Ranunculus L.
buttercup, water crowfoot
Ranunculaceae
Cabomba, Caltha, Comarum, Ficaria, Hydrocotyle, Limnophila, Myriophyllum, Potentilla
cosmopolitancosmopolitan:
(adj) essentially worldwide in distribution
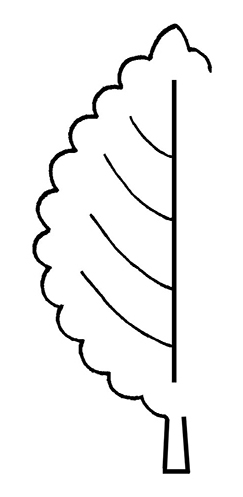
Ranunculus aquatilis L.
R. flagelliformis Sm.
R. flammula L.
R. inundatus R.Br. ex DC.
R. limosella F.Muell. ex Kirk
R. lingua L.
R. papulentus Melville
R. peltatus Schrank
Ranunculus ficaria L., R. acris L. and R. repens L. are introduced into the United States from Europe.
R. flammula is introduced into Australia and New Zealand.
R. sceleratus L. is introduced into New Zealand, Australia and Tasmania, but hasn't been reported here for about 100 years.
Ranunculus acris and R. repens are considered noxious weeds.
submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
 stem plantstem plant:
stem plantstem plant:
(n) (a term used in the aquarium and pond plant trade) having an elongate stem (as opposed to a compact stem)
 to emergentemergent:
to emergentemergent:
(adj) (syn. emersed) with parts raised out of the water; extending up out of the water
 or terrestrialterrestrial:
or terrestrialterrestrial:
(adj) growing on land as opposed to living in water
 , stoloniferous rosetterosette:
, stoloniferous rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 plant
plant
Annual or perennialperennial:
(adj) (of a plant) having a life cycle of more than two years
 . Stem variable, compact or elongate, erect or ascending; submergedsubmerged:
. Stem variable, compact or elongate, erect or ascending; submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
 aquatic species usually with elongate stems while emergentemergent:
aquatic species usually with elongate stems while emergentemergent:
(adj) (syn. emersed) with parts raised out of the water; extending up out of the water
 species often compact. Leaves highly variable, in a rosetterosette:
species often compact. Leaves highly variable, in a rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 or caulinecauline:
or caulinecauline:
(adj) pertaining to or belonging to the stem
 , alternatealternate:
, alternatealternate:
(adj) (of leaves) bearing one leaf per node; placed singly on the stem at different heights
 or whorledwhorled:
or whorledwhorled:
(n) bearing whorls; a type of leaf arrangement (phyllotaxis) in which leaves are in whorls
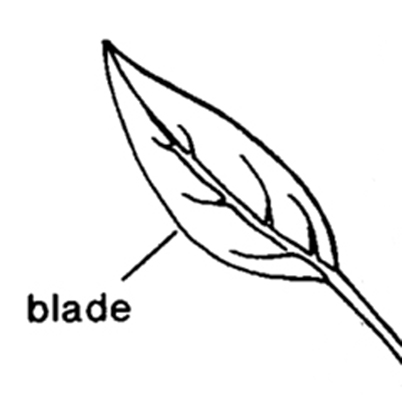
 ; leaf bladeblade:
; leaf bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
 linear to orbicularorbicular:
linear to orbicularorbicular:
(adj) circular in outline
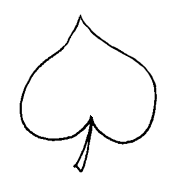
 , lobedlobed:
, lobedlobed:
(adj) divided into (usually rounded) segments
 to palmately divided; segments of submergedsubmerged:
to palmately divided; segments of submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
 leaves capillarycapillary:
leaves capillarycapillary:
(adj) slender, hair-like
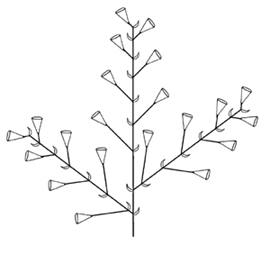
 . Inflorescenceinflorescence:
. Inflorescenceinflorescence:
(n) the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis
 solitary or flowers in a cymosecymose:
solitary or flowers in a cymosecymose:
(adj) in the form of a cyme; bearing cymes
 paniclepanicle:
paniclepanicle:
(n) an indeterminate, branched (often much-branched) inflorescence; the ultimate units may be of a different inflorescence type
 . Flowers actinomorphicactinomorphic:
. Flowers actinomorphicactinomorphic:
(adj) of flowers, having radial symmetry; capable of being bisected into identifical halves along more than one axis
 ; sepals 5; petals (nectar leaves) 5, distinctive, rounded, yellow or white. Dispersal of fruit (nutlets) by water, possibly by animals.
; sepals 5; petals (nectar leaves) 5, distinctive, rounded, yellow or white. Dispersal of fruit (nutlets) by water, possibly by animals.
pond margins, along streams, often on wet ground
Ranunculus consists of approximately 400 species, about 35 of which are aquatic. A highly morphologically variable genus in regard to vegetativevegetative:
(adj) (1) pertaining to or to the growth of plant organs or plant parts that have nonreproductive functions, such as leaves, roots, stems, etc.; (2) concering non sexual propagules such as tubers, turions, stem fragments, root crowns, rhizomes
 morphology, yet its flowers are relatively uniform and distinctive, varying often in petalpetal:
morphology, yet its flowers are relatively uniform and distinctive, varying often in petalpetal:
(n) one segment of the corolla
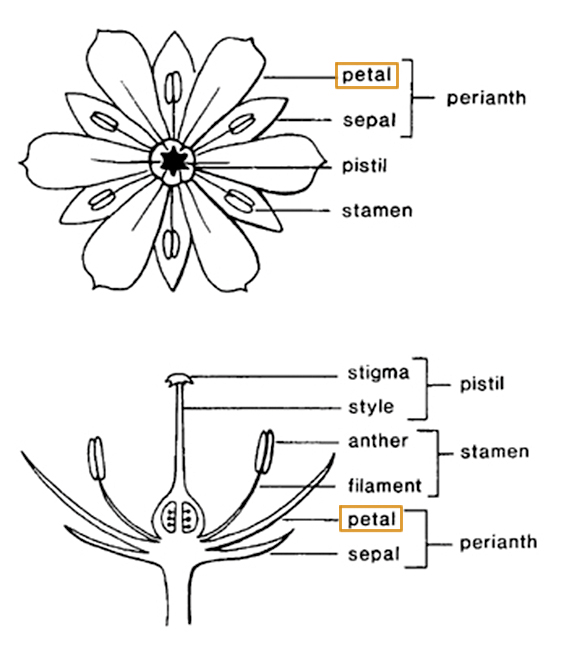 shape, size and presence.
shape, size and presence.