Heteranthera Ruiz & Pavon
mud plantain, duck salad, water stargrass
Pontederiaceae
Eichhornia, Hydrocharis, Limnobium, Monochoria, Najas, Potamogeton
North and South America, Africa
Heteranthera dubia (Jacq.) MacMill. (Zosterella dubia)
H. limosa (Sw.) Willd.
H. reniformis Ru&i acuteacute:
(adj) tapering to a sharp, pointed apex with more or less straight sides; broader than acuminate; forming an angle of less than 90 degrees
 ;z & Pav.
;z & Pav.
H. zosterifolia Mart.
Asia, Caribbean, Australia
Heteranthera limosa and H. reniformis are weeds of rice in several countries; most species, however, are not considered serious weeds.
submersedsubmersed:
see submerged
 , emergentemergent:
, emergentemergent:
(adj) (syn. emersed) with parts raised out of the water; extending up out of the water
 to amphibiousamphibious:
to amphibiousamphibious:
(adj) of a plant able to live on land or in water
 rosetterosette:
rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 or stem plantstem plant:
or stem plantstem plant:
(n) (a term used in the aquarium and pond plant trade) having an elongate stem (as opposed to a compact stem)
Annual or perennialperennial:
(adj) (of a plant) having a life cycle of more than two years
 . Stems submergedsubmerged:
. Stems submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
 , floating or emergentemergent:
, floating or emergentemergent:
(adj) (syn. emersed) with parts raised out of the water; extending up out of the water
 . Leaves alternatealternate:
. Leaves alternatealternate:
(adj) (of leaves) bearing one leaf per node; placed singly on the stem at different heights
 (H. zosterifolia, H. dubia), or appearing to be in a rosetterosette:
(H. zosterifolia, H. dubia), or appearing to be in a rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 (e.g., H. limosa); petiolatepetiolate:
(e.g., H. limosa); petiolatepetiolate:
(adj) relating to or in the form of a petiole; bearing petioles
 or sessilesessile:
or sessilesessile:
(adj) attached directly, without a stalk
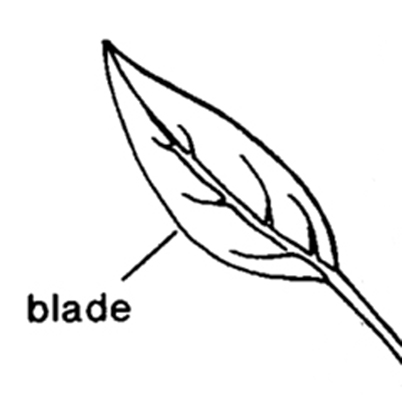
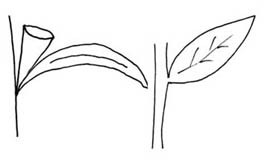 , leaf base sheathed; bladeblade:
, leaf base sheathed; bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
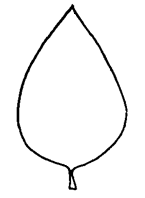
 linear, reniformreniform:
linear, reniformreniform:
(adj) kidney-shaped
 or ovateovate:
or ovateovate:
(adj) egg-shaped in outline; generally with the broad end at or near the base
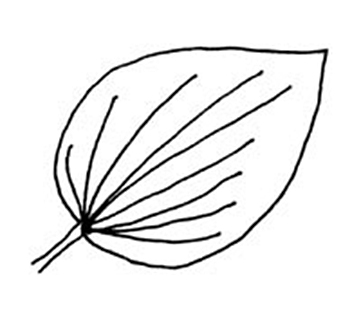
 , venationvenation:
, venationvenation:
(n) the arrangement of veins in a leaf
 parallel or palmatepalmate:
parallel or palmatepalmate:
(adj) (of leaves or venation) with lobes, leaflets, divisions or veins originating from the same point
 , or apparently absent (H. dubia). Inflorescenceinflorescence:
, or apparently absent (H. dubia). Inflorescenceinflorescence:
(n) the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis
 a spikespike:
a spikespike:
(n) an indeterminate, unbranching inflorescence of sessile flowers or flower clusters on a usually elongated axis
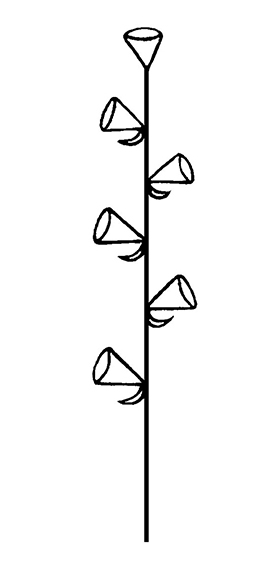 or paired or solitary flowers, subtended by 2 reduced, sheathing leaves (spathes). Flowers showy but delicate; tubulartubular:
or paired or solitary flowers, subtended by 2 reduced, sheathing leaves (spathes). Flowers showy but delicate; tubulartubular:
(adj) (of a corolla, perianth, calyx tube or other structure) (1) tube-shaped; cylindrical: narrow and elongate with more or less straight sides; (2) having segments fused into a tube (of any shape)
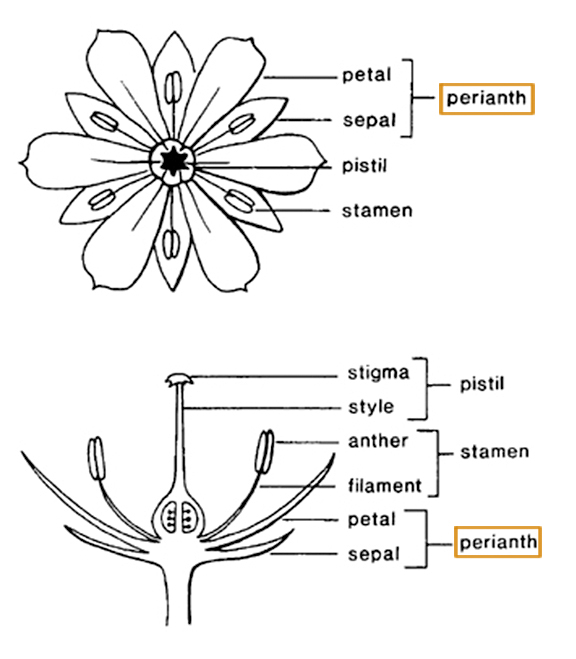
 perianth of 6 tepals in 2 whorls of 3, blue-purple, yellow or white; stamens 3. Dispersal by seed or stem fragments.
perianth of 6 tepals in 2 whorls of 3, blue-purple, yellow or white; stamens 3. Dispersal by seed or stem fragments.
still waters such as ponds, lakes, swamps, and marshes
Heteranthera comprises approximately 12 species, of which H. zosterifolia and H. dubia are cultivated for the aquarium trade, while H. reniformis and H. limosa are cultivated for the pond plant trade. Heteranthera dubia (sometimes placed in Zosterella) has narrow stems, linear leaves that lack apparent venationvenation:
(n) the arrangement of veins in a leaf
 , and a yellow flower. Heteranthera zosterifolia has linear leaves, H. reniformis has cordatecordate:
, and a yellow flower. Heteranthera zosterifolia has linear leaves, H. reniformis has cordatecordate:
(adj) heart-shaped; in the form of two rounded lobes
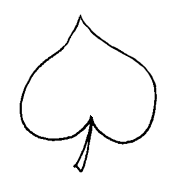 to kidney shaped leaves, and H. limosa has ovateovate:
to kidney shaped leaves, and H. limosa has ovateovate:
(adj) egg-shaped in outline; generally with the broad end at or near the base
 to oblongoblong:
to oblongoblong:
(adj) two to four times longer than wide, with +/- parallel sides
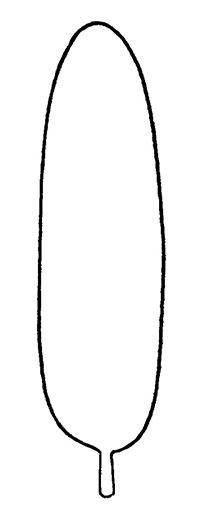 shaped leaves. Monochoria is easily differentiated from Heteranthera by the presence of six stamens, while Heteranthera has three.
shaped leaves. Monochoria is easily differentiated from Heteranthera by the presence of six stamens, while Heteranthera has three.