Alocasia (Schott) G. Don
taro, elephant’s ear
Araceae
Colocasia, Schismatoglottis, Zantedeschia
subtropical eastern Himalayas throughout subtropical and tropical Asia into the tropical western pacific and eastern Australia
numerous species, hybrids, and varieties cultivated and offered as household plants and misleadingly as aquatic plants for ponds
Africa, Asia, Australasia, Pacific, North and South America
may be considered a weed in some countries
amphibiousamphibious:
(adj) of a plant able to live on land or in water
 herb
herb
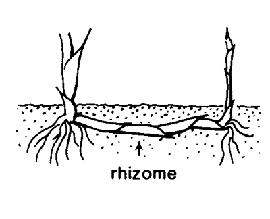
Small to medium-sized rhizomatousrhizomatous:
(adj) possessing rhizomes
 herb, evergreen or seasonally dormant. Stem erect, decumbentdecumbent:
herb, evergreen or seasonally dormant. Stem erect, decumbentdecumbent:
(adj) (of stems) having a portion lying along the ground, with upper parts erect or ascending
 or creeping, with clear to milky latexlatex:
or creeping, with clear to milky latexlatex:
(n) a usually milky-looking liquid found in the cells of many plants
 . Leaves in basalbasal:
. Leaves in basalbasal:
(adj) at or pertaining to the base, or point of attachment
 rosetterosette:
rosetterosette:
(n) a radiating cluster of leaves, usually close to the ground at the base of a plant
 ; sometimes each subtended by a cataphyllcataphyll:
; sometimes each subtended by a cataphyllcataphyll:
(n) a reduced, small leaf resembling a scale
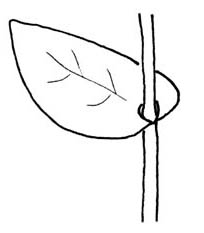
 ; petiolepetiole:
; petiolepetiole:
(n) the stalk of a leaf
 long, glabrousglabrous:
long, glabrousglabrous:
(adj) without hairs or scales
 to pubescentpubescent:
to pubescentpubescent:
(adj) (1) covered with short, soft hairs; (2) bearing hairs
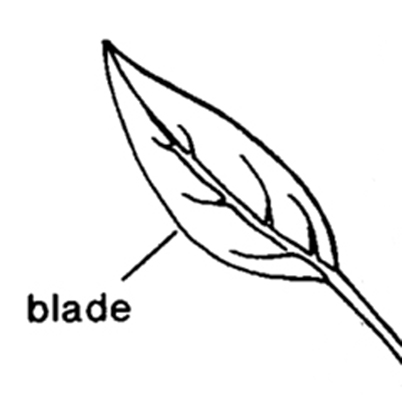
 , often glandular, sheath relatively long; leaf bladeblade:
, often glandular, sheath relatively long; leaf bladeblade:
(n) (syn. lamina) the flat, expanded part of a leaf, frond, or petal (excluding, e.g., the petiole)
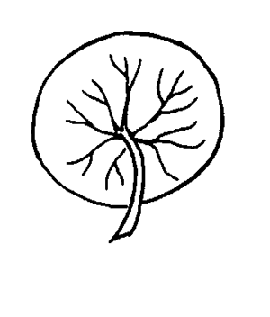
 peltatepeltate:
peltatepeltate:
(adj) of usually flat organs such as leaves: having its stalk attached to its underside away from the margin, near the center
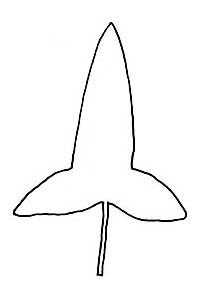
 when young, becoming hastatehastate:
when young, becoming hastatehastate:
(adj) (of a leaf) with a narrow, pointed lamina with two basal lobes spreading more or less at right angles to the petiole
 to sagittatesagittate:
to sagittatesagittate:
(adj) shaped like an arrowhead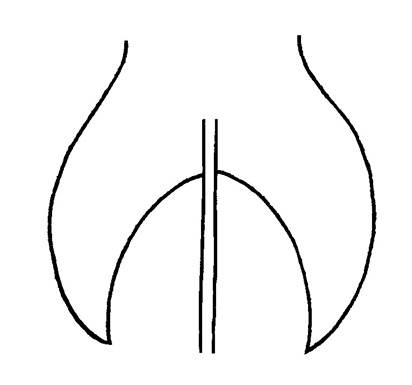 ; marginmargin:
; marginmargin:
(n) edge; rim
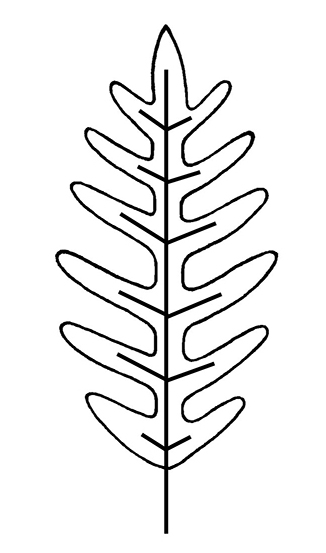
 entire, sinuate or pinnatifidpinnatifid:
entire, sinuate or pinnatifidpinnatifid:
(adj) (of leaves) deeply pinnately lobed half way or more, but not reaching the midrib
 ; primary veins pinnatepinnate:
; primary veins pinnatepinnate:
(adj) in the form of a feather; of, e.g., leaflets, lobes, or veins: arranged in two rows along an axis
 , with waxy glands in axils on lower leaf surface, often with submarginal collective vein. Inflorescenceinflorescence:
, with waxy glands in axils on lower leaf surface, often with submarginal collective vein. Inflorescenceinflorescence:
(n) the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis
 an axillaryaxillary:
an axillaryaxillary:
(adj) in, of, or produced from an axil
 spathespathe:
spathespathe:
(n) a large bract or bracts subtending and often enclosing an inflorescence
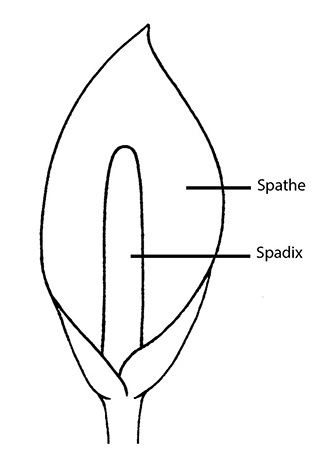 and spadixspadix:
and spadixspadix:
(n) a spike of small flowers borne on a thick, fleshy axis
 ; pedunclepeduncle:
; pedunclepeduncle:
(n) the stalk of a flower cluster or inflorescence
 erect, usually shorter than petiolepetiole:
erect, usually shorter than petiolepetiole:
(n) the stalk of a leaf
 . Spathespathe:
. Spathespathe:
(n) a large bract or bracts subtending and often enclosing an inflorescence
 limb lanceolatelanceolate:
limb lanceolatelanceolate:
(adj) lance-shaped; widest point below the middle, tapering to the apex
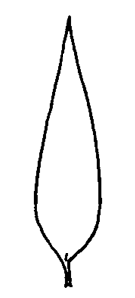 to oblongoblong:
to oblongoblong:
(adj) two to four times longer than wide, with +/- parallel sides
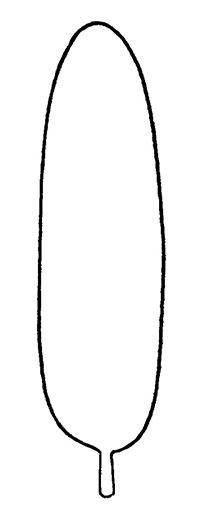 , hooded, purple to green, yellow or white, sometimes spotted or streaked.
, hooded, purple to green, yellow or white, sometimes spotted or streaked.
wide ecological range; open wet disturbed sites, moist to ever-wet areas of primary and secondary tropical rain forests, wetlands, open swamps, banks of rivers and streams, rarely rheophyticrheophytic:
(adj) living or able to live in fast-moving water currents

Alocasia contains 80 species, none of which are truly aquatic. The majority of species are found in rain forests, in humid to wet forest conditions, and/or are amphibiousamphibious:
(adj) of a plant able to live on land or in water
 .
.