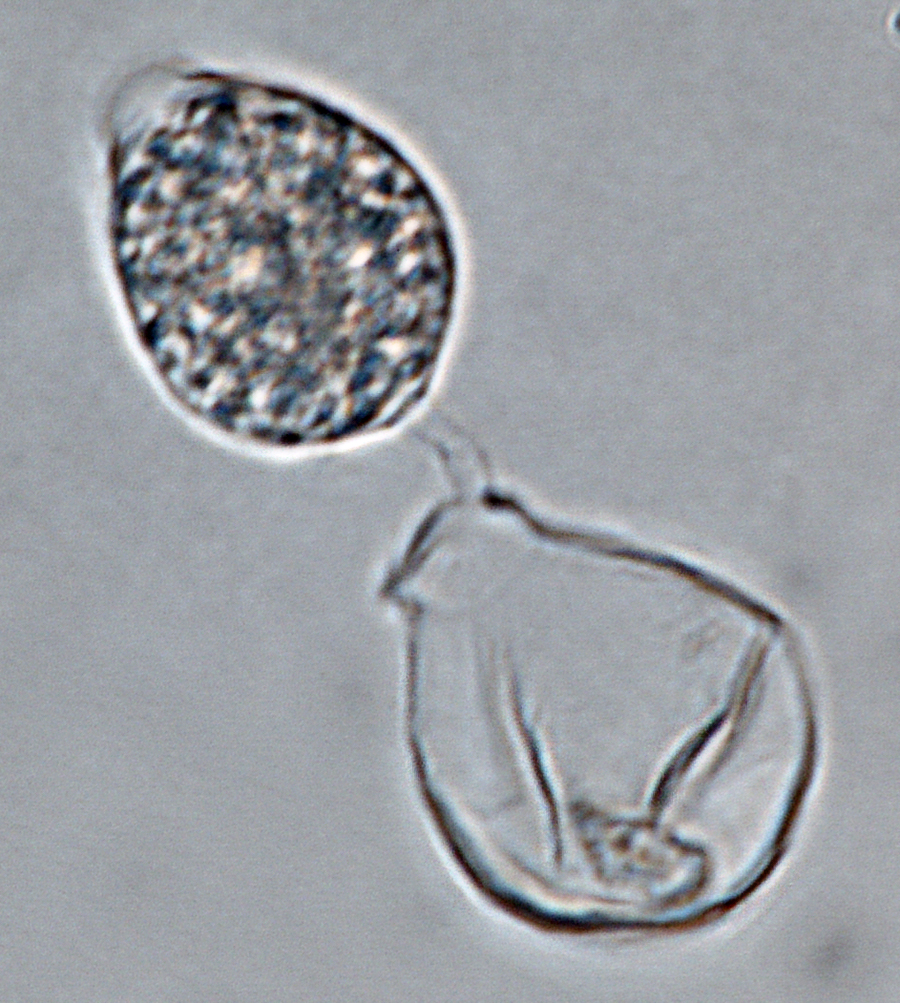
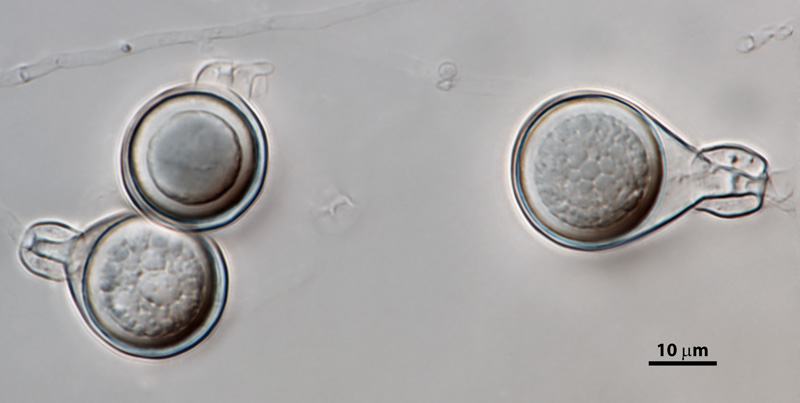
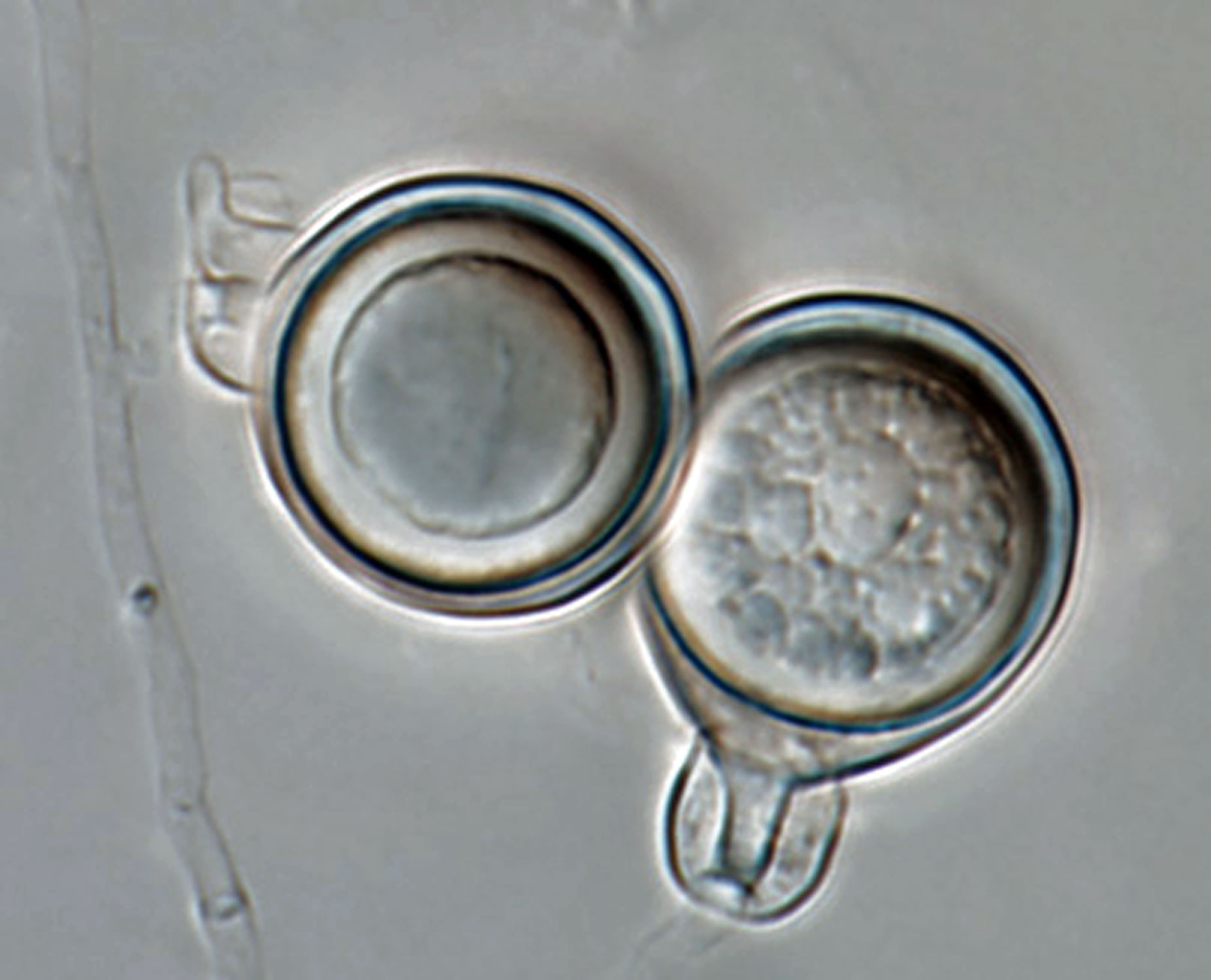
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: (a–d) smooth-walled oogonia frequently with tapered bases; amphigynous antheridia and aplerotic oospores; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: persistent papillate sporangia and sporangiophores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
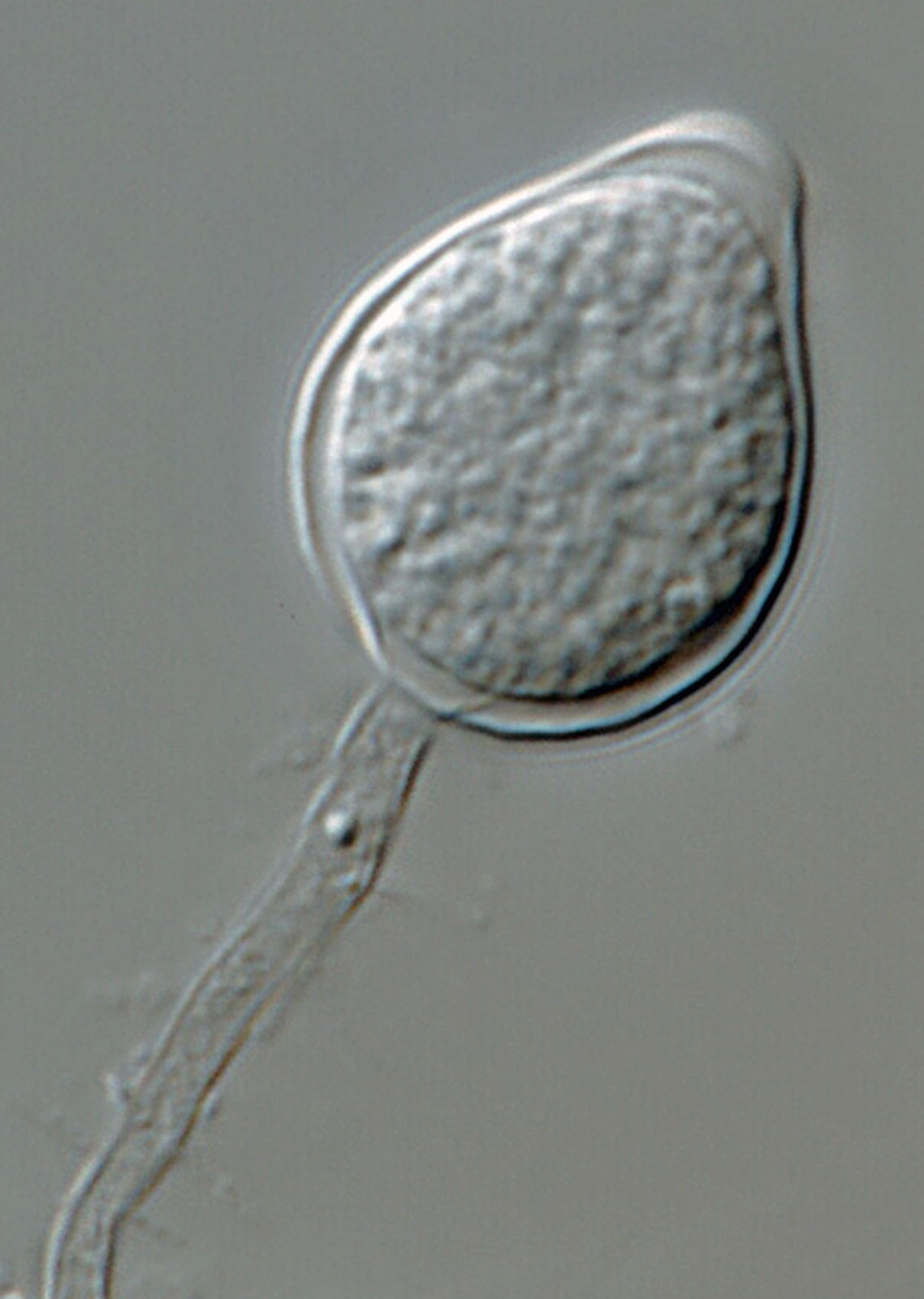
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: papillate sporangium with persistent pedicel; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: papillate sporangium; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: papillate sporangium; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: bipapillate caducous sporangium with pedicel; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: papillate caducous sporangium with pedicel; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) asexual phase: sporangium with external proliferation; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with tapered base; amphigynous antheridium and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with tapered base; amphigynous antheridium and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
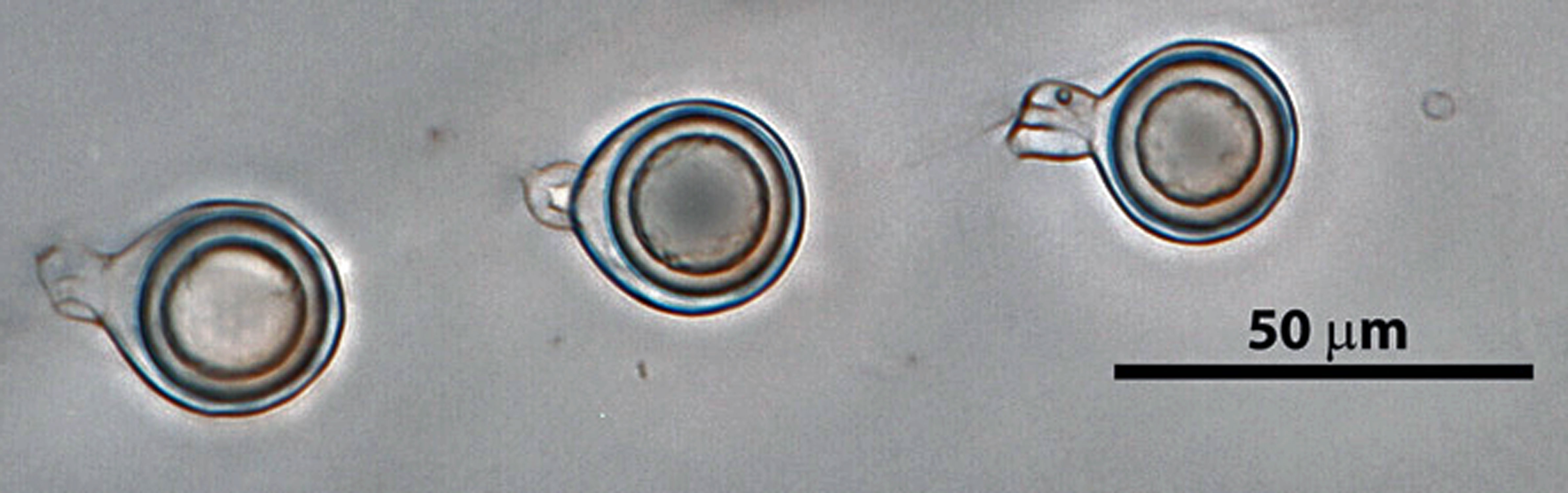
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonia with tapered bases; amphigynous antheridia and aplerotic oospores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonia with tapered bases; amphigynous antheridia and aplerotic oospores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora heveae (P10167, selected specimen) homothallic sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonia with tapered bases; amphigynous antheridia and aplerotic oospores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora heveae A.W. Thomps. (1929)
Thompson A. 1929. Phytophthora species in Malaya. Malayan Agric. J. 17: 53–100.
Nomenclature
Mycobank
Synonymy
≡ Phytophthora palmivora var. heveae (A.W. Thomps.) Orellana, Phytopathology 49: 213 (1959) [MB352396]
Typification
from Thompson (1929)
Type: MALAYSIA, from pod rot of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis), collected in Selangor in December 1927 by Thompson (No 5). Isotype: CBS H-7641
Ex-type: CBS 296.29
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 296.29, ATCC 58815, CABI IMI180616 (AVA), WPC P3428, S&T BL 67 (Abad), 22J1 (Hong), p28 (Gallegly)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora heveae isolate CPHST BL 67 (= P3428 WPC) ITS rDNA MG865505, COI MH136899
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora heveae CPHST BL 67
- NCBI: Phytophthora heveae P3428
- NCBI: Phytophthora heveae CBS 296.29
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora heveae CBS 296.29
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora heveae OOMYA111-07 = CBS 296.29 (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
5
Morphological identification
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Cultures on V8-A and PDA with no distinctive pattern and on MEA with light stellate pattern. Minimum temperature for growth 9°C, optimum 24°C, maximum 27°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Sporangia and oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
freely formed in culture media and water cultures.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
papillatepapillate:
pertaining to the production of a distinct papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. nonpapillate and semipapillate)
, persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
or caducouscaducous:
pertaining to sporangia that become dislodged readily (i.e. deciduous) and separate from the sporangiophore (cf. persistent)
with short to medium pedicelpedicel:
the hyphal base of a sporangium that remains attached after the sporangium separates, or is shed, from the sporangiophore; the pedicel may be short (< 5 µm), medium (5–20 µm), or long (> 20 µm)
up to 10 µm long, with variable shapes including ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
to obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, irregular (mainly asymetrical in shape) (27–66 L x 20–49 W µm), often with elongated necks and formed frequently laterally on the stalk; originated in simple sympodial sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings globose globose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
to subglobose, found in sporulating water cultures. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
spherical with broadly funnel shape (tapering base) (25–35 x 28–32 µm); antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
, spherical, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
or ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
(small 7–13 µm), and occasionally with one or more short spines; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
, wall 3 µm thick.
Most typical characters
Phytophthora heveae is characterized by the presence of oogoniaoogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
with broadly funnel shape (tapering base).
Specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora heveae, ex-type CPHST BL 67, duplicate of P3428 (World Phytophthora Collection)
P10167 World Phytophthora Collection (WPC) selected specimen
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Asia, Australia, North America (USA: NC, TN), South America (Brazil)
Substrate: roots, leaves, buds, seeds, pods, stems
Disease note: rot, leaf blight and stem canker. Disease symptoms on crop species include black stripe of rubber, bud rot and nut fall of coconut, and dieback of rhododendron.
Hosts: multiple hosts, fruits/roots; 12 genera in 11 families including Hevea brasiliensis (Euphorbiaceae) Rhododendron (Ericaceae) and Cocos nucifera (Arecaceae)
Retrieved January 31, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
Weir, B.S., Paredes E.P., Anand N., Uchida J.Y., Shaun R., Pnnycook S.E.B., and Beever R.E. 2015. A taxonomic revision of Phytophthora Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
5 including two new species, Phytophthora agathidicida and Phytophthora cocois. Phytotaxa 205: 21-38.
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora heveae
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora heveae
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora heveae
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora heveae
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora heveae
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora heveae
- Google All Phytophthora heveae
- Google Images Phytophthora heveae
- Google Scholar Phytophthora heveae
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.