Victoria Lindl.
giant water platter
Nymphaeaceae
South America
Victoria amazonica (Poepp.) J.C. Sowerby
V. cruziana A.D. Orb.
none
not weedy
rooted, attached rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 with floating leaves
with floating leaves
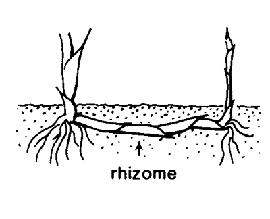
Stem a short rhizomerhizome:
(n) an underground stem, usually growing horizontally, from which both roots and shoots emerge directly; the thick, above-ground stem of ferns
 . Leaves in a rosetterosette:
. Leaves in a rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 ; juvenile leaves submergedsubmerged:
; juvenile leaves submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
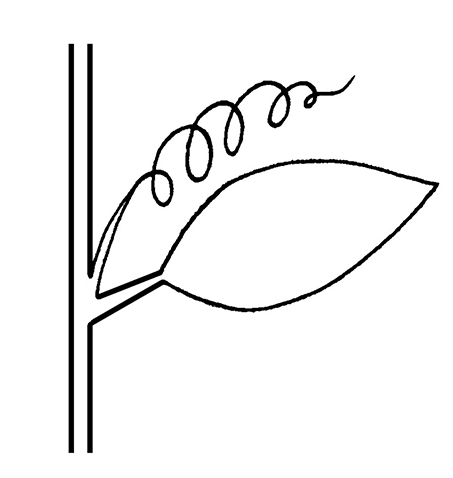 , mature leaves floating; petiolepetiole:
, mature leaves floating; petiolepetiole:
(n) the stalk of a leaf
 elongate; submergedsubmerged:
elongate; submergedsubmerged:
(adj) (syn. submersed) under water; submerged below the water surface
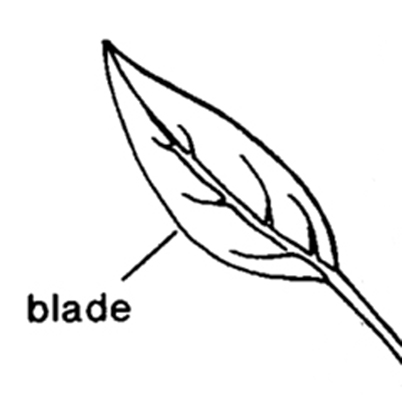
 surface of bladeblade:
surface of bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
 and petiolepetiole:
and petiolepetiole:
(n) the stalk of a leaf
 densely covered with large spines; juvenile leaf bladeblade:
densely covered with large spines; juvenile leaf bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
 linear, sagittatesagittate:
linear, sagittatesagittate:
(adj) shaped like an arrowhead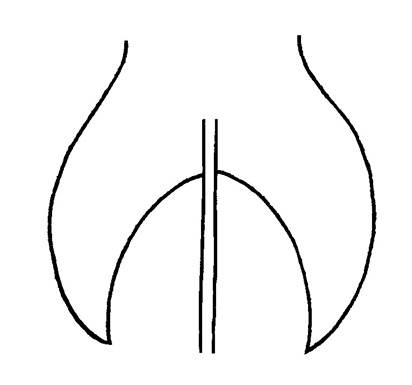 or ovateovate:
or ovateovate:
(adj) egg-shaped in outline; generally with the broad end at or near the base
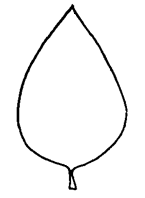 ; mature leaf bladeblade:
; mature leaf bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
 very large (1.8 meters or more in diameter), peltatepeltate:
very large (1.8 meters or more in diameter), peltatepeltate:
(adj) of usually flat organs such as leaves: having its stalk attached to its underside away from the margin, near the center
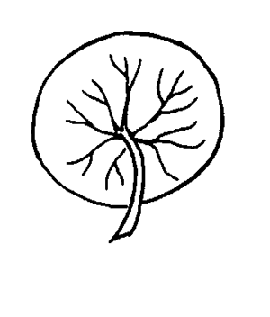 , orbicularorbicular:
, orbicularorbicular:
(adj) circular in outline
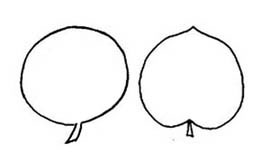 with entireentire:
with entireentire:
(adj) having a continuous margin that is not toothed or lobed
 , upturned marginmargin:
, upturned marginmargin:
(n) edge; rim
 . Flower solitary, large and very showy; pedicelpedicel:
. Flower solitary, large and very showy; pedicelpedicel:
(n) the stalk of a single flower in an inflorescence, or of a grass spikelet
 covered with large spines; sepals 4, with or without spines; petals numerous, large, white, pink or red. Dispersal by seed.
covered with large spines; sepals 4, with or without spines; petals numerous, large, white, pink or red. Dispersal by seed.
lakes, pools, and slow flowing rivers
Victoria is by far one of the largest and most spectacular aquatic plants. Mature leaf blades are large and buoyant enough to support the weight of a human. Two species are known: V. amazonica tends to have larger, redder leaves with rather low rims, while V. cruziana is greener, with higher rims.