Proserpinaca L.
mermaid weed
Haloragaceae
Gratiola, Hottonia, Limnophila, Myriophyllum, Pogostemon
North America
Proserpinaca palustris L.
P. pectinata Lam.
information not available
not weedy
amphibiousamphibious:
(adj) of a plant able to live on land or in water
 stem plantstem plant:
stem plantstem plant:
(n) (a term used in the aquarium and pond plant trade) having an elongate stem (as opposed to a compact stem)
 , stems ascending, with variably dissecteddissected:
, stems ascending, with variably dissecteddissected:
(adj) (of leaves) +/- deeply divided, cut, or lobed, including being compound
 leaves
leaves
Perennial. Stem erect, ascending or prostrateprostrate:
(adj) growing closely along the ground
 . Rhizomerhizome:
. Rhizomerhizome:
(n) an underground stem, usually growing horizontally, from which both roots and shoots emerge directly; the thick, above-ground stem of ferns
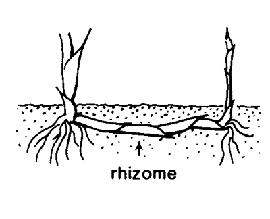 slender, horizontal. Leaves alternatealternate:
slender, horizontal. Leaves alternatealternate:
(adj) (of leaves) bearing one leaf per node; placed singly on the stem at different heights
 , sessilesessile:
, sessilesessile:
(adj) attached directly, without a stalk
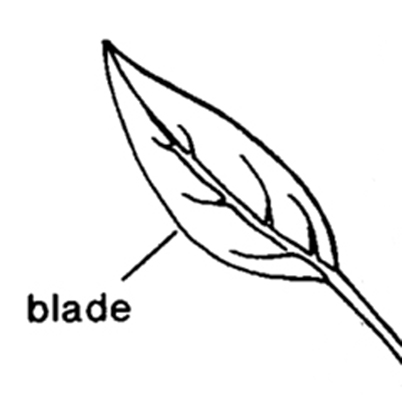
 ; leaf bladeblade:
; leaf bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
 highly variable in shape, typically pinnatepinnate:
highly variable in shape, typically pinnatepinnate:
(adj) in the form of a feather; of, e.g., leaflets, lobes, or veins: arranged in two rows along an axis
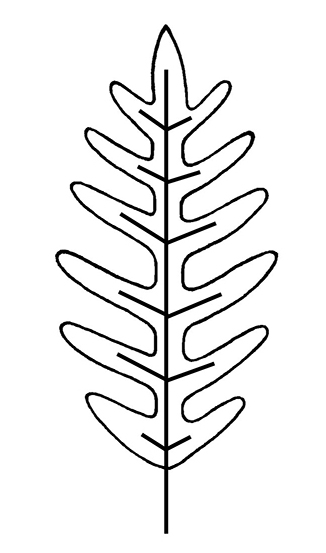 , but ranging from pinnatepinnate:
, but ranging from pinnatepinnate:
(adj) in the form of a feather; of, e.g., leaflets, lobes, or veins: arranged in two rows along an axis
 to entireentire:
to entireentire:
(adj) having a continuous margin that is not toothed or lobed
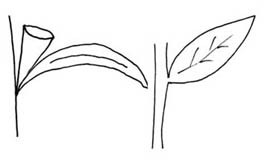
 within a single plant; emersedemersed:
within a single plant; emersedemersed:
see emergent
 leaves sometimes entireentire:
leaves sometimes entireentire:
(adj) having a continuous margin that is not toothed or lobed
 with serrateserrate:
with serrateserrate:
(adj) (of a leaf margin) bearing sharp teeth pointing forward or to the apex
 margin. Inflorescenceinflorescence:
margin. Inflorescenceinflorescence:
(n) the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis
 of solitary flowers, sessilesessile:
of solitary flowers, sessilesessile:
(adj) attached directly, without a stalk
 in leaf axils. Sepals 3; petals absent; stamens 3. Dispersal by seed or stem fragments.
in leaf axils. Sepals 3; petals absent; stamens 3. Dispersal by seed or stem fragments.
shallow marginal waters of lakes, rivers, swamps, ponds, and wet ground
Proserpinaca contains two species from eastern North America. Its leaf morphology is highly variable, which leads to taxonomic problems. When growing emersedemersed:
see emergent
 , P. pectinata has completely pinnatepinnate:
, P. pectinata has completely pinnatepinnate:
(adj) in the form of a feather; of, e.g., leaflets, lobes, or veins: arranged in two rows along an axis
 leaves, while P. palustris has entireentire:
leaves, while P. palustris has entireentire:
(adj) having a continuous margin that is not toothed or lobed
 , but serrateserrate:
, but serrateserrate:
(adj) (of a leaf margin) bearing sharp teeth pointing forward or to the apex
 leaves. Both species are frequently cultivated for ponds and aquaria.
leaves. Both species are frequently cultivated for ponds and aquaria.