Fontinalis Hedw. and Vesicularia (C. Müll.) C. Müll.
Java moss, willow moss, christmas moss
Fontinalaceae (Fontinalis), Hypnaceae (Vesicularia)
Fissidens, Taxiphyllum, and other species of terrestrialterrestrial:
(adj) growing on land as opposed to living in water
 mosses
mosses
cosmopolitancosmopolitan:
(adj) essentially worldwide in distribution
Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw.
Vesicularia dubyana (Müll) Broth.
V. ferriei (Cardot & Th&e acuteacute:
(adj) tapering to a sharp, pointed apex with more or less straight sides; broader than acuminate; forming an angle of less than 90 degrees
 ;r.) Broth.
;r.) Broth.
V. montagnei (Schimp.) Broth.
V. reticulata (Dozy & Molk.) Broth.
information not available
not weedy
creeping, amphibiousamphibious:
(adj) of a plant able to live on land or in water
 , epiphyticepiphytic:
, epiphyticepiphytic:
(adj) of a plant growing on another plant but not parasitic; plant grown on may be alive or, e.g., a dead tree trunk
 , growing on wood and rocks
, growing on wood and rocks
Perennialperennial:
(adj) (of a plant) having a life cycle of more than two years
 mosses. Non spore-producing generation (gametophytegametophyte:
mosses. Non spore-producing generation (gametophytegametophyte:
(n) the gamete-producing haploid phase in the plant life cycle; in some lower vascular plants it is multicellular and independent
 ) is dominant, forming a mat of light to dark green stems. Stems leafy, relaxed or flattened, soft, simple or much-branched, naked or bearing elongate rhizoids along ventralventral:
) is dominant, forming a mat of light to dark green stems. Stems leafy, relaxed or flattened, soft, simple or much-branched, naked or bearing elongate rhizoids along ventralventral:
(adj) of the front of an organ or the side facing or nearest the axis (syn. adaxial) (compare dorsal); upper surface
 surface (roots absent); branching pattern variable, pinnatepinnate:
surface (roots absent); branching pattern variable, pinnatepinnate:
(adj) in the form of a feather; of, e.g., leaflets, lobes, or veins: arranged in two rows along an axis
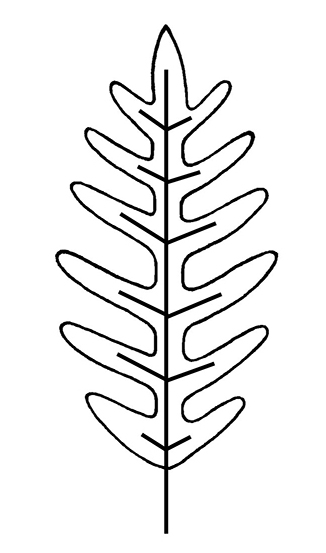 to dichotomous to apparently random. Leaves alternatealternate:
to dichotomous to apparently random. Leaves alternatealternate:
(adj) (of leaves) bearing one leaf per node; placed singly on the stem at different heights
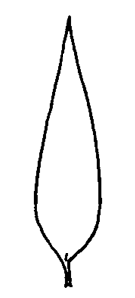
 (3-ranked in Fontinalis), lanceolatelanceolate:
(3-ranked in Fontinalis), lanceolatelanceolate:
(adj) lance-shaped; widest point below the middle, tapering to the apex
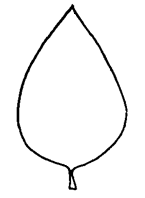
 to ovateovate:
to ovateovate:
(adj) egg-shaped in outline; generally with the broad end at or near the base
 . Spore-producing generation (sporophyte) emersedemersed:
. Spore-producing generation (sporophyte) emersedemersed:
see emergent
 . Dispersal by spores and stem fragments.
. Dispersal by spores and stem fragments.
shallow water, splash zone, and boggy ground
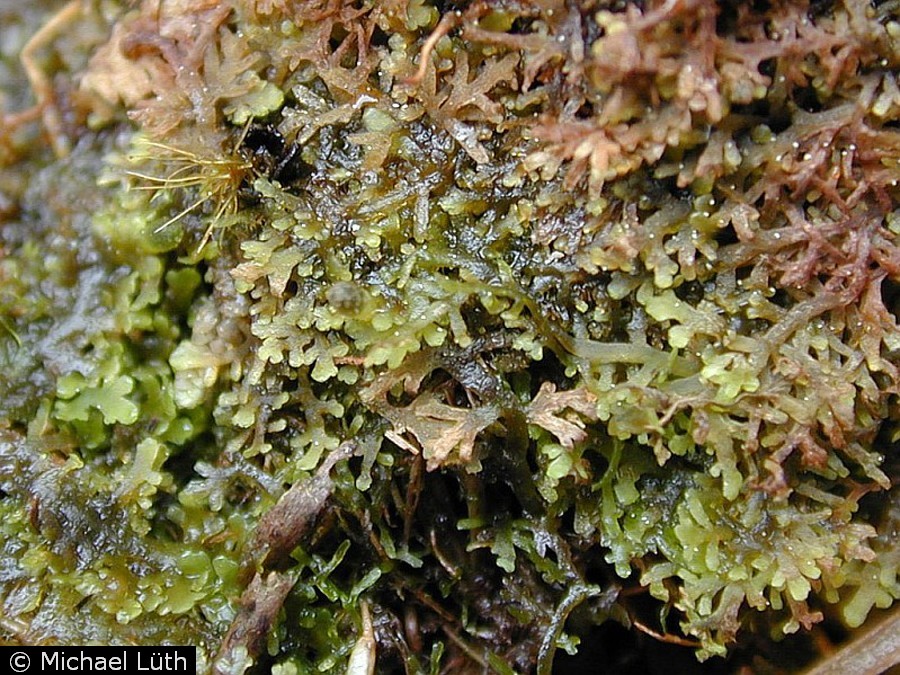
Fontinalis and Vesicularia are genera in Bryophyta (mosses). Fontinalis is less common in the aquarium trade, while Vesicularia, which adapts easily to underwater culture, is frequently utilized. Vesicularia has smaller leaves than Fontinalis. It is sold in various different forms, e.g., willow moss, christmas moss, and Java moss. All clearly have different growth forms, varying in the degree and pattern of stem branching. It is unknown which species or varieties these represent. Critical taxonomic appraisal is required before they can be accurately identified. At present, they are all considered varieties of V. dubyana. There is also some debate as to the actual species identity of the Vesicularia that is widely distributed. Some sources suggest that the species is actually V. reticulata (Dozy & Molk.) Broth., and not V. dubyana. Vesicularia reticulata also originates from Southeast Asia.
Fontinalis has high morphological variability throughout the genus as well as within single collections of one species. Fontinalis is generally larger, with swollen stem and branch tips, but this is often dependent on growing conditions. The leaves of Fontinalis are keeledkeeled:
(adj) having a keel; sharply creased
 with a decurrentdecurrent:
with a decurrentdecurrent:
(adj) extending downward, beyond the point of insertion
 base and typically lack a costacosta:
base and typically lack a costacosta:
(n) midvein of leaf or pinna or rachis of pinnately compound leaf
 . If growing in swift waters the keelkeel:
. If growing in swift waters the keelkeel:
(n) a sharp crease or ridge
 can easily tear, appearing as two separate leaves.
can easily tear, appearing as two separate leaves.
Vesicularia is poorly studied, and synonymy within the genus and with other genera is to be expected until further taxonomic studies are done. The leaves of Vesicularia are often dimorphic with smaller ventralventral:
(adj) of the front of an organ or the side facing or nearest the axis (syn. adaxial) (compare dorsal); upper surface
 leaves, they lack a keelkeel:
leaves, they lack a keelkeel:
(n) a sharp crease or ridge
 , and they have a short and double costacosta:
, and they have a short and double costacosta:
(n) midvein of leaf or pinna or rachis of pinnately compound leaf
 . Vesicularia and Taxiphyllum are similar in both gametophytic and sporophytic characteristics, making the two very difficult to distinguish. Vesicularia is often more pinnately branched, while Taxiphylllum is irregularirregular:
. Vesicularia and Taxiphyllum are similar in both gametophytic and sporophytic characteristics, making the two very difficult to distinguish. Vesicularia is often more pinnately branched, while Taxiphylllum is irregularirregular:
(adj) asymmetrical
 , but again this feature is variable depending on growing conditions.
, but again this feature is variable depending on growing conditions.