IDaids for the polyphagous shot hole borer (PSHB)
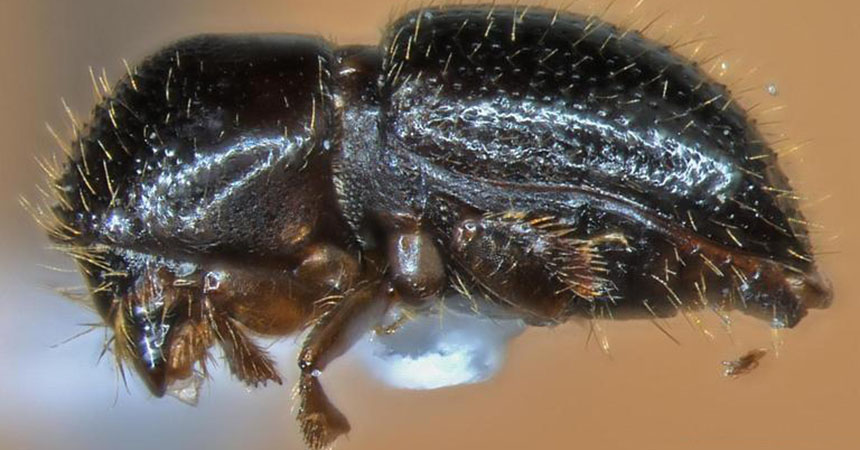
The polyphagous shot hole borer (PSHB), an ambrosia beetle known as Euwallacea sp., has become a serious pest in southern California, threatening urban, forest, and agricultural hardwood trees and shrubs. Notoriously difficult to spot and equally difficult to kill, these beetles are very small, about the size of a sesame seed, and have been observed on over 200 host species. The females bore into healthy hosts and disperse a fungus (such as Fusarium euwallacea) they carry with them as they make their galleries. The fungus is the insect’s food, but it is pathogenic to the plant as it spreads through the plant's xylem. The infection blocks the flow of water and nutrients, causing a range of symptoms from staining and gumming to Fusarium dieback and fatality.
Bark Beetle Genera of the United States: Key
United States Department of Agriculture, Identification Technology Program (ITP)
The interactive key from ITP’s Bark Beetle Genera of the United States identification tool allows users to distinguish Euwallacea from other beetle genera within the subfamily Scolytinae. Includes links to fact sheets with excellent photos.
Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer ID
OutSmart Invasive Species Project, United States of America
This brief video shows host symptoms indicative of PSHB infestation, particularly the differing symptoms various hosts may display.
Comparative Morphometric and Chemical Analyses of Phenotypes of 2 Invasive Ambrosia Beetles (Euwallacea spp.) in the United States
Insect Science, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
When PSHB first appeared in California, it was erroneously identified as tea shot hole borer (TSHB) (Euwallacea fornicates), as the two are nearly indistinguishable morphologically. This research paper describes morphometric and cuticular hydrocarbon differences between PSHB and TSHB.