Phytophthora sojae (in progress - Abad et al. 2023b)
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7b: portion of the seven-loci ML phylogeny featuring the type cultures of 212 described species (by T. Bourret). Notice the position of P. sojae selected specimen CBS 149406 = S&T BL 56G. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
Phytophthora spp. in subclade 7b: Morphological Tabular key (PDF) and Tabular key legends (PDF) in IDphy2 KEY SECTION. Notice the data of P. sojae selected specimen CBS 149406 = S&T BL 56G. Gloria Abad, USDA S&T.
|
|
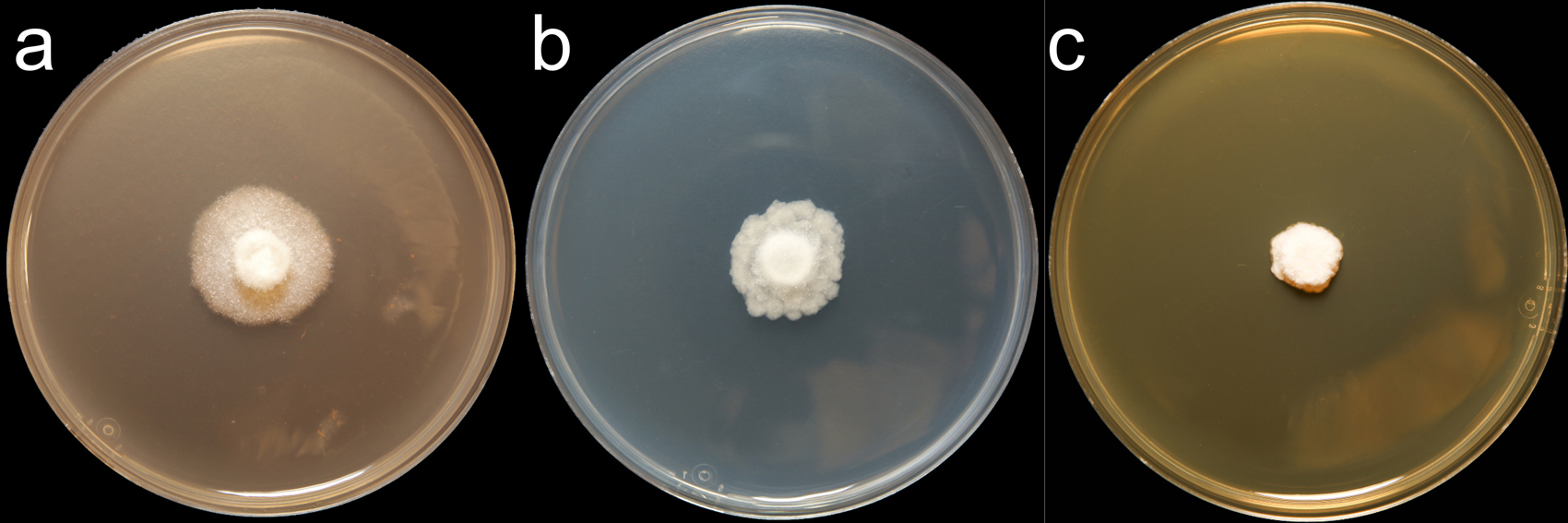
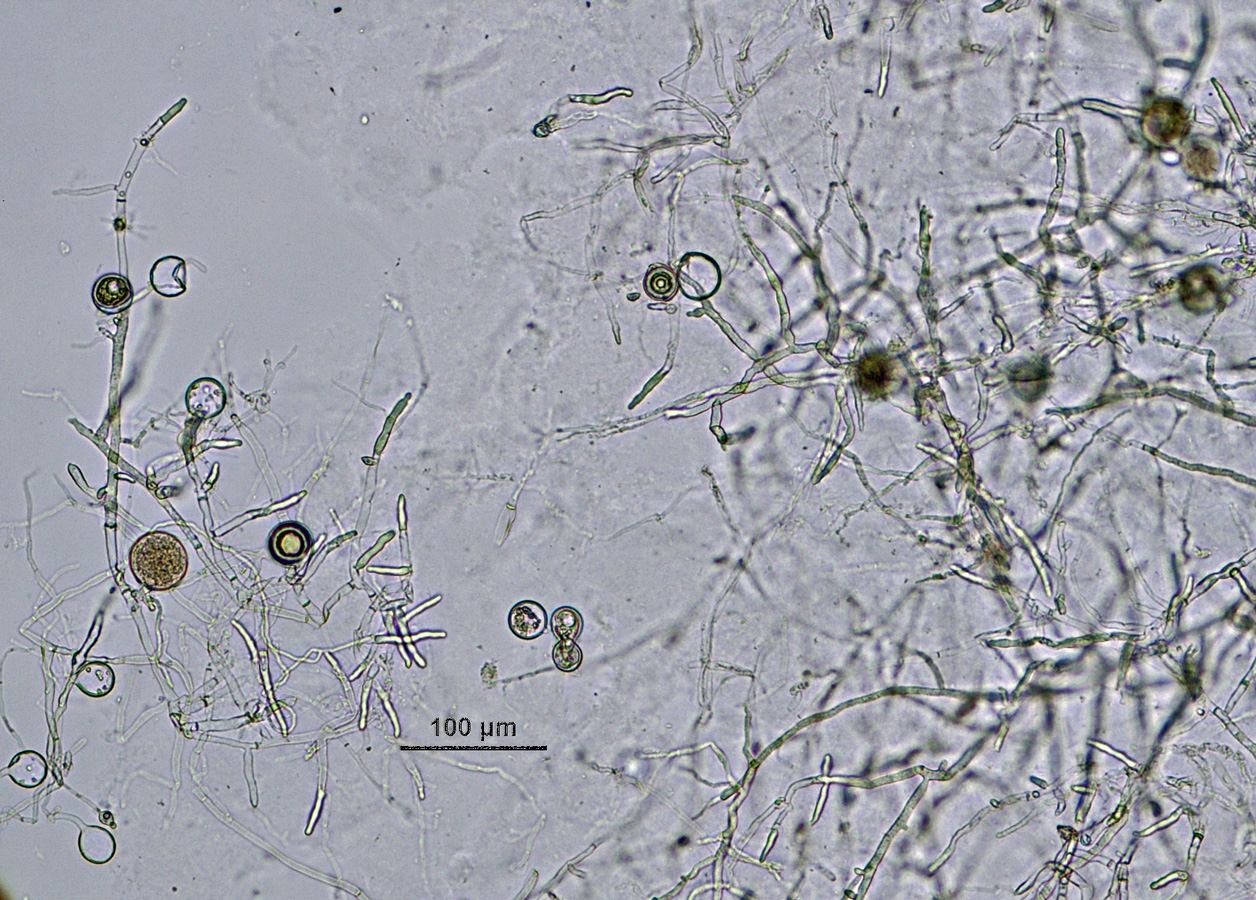
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G) colonies of a selected specimen grown for 7 days on (a) V8® Agar, (b) potato dextrose agar, and (c) malt extract agar; photo by Krysta Jennings and Leandra Knight, USDA-APHIS-PPQ |
|
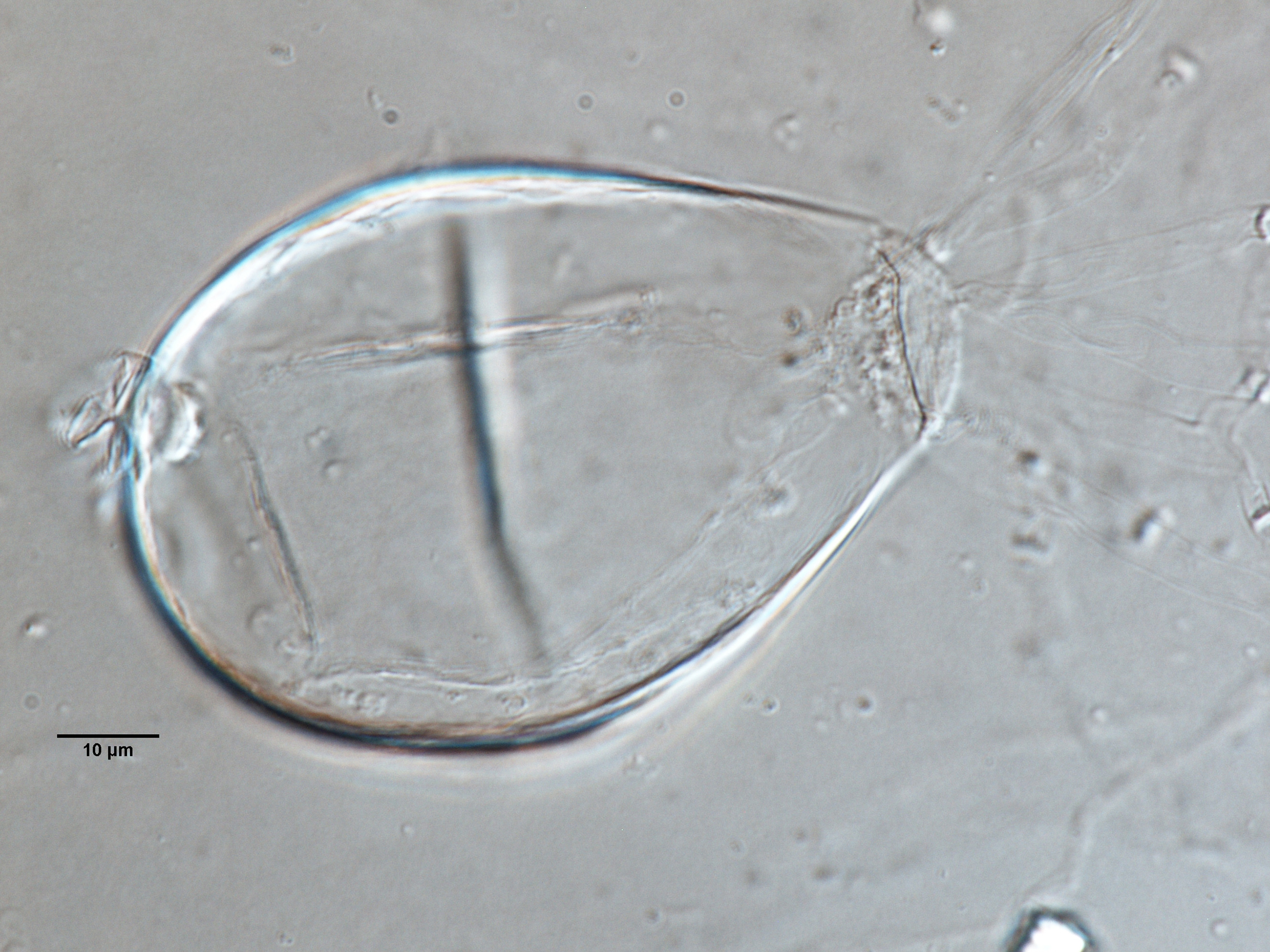
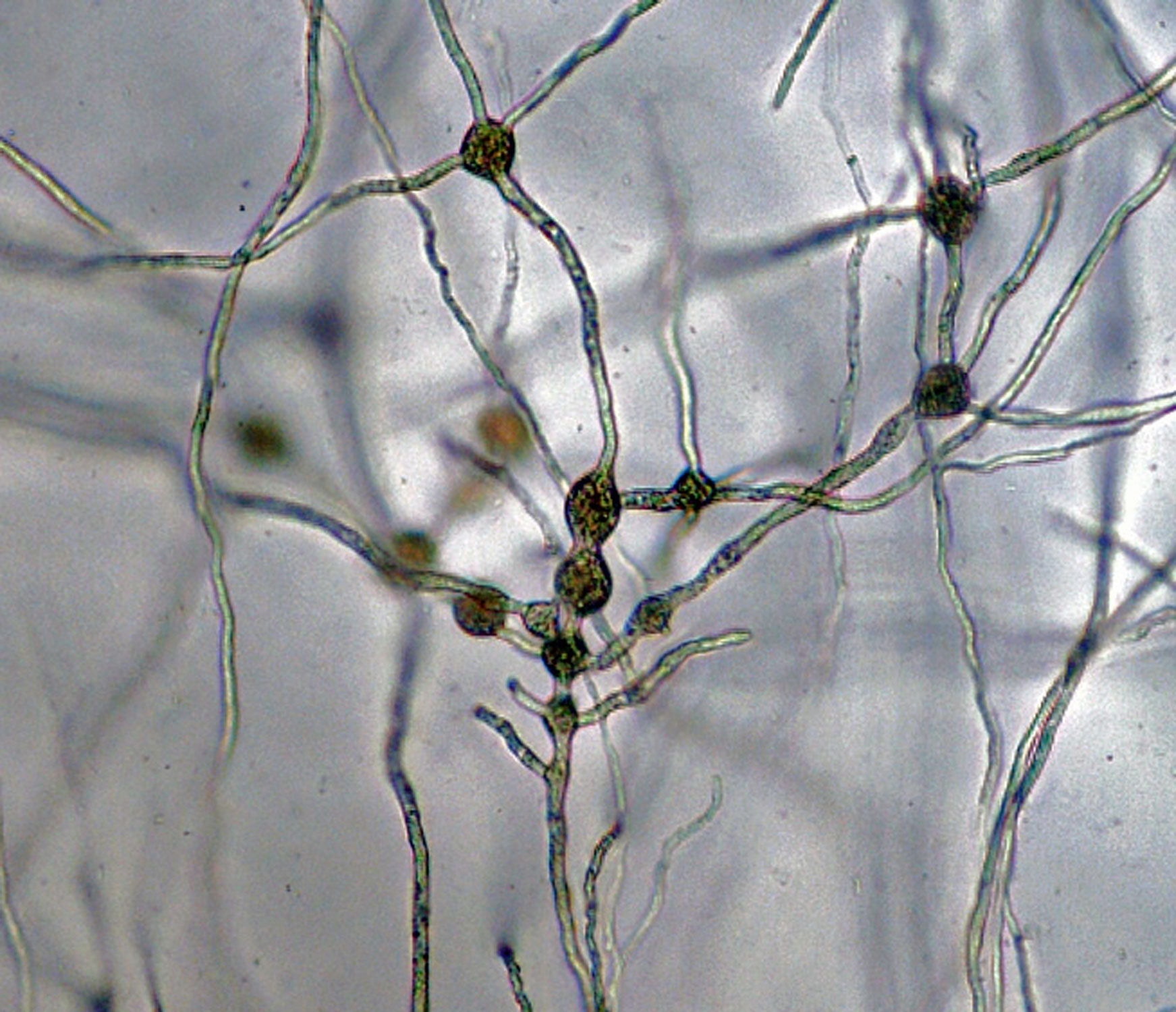
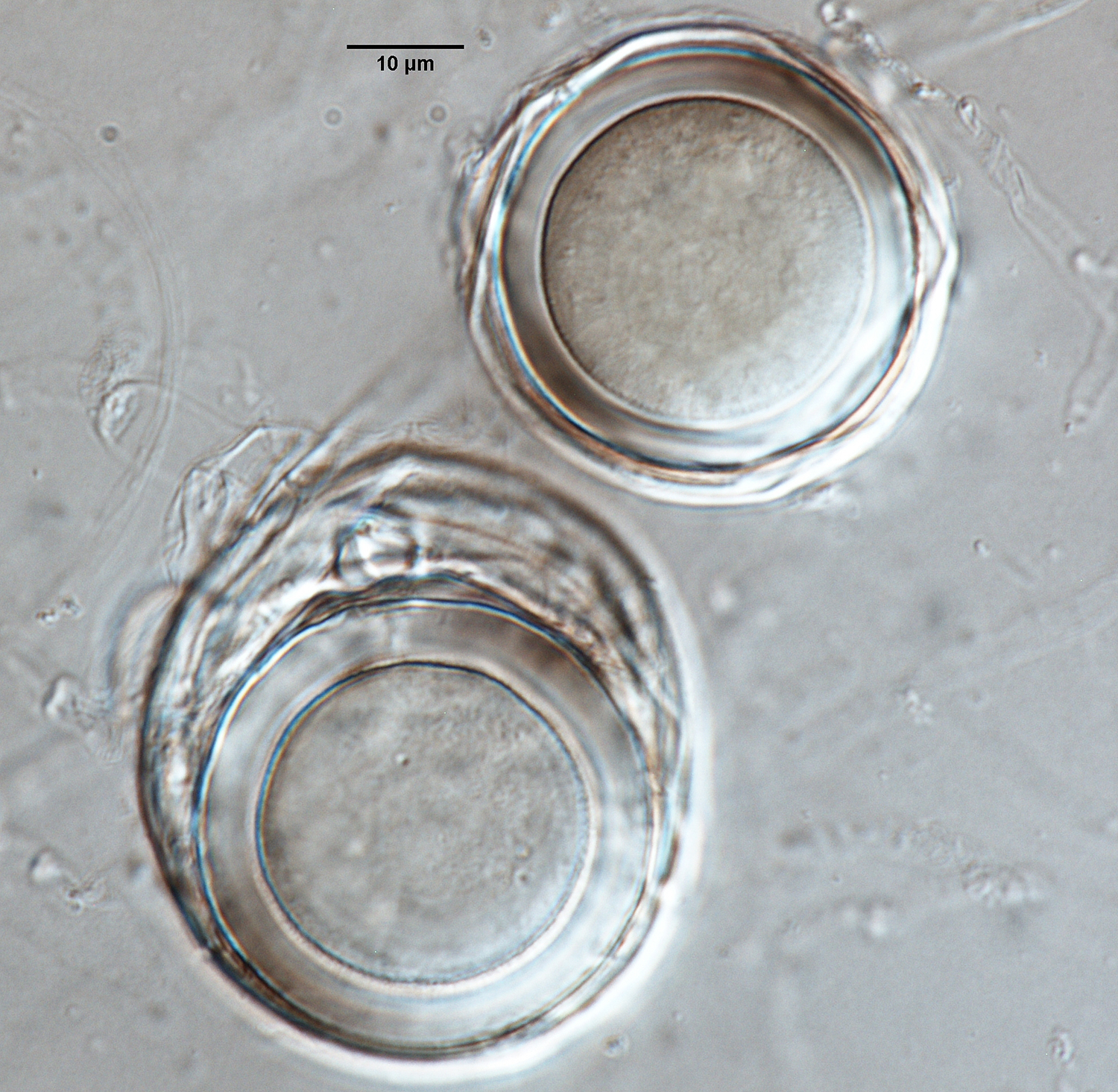
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) asexual (a–c) and sexual phases (d, e): (a) sporangium, (b, c) hyphal swellings, (d, e) oogonia with paragynous antheridia and plerotic, slightly aplerotic, and plerotic oopores; photos by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
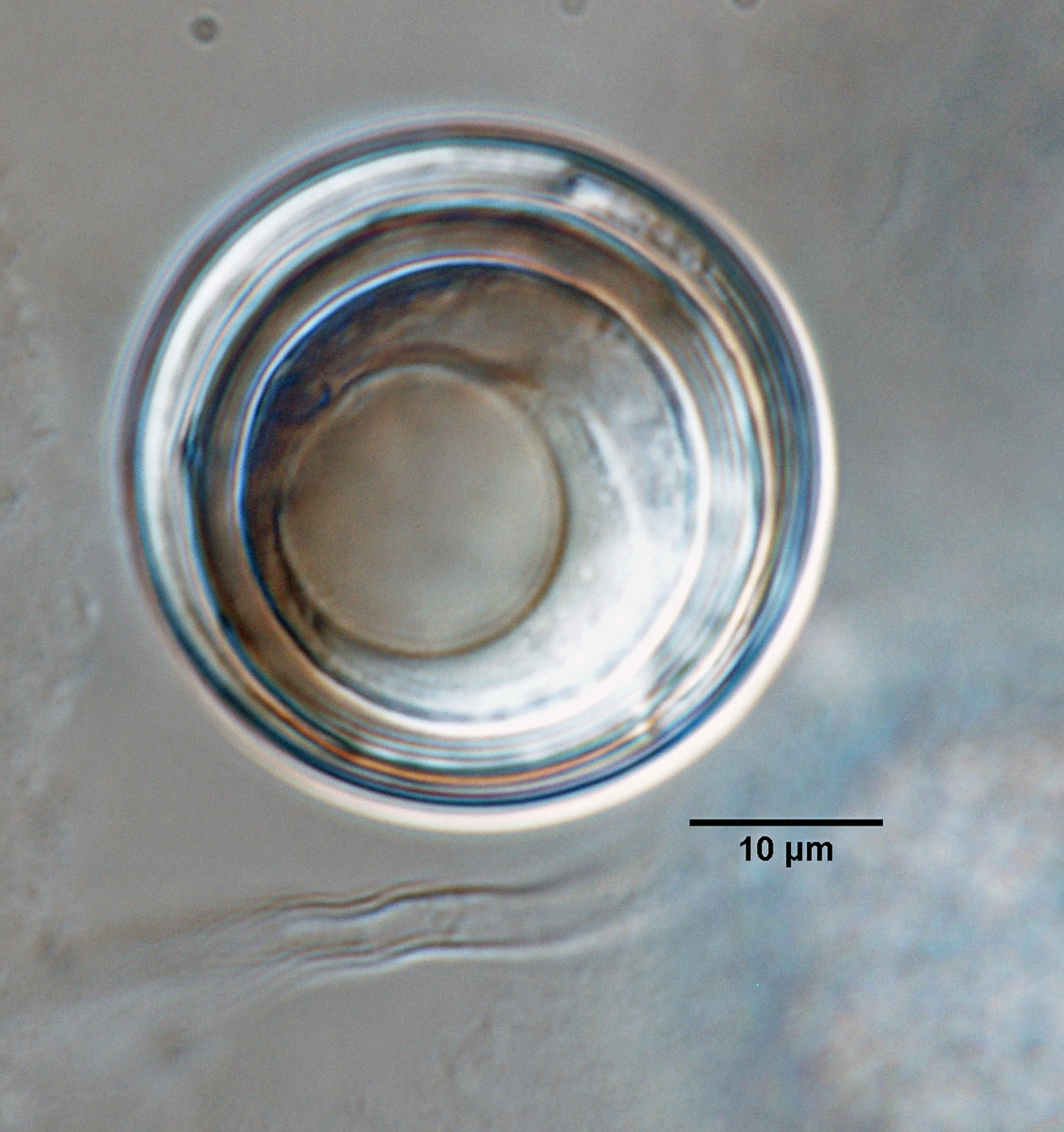
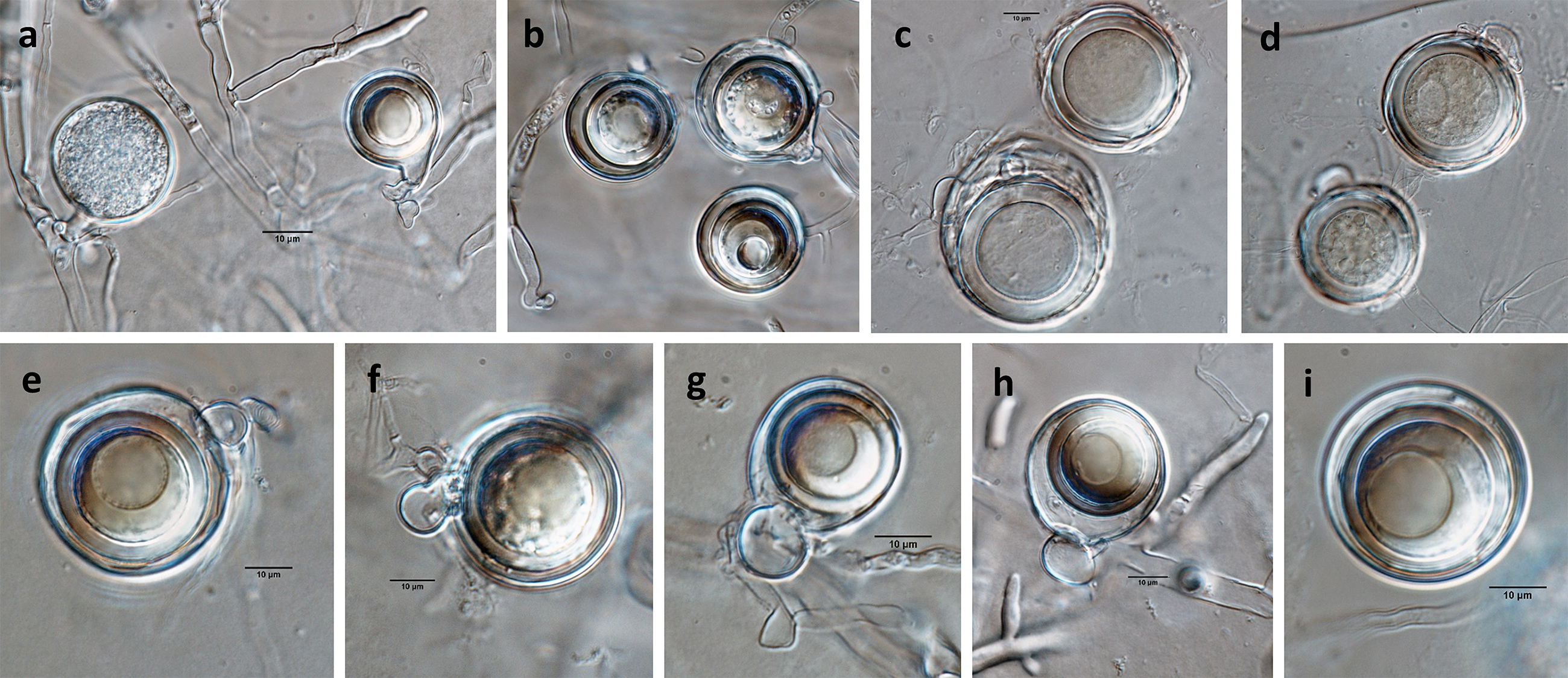
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase (a-i): (a) oospore and hyphal swelling, (b-i) smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and mostly aplerotic oospores; photos by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) asexual phase: sporangium; photo by G. Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen): hyphal swellings; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen): hyphal swellings; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
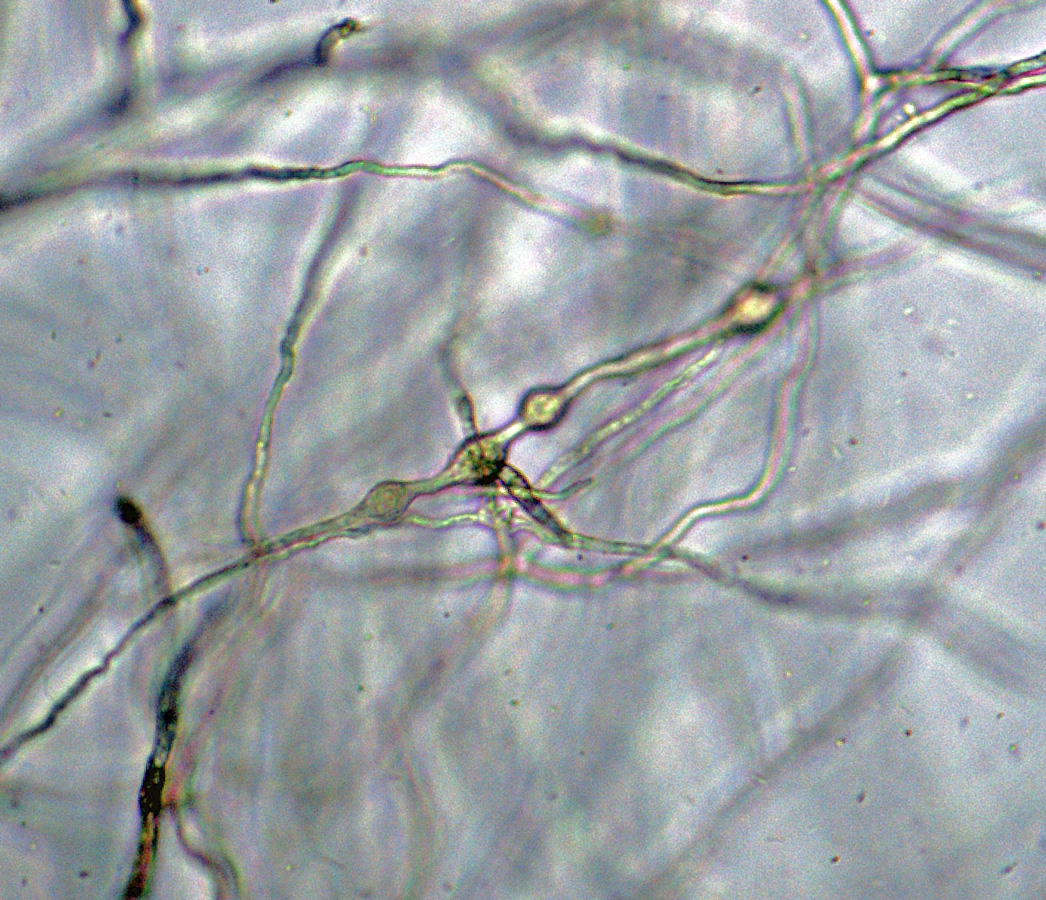
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with paragynous antheridium and mostly aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen): intercalary hyphal swellings; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with paragynous antheridium and mostly aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: hyphal swelling and oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with paragynous antheridium and mostly aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen): intercalary hyphal swellings; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
hytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and mostly aplerotic oospores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonium with paragynous antheridium and mostly aplerotic oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen): hyphal swellings and oospore in bottom of frame; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
Phytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: smooth-walled oogonia with paragynous antheridia and mostly aplerotic oospores; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
|
hytophthora sojae (CPHST BL 56G, selected specimen) sexual phase: hyphal swelling and oospore; photo by Gloria Abad, USDA-APHIS-PPQ. |
Name and publication
Phytophthora sojae Kaufm. & Gerd. (1958)
Kaufmann MJ and Gerdemann JW. 1958. Root and stem rot of soybean caused by Phytophthora sojae n. sp. Phytopathology 48: 201–208.
Nomenclature
Mycobank
Typification
from Kaufmann and Gerdemann (1958)
Type: UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, collected from roots and stems of soybean (Glycine max) in Illinois, Ohio, North Carolina, Missouri, and Indiana, USA, and in Ontario, Canada. The type is represented by a culture isolated from a diseased soybean stem from a field near Blackstone, Illinois in 1955. Material of the type has been placed in the Herbarium of the University of Illinois, Urbana.
Ex-type: LOST
Well-authenticated specimens selected by Gloria Abad:
Selected specimen #1: CPHST BL 180 = P3248 (WPC) from UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Glycine max, Illinois
Selected specimen #2: CPHST BL 56G = P3114 (WPC) from UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Glycine max, Wisconsin
Selected specimen in other collections
(SE) CBS 149406, NRRL 64266 (Race 1), WPC P3114, S&T BL 56G (Abad)
Molecular identification
Voucher sequences for barcoding genes (ITS rDNA and COI) of the selected specimen (see Molecular protocols page)
Phytophthora sojae isolate CPHST BL 180 (= P3248 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG865587, COI MH136979
Phytophthora sojae isolate CPHST BL 56G (= P3114 WPC) = ITS rDNA MG865588, COI MH136980
Voucher sequences for Molecular Toolbox with seven genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Voucher sequences for Metabarcoding High-throughput Sequencing (HTS) Technologies [Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU)]
(see Molecular protocols page) (In Progress)
Sequences with multiple genes for selected specimen in other sources
- NCBI: Phytophthora sojae CPHST BL 180
- NCBI: Phytophthora sojae CPHST BL 56G
- EPPO-Q-bank: Phytophthora sojae CBS 382.61
- BOLDSYSTEMS: Phytophthora sojae (barcoding COI & ITS)
Position in multigenic phylogeny with 7 genes (ITS, β-tub, COI, EF1α, HSP90, L10, and YPT1)
Clade clade:
a taxonomic group of organisms classified together on the basis of homologous features traced to a common ancestor
7b
Morphological identification
Colonies and cardinal temperatures
Colony colony:
assemblage of hyphae which usually develops form a single source and grows in a coordinated way
after 7 days of growth on potato dextrose agar and malt extract agar is very small, and on V8A grows well and with no defined pattern. Minimum growth temperature 10°C, optimum 22–30°C, and maximum 33°C.
Asexual phase
SporangiaSporangia:
sac within which zoospores form, especially when water is cooled to about 10°C below ambient temperature; in solid substrates, sporangia usually germinate by germ tubes
nonpapillatenonpapillate:
pertaining to the production of a non-distinct, or inconspicuous, papilla at the distal end of the sporangium (cf. papillate and semipapillate)
; ovoidovoid:
egg-shaped, with the widest part at the base of the sporangium and the narrow part at the apex
, ellipsoidellipsoid:
refers to a solid body that forms an ellipse in the longitudinal plane and a circle in cross section; many fungal spores are ellipsoidal or elliptic
, obpyriformobpyriform:
inversely pear-shaped, i.e. with the widest part at the point of attachment (cf. pyriform)
, obovoidobovoid:
inversely egg-shaped; ovoid, but with the widest part at the apex
(43–101 L x 24–55 W µm) with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
, originated in simple sympodial and undifferentiated sporangiophores, sometimes showing internal and external proliferationexternal proliferation:
formation of a sporangium after a sporangiophore has emerged from beneath and external to an empty sporangium that has previously emitted its zoospores (cf. internal proliferation)
. Hyphal swellings intercalaryintercalary:
positioned within a hypha (cf. terminal)
, spherical to irregular in shape. ChlamydosporesChlamydospores:
an asexual spore with a thickened inner wall that is delimited from the mycelium by a septum; may be terminal or intercalary, and survives for long periods in soil
absent.
Sexual phase
Homothallic. Oogonia spherical to subspherical (24–45 x 23–41 µm), some with distorted shapes, some with tapered basetapered base:
pertaining to the base of a sporangium or oogonium; funnel-shaped
, some with tangled or knotted hyphaehyphae:
single, tubular filament of a fungal or oomycete thallus; the basic structural unit of a fungus or oomycete
around the antheridiumantheridium:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
; antheridiaantheridia:
the male gametangium; a multinucleate, swollen hyphal tip affixed firmly to the wall of the female gametangium (the oogonium)
predominantly paragynousparagynous:
pertaining to the sexual stage in which the antheridium is attached to the side of the oogonium (cf. amphigynous)
(9–18 L x 8–16 W µm), frequently with a single long spine or digitate projection; oosporesoospores:
zygote or thick-walled spore that forms within the oogonium after fertilization by the antheridium; may be long-lived
pleroticplerotic:
pertaining to an oospore that fills the oogonium (cf. aplerotic)
, apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
, and slightly apleroticaplerotic:
pertaining to a mature oospore that does not fill the oogonium; i.e. there is room left between the oospore wall and oogonium wall (cf. plerotic)
(18–39 µm diam).
Specimen(s) evaluated
Phytophthora sojae CPHST BL 180, duplicate of P3248 (World Phytophthora Collection)
Phytophthora sojae CPHST BL 56G, P3114 (World Phytophthora Collection) Wisconsin, soybean (Glycine max) (Maxwell #115)
Hosts and distribution
Distribution: Australia, North America (Canada, USA); also reported from South America (Brazil, Chile), Asia (Korea, China) and New Zealand
Substrate: roots, stems
Disease note: root and stem rot of soybeans; seedling wilt, seedling blight of lupines
Host: Glycine max (soybeans), Lupinus spp. (lupine) (Fabaceae); also reported from six other genera in five families
Retrieved February 01, 2018 from U.S. National Fungus Collections Nomenclature Database.
Quarantine status
Phytophthora sojae is listed in the U.S. Regulated Plant Pest Table (last modified Nov. 15, 2017).
Additional references and links
- SMML USDA-ARS: Phytophthora sojae
- EPPO Global Database: Phytophthora sojae
- Forest Phytophthoras of the world: Phytophthora sojae
- CABI Digital Library: Phytophthora sojae
- Encyclopedia of Life (EOL): Phytophthora sojae
- Index Fungorum (IF): Phytophthora sojae
- Google All Phytophthora sojae
- Google Images Phytophthora sojae
- Google Scholar Phytophthora sojae
Fact sheet author
Z. Gloria Abad, Ph.D., USDA-APHIS-PPQ-S&T Plant Pathogen Confirmatory Diagnostics Laboratory (PPCDL), United States of America.