Phytophthora rubi
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7a: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. rubi Ex-type CBS 967.95 = S&T BL 54. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7a: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. rubi Ex-type CBS 967.95 = S&T BL 54. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
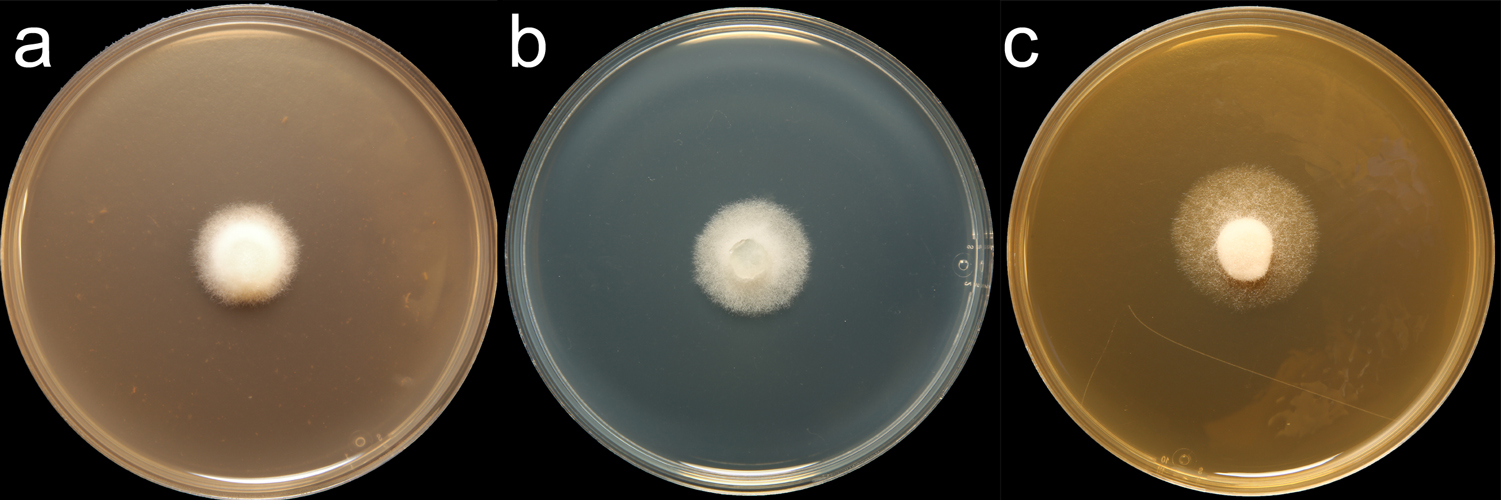
Phytophthora rubi (CPHST BL 4) colonies of the ex-type grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
Name and publication
Phytophthora rubi (W.F. Wilcox & J.M. Duncan) Man in 't Veld (2007)
Man in ’t Veld WA. 2007. Gene flow analysis demonstrates that Phytophthora fragariae var. rubi constitutes a distinct species, Phytophthora rubi comb. nov. Mycologia 99: 222–226.
Wilcox WF, Scott PH, Hamm PB, Kennedy DM, Duncan JM, Brasier CM, and Hansen EM. 1993. Identity of a Phytophthora species attacking raspberry in Europe and North America. Mycol. Res. 97 (7): 817–831 (pg. 830).
Nomenclature
Mycobank
Synonymy
≡ Phytophthora fragariae var. rubi W.F. Wilcox & J.M. Duncan, Mycological Research 97: 830 (1993) [MB360234]
Typification
from Wilcox et al. (1993)
Type: UNITED KINGDOM, Scotland collected from the base of a red raspberry cane Rubus idaeus in Perthshire in 1985, dried culture deposited in the herbarium at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, USA (CUP62528)
Ex-type: R49 = NY 588 = ATCC 90442 = IMI 355974
Note from manuscript: "A type specimen, consisting of a dried culture from material originally recovered from the base of a red raspberry cane in Perthshire, Scotland, has been deposited in the herbarium at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, USA (CUP no. 62528). Live material is maintained as a single zoosporezoospore:
motile spore that forms within the sporangium and exits through the exit pore and is capable of swimming for several hours; it has both a tinsel flagellum and a whip-like flagellum
derived culture in the collection of the Scottish Crop Research Institute (isolate number R49), the New York State Agricultural Experiment Station (isolate no. NY 588), and has been deposited with the American Type Culture Collection and the CAB International Mycological Institute."
Sequences for ex-type in Man in ’t Veld (2007): R49 COI DQ674736
Ex-type in other collections
(ET) CBS 967.95, ATCC 90442, CABI IMI355974 (PA), WPC P15597 P16899, S&T BL 54 (Abad), 46C7 (Hong), p389 (Gallegly), No R49, FVR 11, NY 588
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the ex-type (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora rubi isolate CPHST BL 54 (= P16899 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG865584, COI MH136976
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for ex-type in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora rubi CPHST BL 54
- NCBI: Phytophthora rubi P15597
- NCBI: Phytophthora rubi CBS 967.95
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora rubi CBS 967.95 ITSrDNA, β-tub, TEF, COI, Ypt1
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora rubi (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
7a
Morphological identification
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
morphology on V-8A, PDA, and MEA with no distinctive pattern. Minimum growth temperature 4°C, optimum 19–22°C, and maximum 25–28°C.
Conditions for growth and sporulation
Gametangia produced in the vascular tissue of raspberry roots and on some agar media, sometimes more commonly in the area around the inoculum plug.
Asexual phase
Sporangia nonpapillate, persistentpersistent:
pertaining to sporangia that remain attached to the sporangiophore and do not separate or detach easily (cf. caducous)
; ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, obpryriform, sometimes with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
(36–68 µm length x 26–44 µm width); showing internal nested and extended proliferationextended proliferation:
a type of internal proliferation in which the sporangiophore originates from inside of an empty sporangium, and continues to grow through and out of the old sporangium
; originated on simple sympodial or irregular branched sporangiophores. Hyphal swellings absent. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. OogoniaOogonia:
the female gametangium in which the oospore forms after fertilization by the antheridium
smooth-walled, globoseglobose:
having a rounded form resembling that of a sphere
(24–42 µm diam.) sometimes with a tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
, becoming golden brown with age; antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
predominantly amphigynousamphigynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium completely surrounds the stalk of the oogonium (cf. paragynous)
, short cylindrical, ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, or irregular (8–17µm), sometimes producing digitated projections; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(19–40 µm diam.).
Additonal specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora rubi ex-type CPHST BL 54 = P16899 (World Phytophthora Collection)
WPC P15597
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: cosmopolitan (Erwin & Ribeiro 1996)
Substrate: roots
Disease note: root rot; one of the most important diseases of red raspberries (Erwin & Ribeiro 1996)
Host: Rubus idaeus var. idaeus (Rosaceae)
Retrieved February 01, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora rubi
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora rubi
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora rubi
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora rubi
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora rubi
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora rubi
- Google All Phytophthora rubi
- Google Images Phytophthora rubi
- Google Scholar Phytophthora rubi
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.