Phytophthora nagaii
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7d: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. nagaii Ex-type CBS 133348 = S&T BL 121. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7d: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. nagaii Ex-type CBS 133348 = S&T BL 121. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
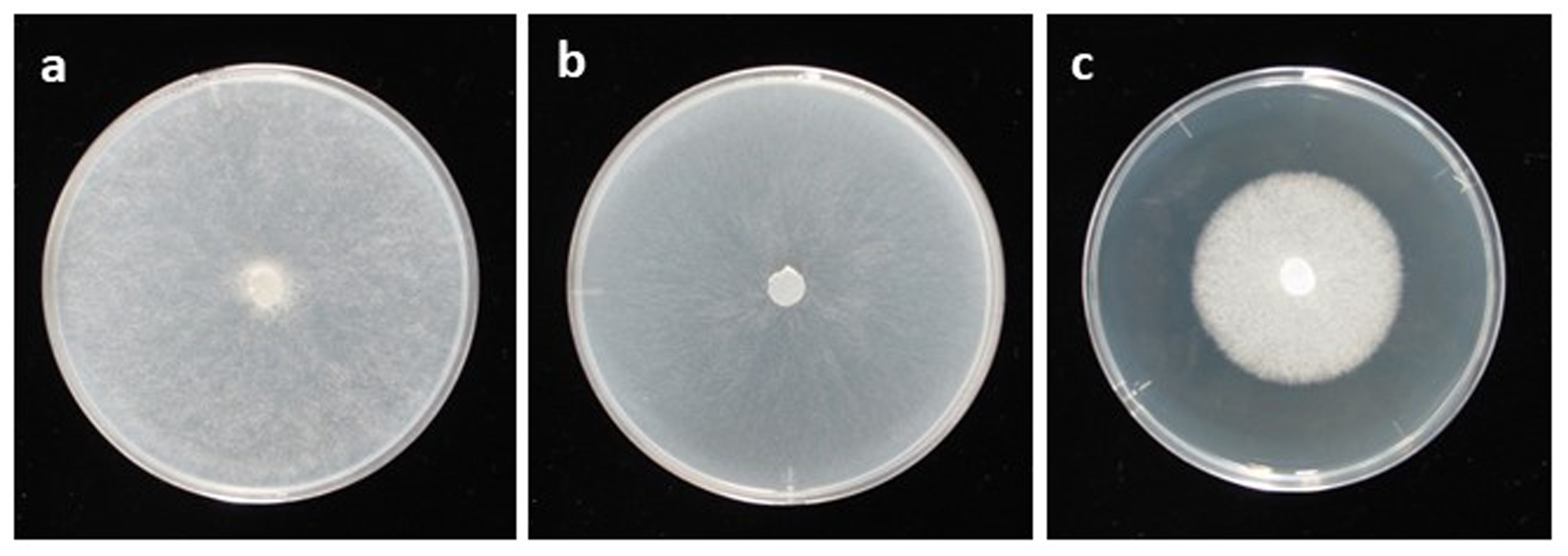
Phytophthora nagaii (ex-type CH04PHR12) colony of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8 agar, (b) corn meal agar and (c) potato dextrose agar; photos by Mohamed Rahman and Koji Kageyama, Gifu University, Japan |
|
Phytophthora nagaii (ex-type CH04PHR12) asexual phase: (a–e) nonpapillated persistent sporangia, (b–d) with internal and (e) external proliferation; (f, g) spherical and subspherical hyphal swellings; (h) spherical chlamydospore; photos by Mohamed Rahman and Koji Kageyama, Gifu University, Japan |
|
Phytophthora nagaii (ex-type CH04PHR12) sexual phase: (a–d) smooth-walled oogonia with aplerotic oospores; (b, c) with paragynous antheridia; (b) funnel-shaped oogonium; (c) paragynous antheridium with finger-like projection; (d) amphigynous antheridium; (e) distorted oogonium; photos by Mohamed Rahman and Koji Kageyama, Gifu University, Japan |
Name and publication
Phytophthora nagaii M.Z. Rahman, S. Uematsu, Toru Takeuchi, K. Shirai & Kageyama (2014)
Rahman MZ, Uematsu S, Takeuchi T, Shirai K, Ishiguro Y, Suga H, and Kageyama K. 2014. Two new species, Phytophthora nagaii sp. nov. and P. fragariaefolia sp. nov., causing serious diseases on rose and strawberry plants, respectively, in Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 80: 348–365.
Corresponding author: rahman@green.gifu-u.ac.jp
Nomenclature
from Ramhman et al. (2014)
Mycobank
Etymology
nagaii = Y. Nagai, the first to isolate this oomycete
Typification
Type: JAPAN, Chiba Prefecture, from leaf and stem blight of rose (Rosa sp.), 1968, collector S. Uematsu; isolate NBRC H-13102, holotypus (freeze-dried specimen)
Ex-type: NBRC 109131 = CBS 133248
Sequences for ex-type in original manuscript: CH04PHR12 = ITS rDNA AB688356, LSU AB688499, EF1-α AB736248, β-tubulin AB736249, and coxI AB688226
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 133348, NBRC 109131, WPC P19989, S&T BL 121 (Abad), 61H5 (Hong)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora nagaii isolate CPHST BL 121 (= P19989 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG865547, COI MH136940
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora nagaii CPHST BL 121
- NCBI: Phytophthora nagaii CH04PHR12
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora nagaii
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora nagaii (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
7d
Morphological identification
adapted from Rahman et al. (2014)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology on V-8 agar, potato dextrose agar, and malt extract agar with no distinct pattern. Minimum temperature for growth 5°C, optimum 28°C, and maximum 33°C.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
; persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
; ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
often with tapered bases (27–79 μm x 24–55 μm); proliferating internally by extended, or nested, or external proliferationexternal proliferation:
formation of a sporangium after a sporangiophore has emerged from beneath and external to an empty sporangium that has previously emitted its zoospores (cf. internal proliferation)
; produced in single or in simple sympodial sporangiophores. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
spherical (30–40 μm diam.), intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
. Hyphal swellings spherical or sub-spherical (21–28 μm diam.).
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled (32–53 μm diam.), sometimes with tapered bases and sometimes with elongated, curved oogonial stalks; antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
predominantly paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
and sometimes amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
, generally one and occasionally two antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
attached to the oogoniumoogonium:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(29–48 μm diam.).
Most typical characters
Phytophthora nagaii is characterized by the presence of intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
chlamydosporeschlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
, and spherical or sub-spherical hyphal swellings.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora nagaii ex-type CPHST BL 121, duplicate of P19989 (World Phytophthora Collection), which is a duplicate of ex-type CBS 133248
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Asia (Japan)
Substrate: leaves, stems
Disease note: blight, wilting, yellowing, defoliation
Host: Rosa odorata, Rosa sp. (Rosaceae)
Retrieved January 31, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora nagaii
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora nagaii
- Forest Phytophthora of the world: Phytophthora nagaii
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora nagaii
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora nagaii
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora nagaii
- Google All Phytophthora nagaii
- Google Images Phytophthora nagaii
- Google Scholar Phytophthora nagaii
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.