Phytophthora pistaciae
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7b: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. pistaciae Ex-type CBS 137185 = S&T BL 99. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7b: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. pistaciae Ex-type CBS 137185 = S&T BL 99. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
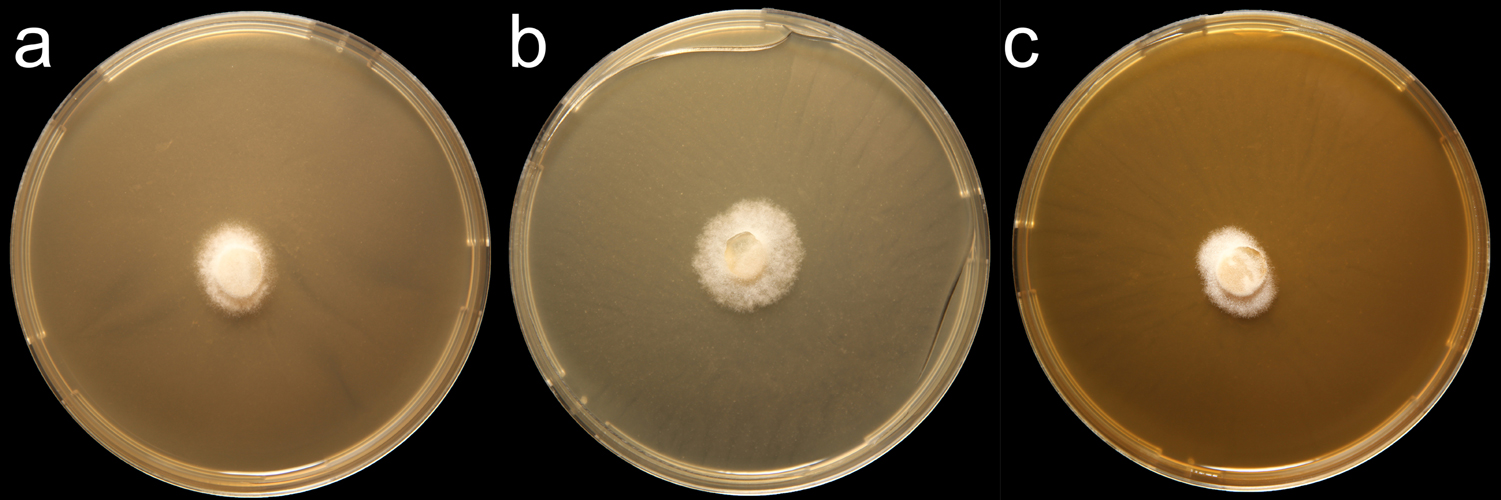
Phytophthora pistaciae (CPHST BL 99) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
Name and publication
Phytophthora pistaciae Mirab. (2001)
Mirabolfathy M, Cooke DEL, Duncan JM, Williams NA, Ershad D, and Alizadeh A. 2001. Phytophthora pistaciae sp. nov. and P. melonis: the principal causes of pistachio gummosis in Iran. Mycol. Res. 105: 1166–1175.
Corresponding author: j.duncan@scri.sari.ac.uk
Nomenclature
from Mirabolfathy et al. (2001)
Mycobank
Etymology
named after its only known host Pistacia vera
Typification
Type: IRAN, Kerman Province, Ferdosieh, Nogh, Rafsanjan, isolated from Pistachia vera, 1986, collector unknown, PIS16 (IMI 386658 holotypus)
Ex-type: P19883 (= PIS16 = SCRP 533)
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 137185, ATCC MYA-4082, CABI IMI386658 (PA), WPC P19883, PIS16, S&T BL 99 (Abad), SCRP 533, 33D6 (Hong), p216 (Gallegly)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora pistaciae isolate ATCC MYA-4082 ITS rDNA FJ746648
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora pistaciae MYA-4082
- NCBI: Phytophthora pistaciae 33D6
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora pistaciae
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora pistaciae (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
7b
Morphological identification
adapted from Mirabolfathy et al (2001)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology on PDA, V8A, MEA with no distinct pattern. Minimum growth temperature 9°C, optimum 27°C, and maximum 33°C.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
; persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
; ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
, pyriformpyriform:
pear-shaped, with the narrowest part at the base (cf. obpyriform)
(41–75 L x 18–34 W µm), mostly with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
; showing internal proliferationinternal proliferation:
internal proliferation occurs when the sporangiophore continues to grow through an empty sporangium
(nested) and originated in unbranched sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
or subglobose with radiating hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled (25–44 µm diam), antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
predominantly paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
, spherical, ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
; showing knotted hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
or digital projections; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(21–33 µm diam).
Most typical characters
Phytophthora pistaciae is characterized by the presence of homothallichomothallic:
pertaining to sexual reproduction that can take place within a single thallus (i.e. self-fertile, non-outcrossing) (cf. heterothallic).
oogonia with antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
radiating knotted hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
and the presence of globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
or subglobose hyphal swellings with radiating hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora pistaciae ex-type CPHST BL 99 = P19883 (World Phytophthora Collection)
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Asia (Iran, type)
Substrate: roots, crown, soil
Disease note: associated with gummosis
Host: Pistacia vera (pistachio, Anacardiaceae)
Retrieved February 01, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional info:
Substrate: trunk
Quarantine status
USA: This species was listed as a species of concern during the 2009 Phytophthora prioritization project conducted by USDA APHIS PPQ CPHST PERAL (Schwartzburg et al.).
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora pistaciae
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora pistaciae
- Forest Phytophthora of the world: Phytophthora pistaciae
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora pistaciae
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora pistaciae
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora pistaciae
- Google All Phytophthora pistaciae
- Google Images Phytophthora pistaciae
- Google Scholar Phytophthora pistaciae
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.