Phytophthora rosacearum
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 6a: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. rosacearum Ex-type CBS 124696 = S&T BL 53. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 6a: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. rosacearum Ex-type CBS 124696 = S&T BL 53. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
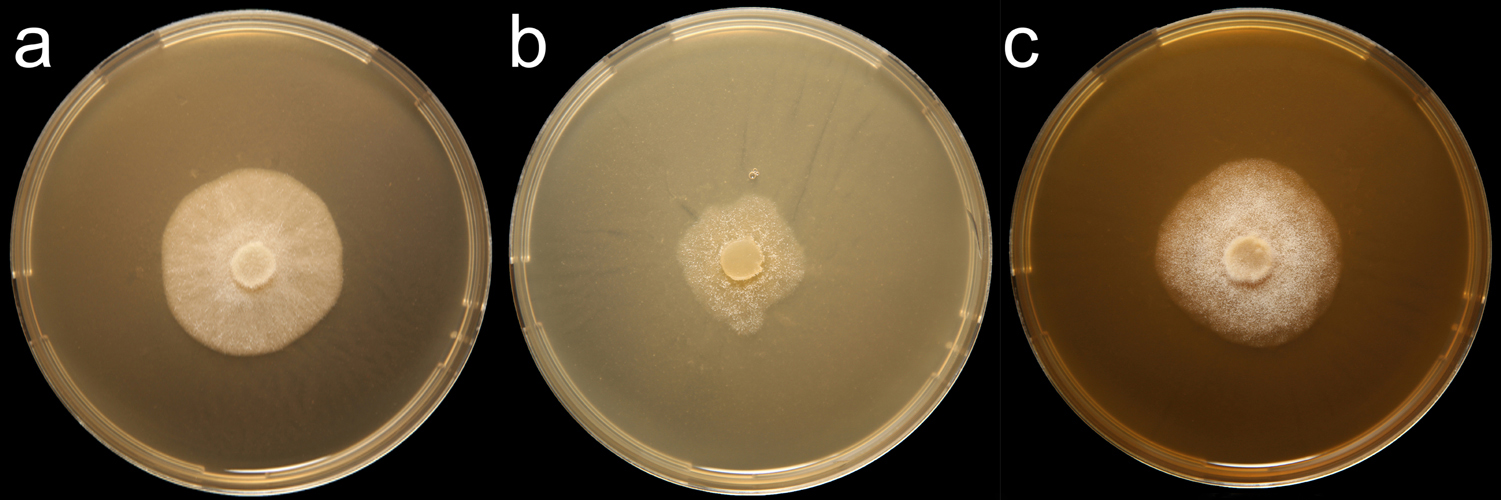
Phytophthora rosacearum (CPHST BL 53) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
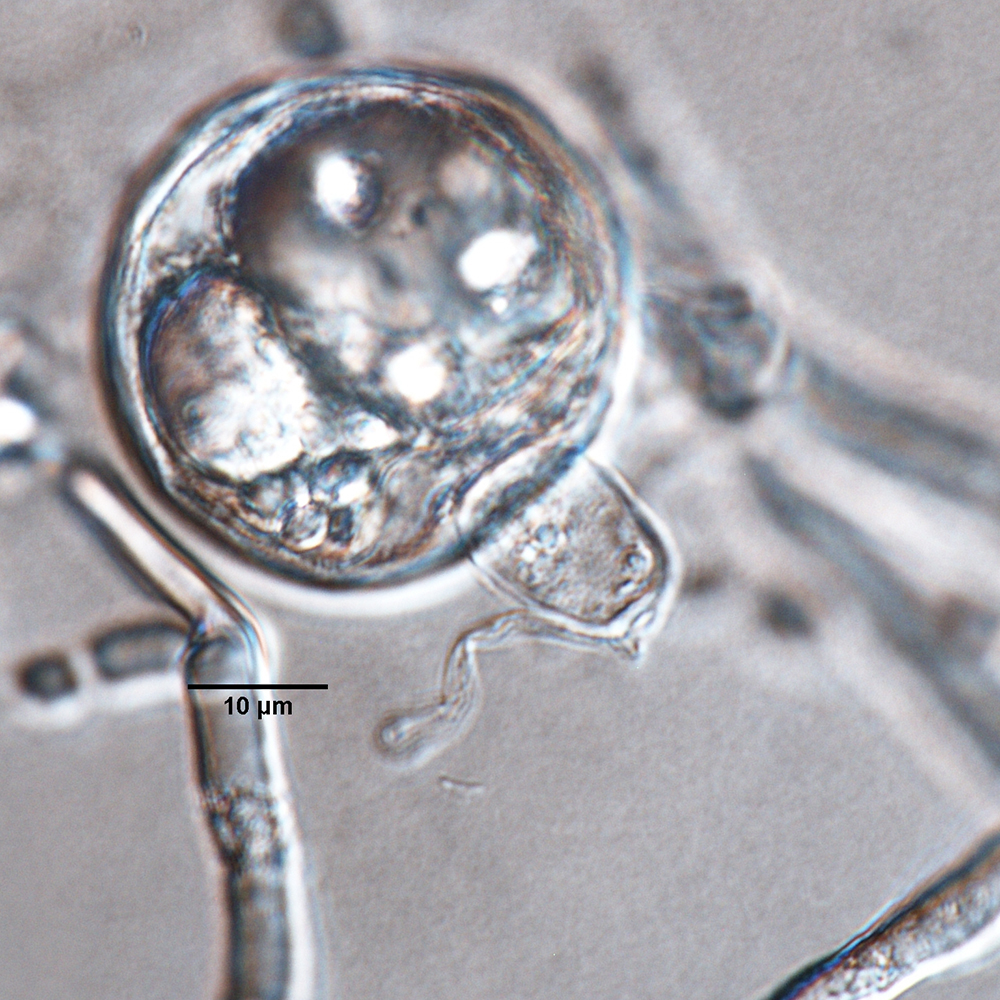
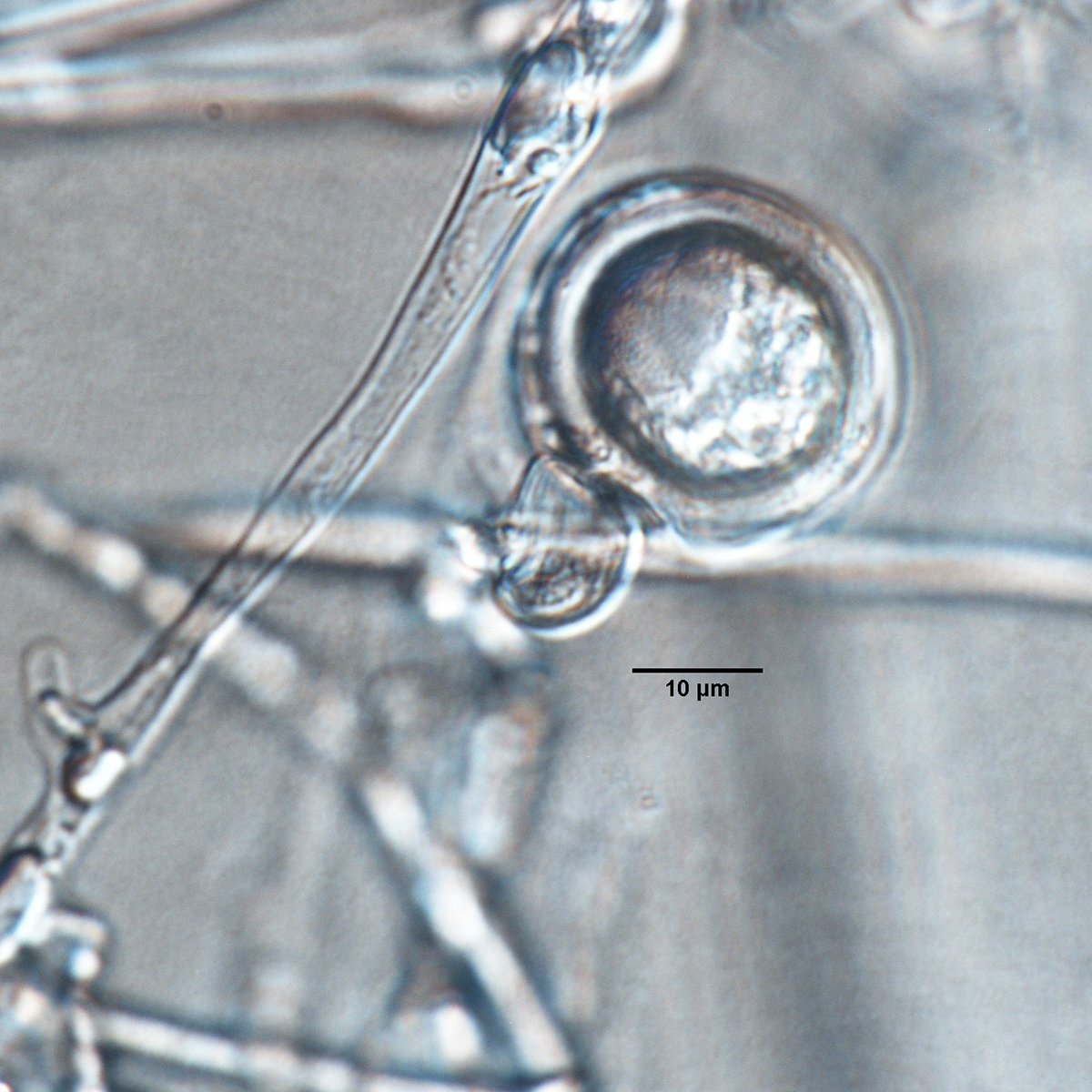
Phytophthora rosacearum (CPHST BL 53) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled, paragynous antheridium, and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
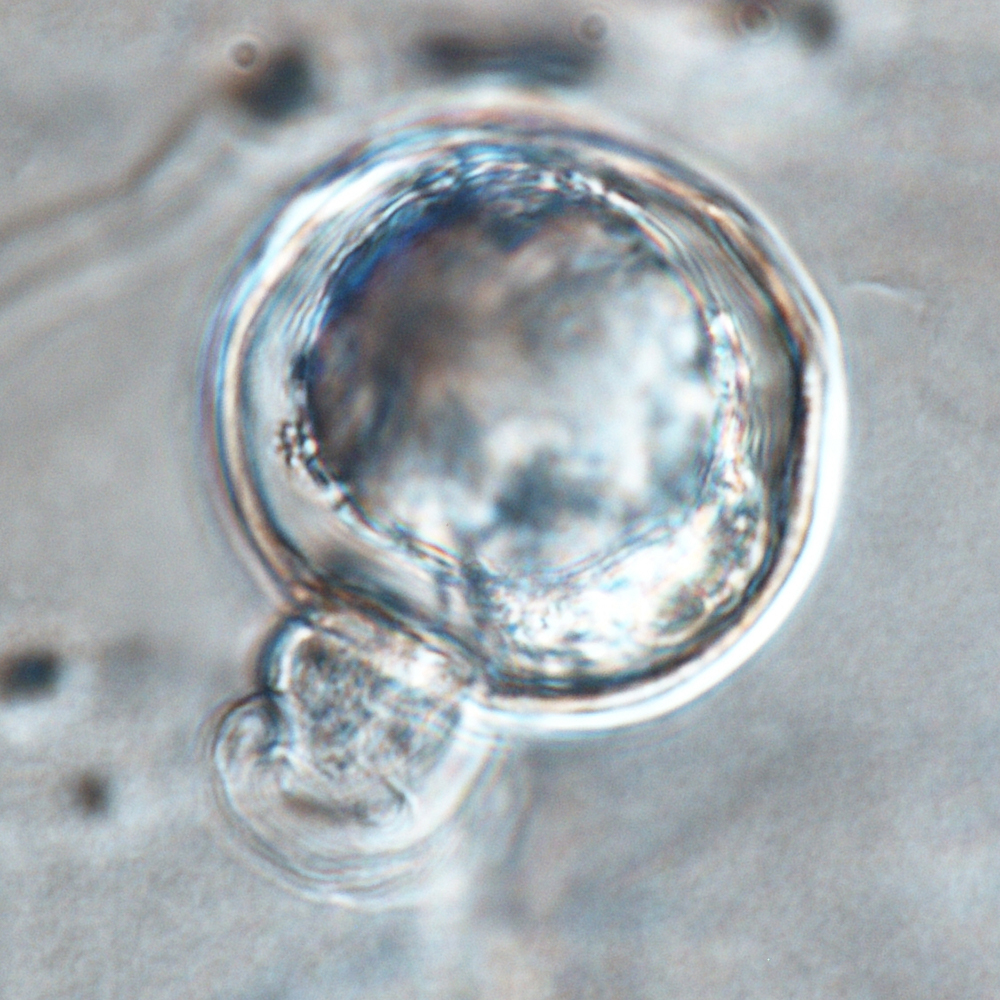
Phytophthora rosacearum (CPHST BL 53) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled, paragynous antheridium, and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora rosacearum (CPHST BL 53) sexual phase: oogonium smooth-walled, paragynous antheridium, and aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora rosacearum E.M. Hansen & W.F. Wilcox (2009)
Hansen EM, Wilcox WF, Reeser PW, and Sutton W. 2009. Phytophthora rosacearum and P. sansomeana, new species segregated from the Phytophthora megasperma "complex". Mycologia 101: 129–135.
Corresponding author: hansene@science.oregonstate.edu
Nomenclature
from Hansen et al. (2009)
Mycobank
Etymology
derived from Rosaceae, the family of fruit trees most frequently parasitized by this pathogen
Typification
Type: UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, from California, collected from apple by John Mircetich as isolate 20-3-9; holotype, OSU52, in Herbarium OSC (dried culture)
Ex-type: ATCC MYA-4456
Sequences for ex-type in original manuscript: isolate 52: ITSrDNA EU925376
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 124696, NRRL 66998, ATCC MYA-4456,WPC P3112, S&T BL 53 (Abad), 47J1 (Hong), Isolate 52 (Hansen), Mircetich 20-3-9, P462 Brazier
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora rosacearum isolate 52 ITS rDNA EU925376
Phytophthora rosacearum isolate CPHST BL 53 (= P3112) COI MH477758
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora rosacearum CPHST BL 53
- NCBI: Phytophthora rosacearum 52
- NCBI: Phytophthora rosacearum CBS 124696
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora rosacearum CBS 124696 ITSrDNA, β-tub, TEF, COI
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora rosacearum (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
6a
Morphological identification
adapted from Hansen et al. (2009)
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology on PDA, V8, and MEA with non-distinct pattern. Minimum growth temperature 3°C, optimum 27°C, and maximum 33°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Sporangia and hyphal swellings produced on plugs of culture media flooded in soil extract.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
; persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
; ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, obturbinate (46–79 L x 26–48 W µm), some constricted and some with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
; showing simple and extended internal proliferationinternal proliferation:
internal proliferation occurs when the sporangiophore continues to grow through an empty sporangium
; originated in unbranched sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
, subglobose, sometimes with radiating hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
, sometimes catenulatecatenulate:
having a chain-like form
. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallichomothallic:
pertaining to sexual reproduction that can take place within a single thallus (i.e. self-fertile, non-outcrossing) (cf. heterothallic).
. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled, globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
(19–40 µm diam); antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
, spherical, ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, club-shaped with abundant knotted hyphae; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
pleroticplerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
, apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
, and slightly apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(18–33 µm diam). Many aborted oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
and showing thick wall.
Most typical characters
Phytophthora rosacearum is characterized by the sporangiasporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
shape and proliferationproliferation:
formation of a sporangium within an empty sporangium that has previously emitted zoospores (internal or nested) or after the sporangiophore has emerged from the empty sporangium (external)
and the morphological characters of the antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
.
Additional specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora rosacearum ex-type CPHST BL 53, duplicate of P3112 World Phytophthora Collection)
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: North America (CA, OH, MD, NY)
Substrate: fruit
Disease note: pathogenic
Host: Malus domestica, Prunus spp. (Rosaceae)
Retrieved February 01, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional info:
Substrate: rhizosphere
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora rosacearum
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora rosacearum
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora rosacearum
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora rosacearum
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora rosacearum
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora rosacearum
- Google All Phytophthora rosacearum
- Google Images Phytophthora rosacearum
- Google Scholar Phytophthora rosacearum
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.